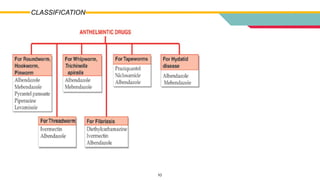
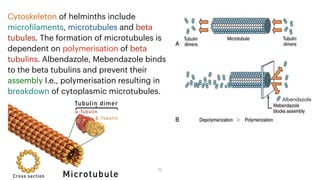
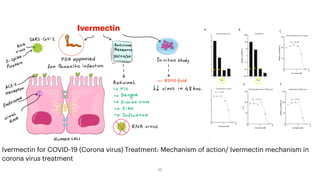
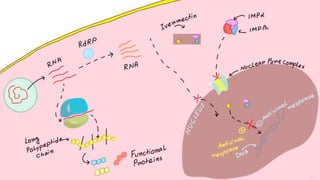
This document provides information on various antihelmintic drugs used to treat helminth infections. It discusses the epidemiology of soil-transmitted helminth infections and mechanisms of action of different classes of antihelmintics. Key drugs discussed include mebendazole, albendazole, ivermectin, praziquantel, diethylcarbamazine, and piperazine. Each drug's indications, mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, clinical uses, and adverse effects are summarized.




















![29
•Pharmacology for medical graduates Third edition by Tara V Shanbhag.
•Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of THERAPEUTICS
•Essentials of Medical Pharmacology [7th Edition] by KD Tripathi
•Rang and Dale 8th Edition By H.P.Rang, J.M. Ritter
REFERENCES
Thank You](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antihelmintics-210531050845/85/Antihelmintics-29-320.jpg)