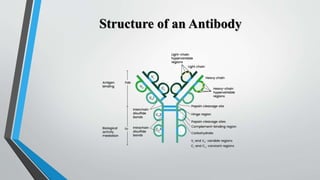
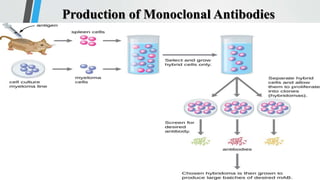
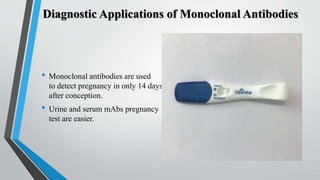
Monoclonal antibodies are identical antibodies produced by a single clone of B cells that recognize the same epitope on an antigen. They can be produced in a laboratory by fusing B cells that produce a desired antibody with myeloma cells to form hybridomas. Monoclonal antibodies have many diagnostic applications as they can be used to detect specific substances like proteins, pathogens, and tumor markers. They allow for rapid diagnosis of diseases like hepatitis, influenza, and cancer. Monoclonal antibodies are also used in pregnancy tests and monitoring drug levels in the body.











![MAJOR REFRENCE MATERIALS
• Fedorova VA, Samelia ZhG, Devdariani ZL, Utkin DV, Eremina OF, Liapina EP, et al. Development of
competitive immuno-assay based on monoclonal antibodies for the detection of specific antibodies to
pseudotuberculosis pathogen. Klin Lab Diagn. 2003;11:45–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
• Marcilla A, Monteagudo C, Mormeneo S, Sentandreu R. Monoclonal antibody 3H8: a useful tool in the
diagnosis of candidiasis. Microbiol. 1999;145:695–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
• Trowbridge IS. Interspecies spleen myeloma hybrid producing monoclonal antibodies against mouse
lymphocyte surface glycoprotein T 200. J Exp Med. 1978;148:313–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google
Scholar]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/girasu20000021-210329000837/85/Monoclonal-Antibodies-15-320.jpg)
