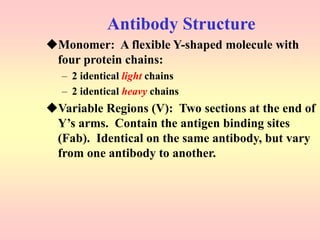
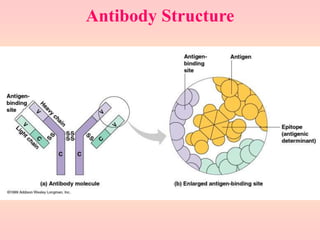
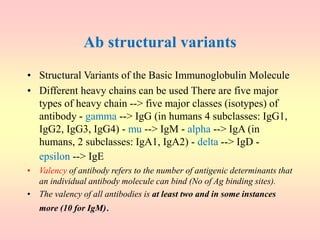
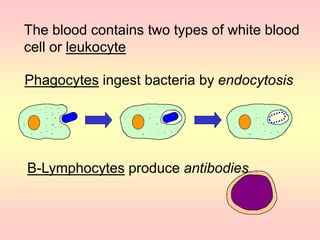
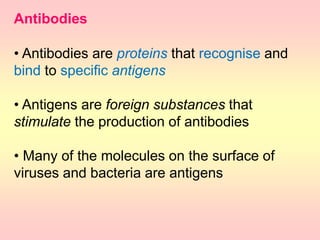
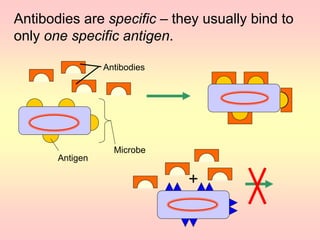
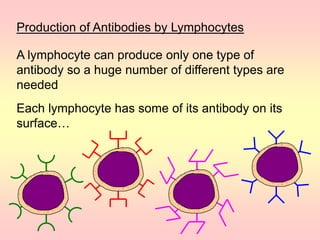
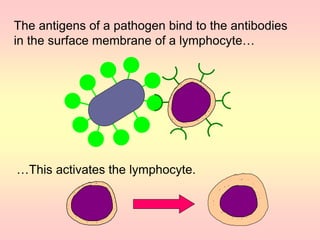
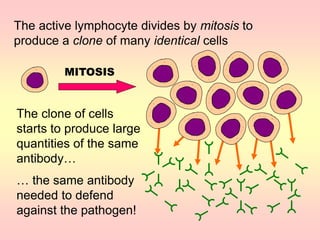
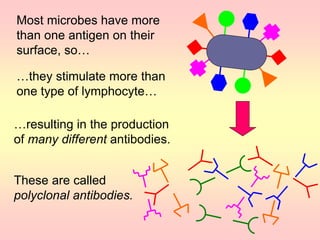
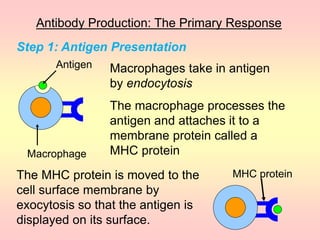
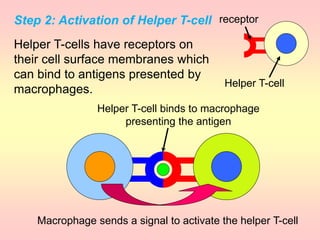
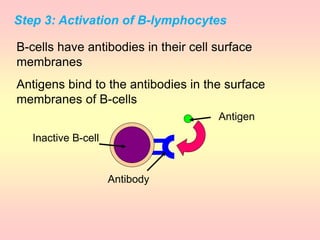
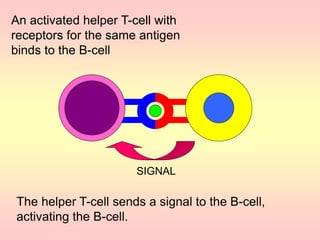
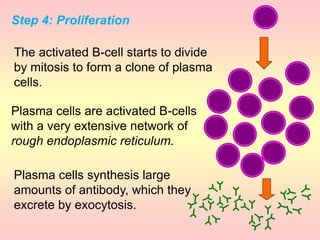
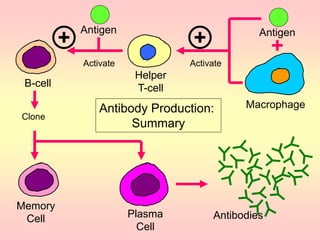
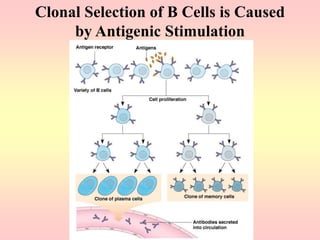
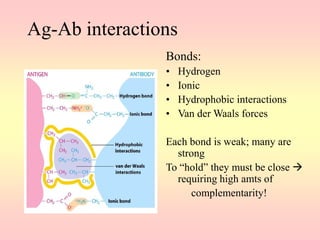
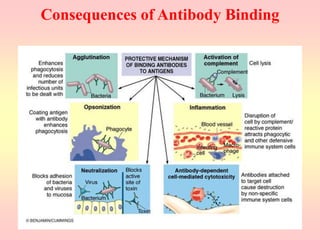
Antibodies are proteins called immunoglobulins that are produced by B cells in response to antigens. They bind to antigens with high specificity. Antibodies have a Y-shaped structure with two light chains and two heavy chains that form the variable regions for antigen binding and constant regions that interact with other immune cells. The variable regions contain hypervariable regions that provide specificity for different antigens. Antibody production involves B cell activation by antigens, T cell help, clonal selection and proliferation, and generation of memory B cells. Antibodies have various functions including neutralization, opsonization, agglutination, and activation of complement.