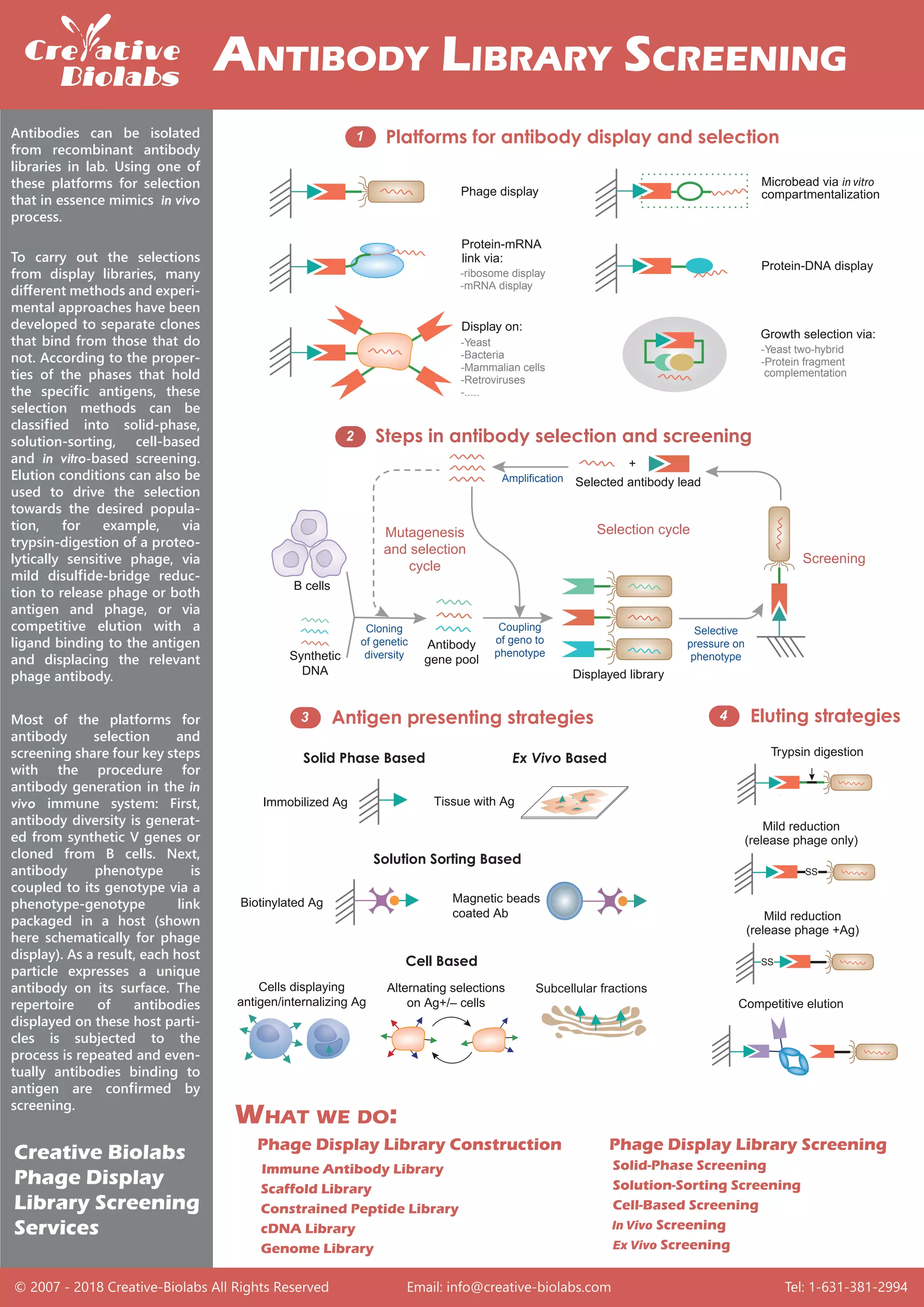
The document discusses methods for isolating antibodies from recombinant antibody libraries using various selection platforms that mimic in vivo processes. It outlines different classification methods for selection, including solid-phase, solution-sorting, cell-based, and in vitro-based screening, and describes how elution conditions can enhance selection. Key steps in antibody generation through these methods involve generating diversity, coupling phenotype to genotype, and confirming binding through screening.