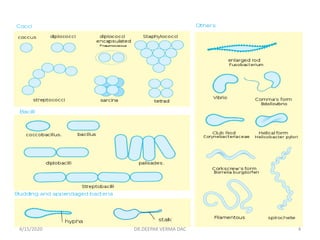
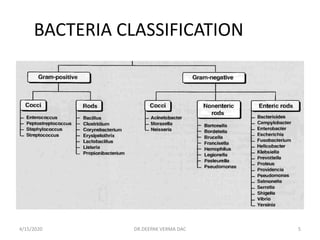
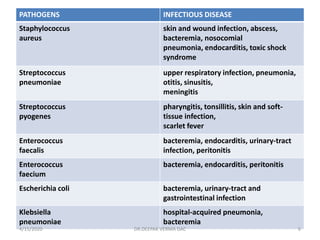
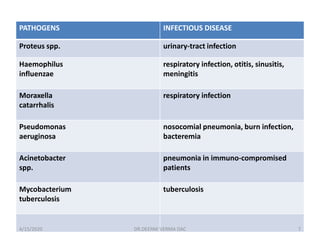
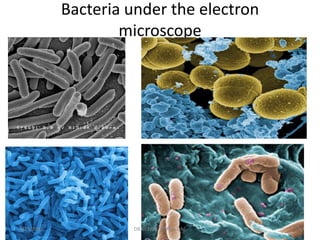
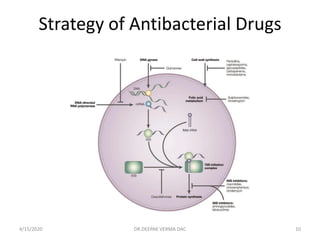
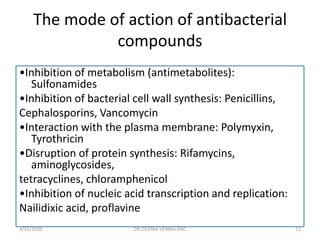
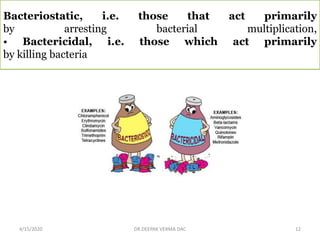
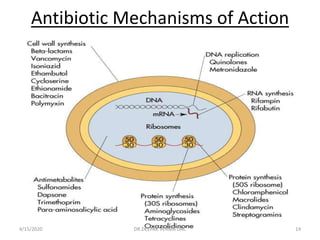
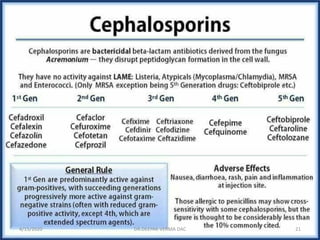
This document provides an overview of antibiotics, including their classification, mechanisms of action, and commonly prescribed types. It discusses how antibiotics are produced by microorganisms and were first discovered in 1928. The main classes covered are penicillins, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones, macrolides, and tetracyclines. Each class is described in terms of its antimicrobial spectrum, indications for use, mechanisms of action, and examples of commonly prescribed drugs. Side effects are also summarized.