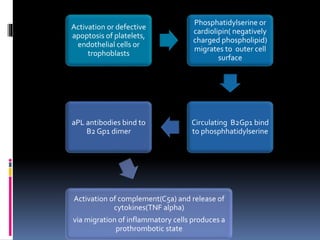
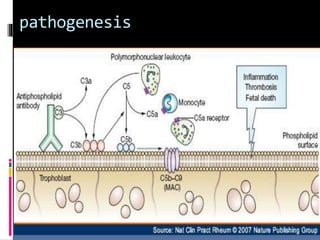
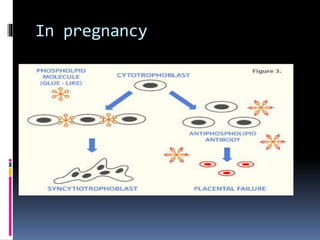
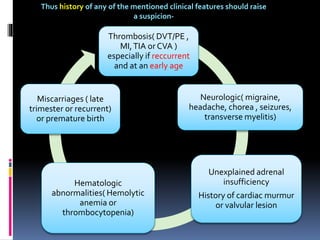
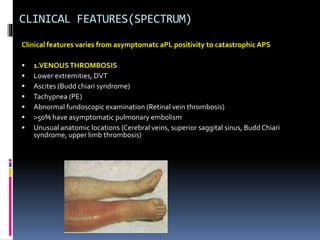
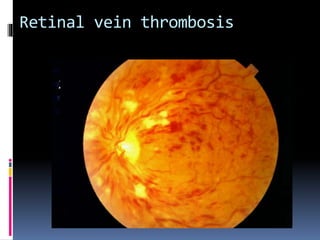
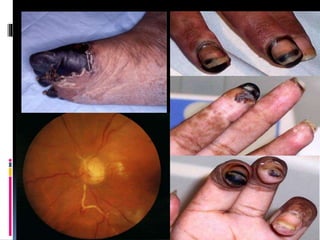
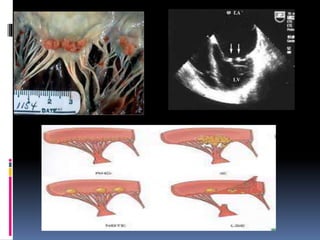
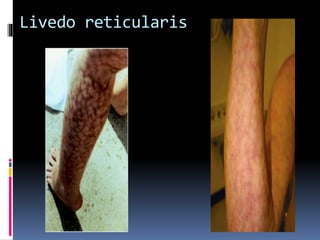
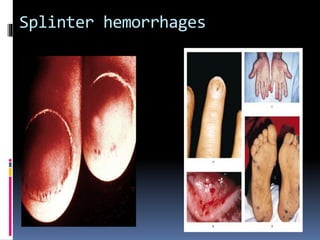
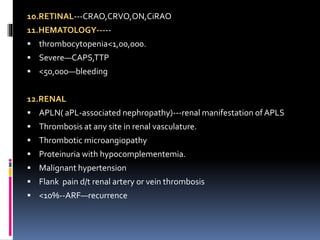
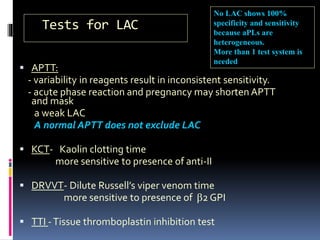
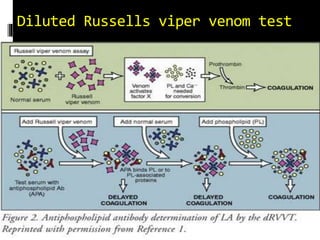
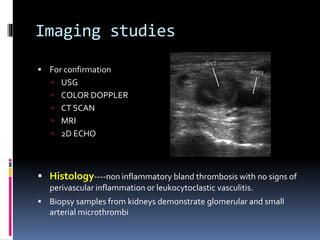
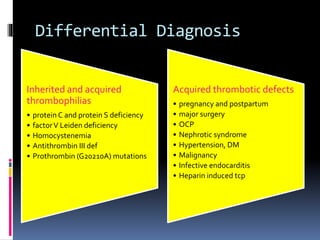
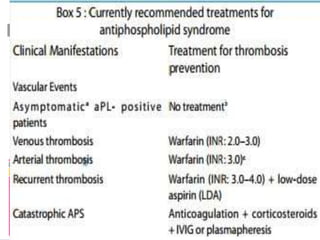
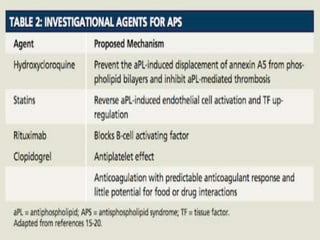
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by arterial or venous blood clots and/or pregnancy morbidity. It results from antibodies that target phospholipids or proteins that bind phospholipids. APS can occur alone (primary) or with other autoimmune diseases like lupus (secondary). The antibodies are associated with an increased risk of blood clots, heart attacks, strokes, preeclampsia, and fetal loss. Diagnosis requires both clinical criteria of vascular events or pregnancy complications and laboratory detection of antiphospholipid antibodies. Treatment focuses on blood thinners to prevent new clots.






![Antiphospholipid syndrome is an autoimmune disease, in which
"antiphospholipid antibodies" :
1.anticardiolipin antibodies (ACA)
2. lupus anticoagulant(LA)
3. Anti beta-2 glycoprotien 1 antibodies
They may be b2 gp1 dependent (aotuimmune aPLs) or
independent(infection and drug induced aPLs)
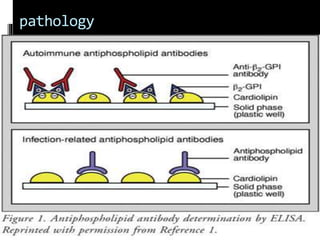
The presence of aPL, may be demonstrated directly by:
•Serum assays (ELISA)--- anticardiolipin antibody(ACA) and
-----anti beta2-glycoprotein (GP) I antibody
•Clotting assay ----- effects of an aPL on the phospholipid-dependent factors
in the coagulation cascade (lupus anticoagulant [LA] test)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antiphospholipidsyndrome-141019122948-conversion-gate01/85/Antiphospholipid-syndrome-7-320.jpg)