This document provides an overview and introduction to Ansible. It discusses the motivation for IT automation and introduces some key Ansible concepts including Ansible Core, command line tools, playbooks, inventory, modules, and plugins. It also demonstrates how to get started with Ansible, use ad-hoc commands, and write playbooks. The presenter provides examples of installing packages and copying files using playbooks.






![INSERT DESIGNATOR, IF NEEDED7
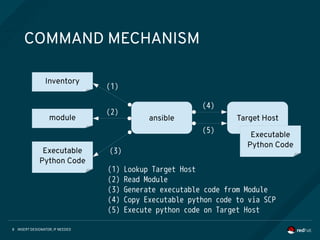
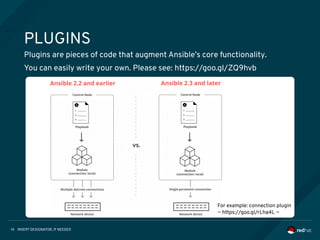
COMMAND LINE TOOLS
Ansible Core contains some command line tools. Following 2 commands are
able to control your target hosts.
[Usage] ansible %Target% -i %Inventory% -m %Module%
$ ansible www -i inventory -m ping
[Usage] ansible %Target% -i %Inventory% -a %Ad-Hoc Command%
$ ansible www -i inventory -a “/sbin/reboot”
[Usage] ansible %Target% -i %Inventory% -m %Module%
$ ansible www -i inventory -m ping
[Usage] ansible %Target% -i %Inventory% -a %Ad-Hoc Command%
$ ansible www -i inventory -a “/sbin/reboot”
[Usage] ansible-playbook -i %Inventory% %Playbook%
$ ansible-playbook -i inventory playbook.yml
[Usage] ansible-playbook -i %Inventory% %Playbook%
$ ansible-playbook -i inventory playbook.yml
1. ansible command
2. ansible-playbook command](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ansible101jtf2017-170827042739/85/Ansible101-7-320.jpg)

![INSERT DESIGNATOR, IF NEEDED10
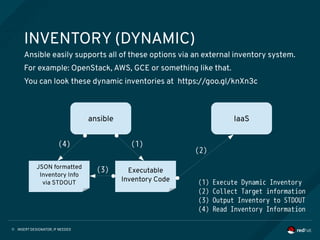
INVENTORY (STATIC)
Ansible is able to working against multiple system at the same time.
You can select portions of systems listed in the inventory at running time.
01: [localhost]
02: 127.0.0.1
03:
04: [staging]
05: 192.168.0.1
06: 192.168.0.2
07:
08: [production]
09: www1.example.com
10: www2.example.com
11:
12: [vars:local]
13: ansible_connection=local
01: [localhost]
02: 127.0.0.1
03:
04: [staging]
05: 192.168.0.1
06: 192.168.0.2
07:
08: [production]
09: www1.example.com
10: www2.example.com
11:
12: [vars:local]
13: ansible_connection=local](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ansible101jtf2017-170827042739/85/Ansible101-10-320.jpg)

![INSERT DESIGNATOR, IF NEEDED17
Getting started (2)
Writing inventory file.
01: [linux]
02: 192.168.100.100 ansible_user=ec2-user
03: 192.168.100.101 ansible_user=ec2-user
04: 192.168.100.102 ansible_user=ec2-user
05:
06: [win]
07: WIN-PC1.example.com
08: WIN-PC2.example.com
09: WIN-PC3.example.com
10:
11: [win:vars]
12: ansible_port=5986
13: ansible_connection=winrm
14: ansible_winrm_server_cert_validation=ignore
15: ansible_winrm_transport=kerberos
16: ansible_winrm_kerberos_delegation=true
01: [linux]
02: 192.168.100.100 ansible_user=ec2-user
03: 192.168.100.101 ansible_user=ec2-user
04: 192.168.100.102 ansible_user=ec2-user
05:
06: [win]
07: WIN-PC1.example.com
08: WIN-PC2.example.com
09: WIN-PC3.example.com
10:
11: [win:vars]
12: ansible_port=5986
13: ansible_connection=winrm
14: ansible_winrm_server_cert_validation=ignore
15: ansible_winrm_transport=kerberos
16: ansible_winrm_kerberos_delegation=true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ansible101jtf2017-170827042739/85/Ansible101-17-320.jpg)


![INSERT DESIGNATOR, IF NEEDED23
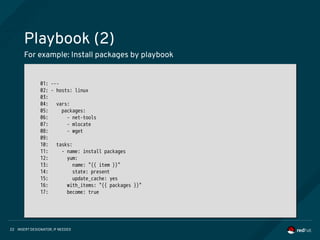
Playbook (3)
An operation is idempotent if the result of performing it once is exactly the
same as the result of performing it repeatedly without any intervening
actions.
# Try to launch playbook - 1st time (state: changed)
$ ansible-playbook -i hosts install_packages.yml
…
TASK [install packages]
**********************************************************************
changed: [172.31.3.136] => (item=[u'net-tools', u'mlocate', u'wget'])
...
# Try to launch playbook - 2nd time (state: ok)
$ ansible-playbook -i hosts install_packages.yml
…
TASK [install packages]
**********************************************************************
ok: [172.31.5.233] => (item=[u'net-tools', u'mlocate', u'wget'])
# Try to launch playbook - 1st time (state: changed)
$ ansible-playbook -i hosts install_packages.yml
…
TASK [install packages]
**********************************************************************
changed: [172.31.3.136] => (item=[u'net-tools', u'mlocate', u'wget'])
...
# Try to launch playbook - 2nd time (state: ok)
$ ansible-playbook -i hosts install_packages.yml
…
TASK [install packages]
**********************************************************************
ok: [172.31.5.233] => (item=[u'net-tools', u'mlocate', u'wget'])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ansible101jtf2017-170827042739/85/Ansible101-23-320.jpg)
![INSERT DESIGNATOR, IF NEEDED26
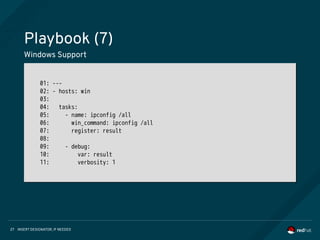
Playbook (6)
Windows Support
1. Install krb packages and related python modules
2. Configure /etc/krb5.conf
3. kinit user@DOMAIN
- http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/intro_windows.html
$ yum -y install python-devel krb5-devel krb5-libs krb5-workstation
$ pip install ntlm-auth==1.0.2
$ pip install pywinrm[kerberos]
$ pip install requests-kerberos
$ pip install pykerberos
$ sudo vi /etc/krb5.conf
$ kinit Administrator@EXAMPLE.COM
$ yum -y install python-devel krb5-devel krb5-libs krb5-workstation
$ pip install ntlm-auth==1.0.2
$ pip install pywinrm[kerberos]
$ pip install requests-kerberos
$ pip install pykerberos
$ sudo vi /etc/krb5.conf
$ kinit Administrator@EXAMPLE.COM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ansible101jtf2017-170827042739/85/Ansible101-26-320.jpg)

![INSERT DESIGNATOR, IF NEEDED29
Modules document
You will see the documentation for modules by ansible-doc command
$ ansible-doc --help
Usage: ansible-doc [options] [module...]
Options:
-a, --all Show documentation for all modules
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-l, --list List available modules
-M MODULE_PATH, --module-path=MODULE_PATH
specify path(s) to module library (default=None)
-s, --snippet Show playbook snippet for specified module(s)
-v, --verbose verbose mode (-vvv for more, -vvvv to enable
connection debugging)
--version show program's version number and exit
$ ansible-doc --help
Usage: ansible-doc [options] [module...]
Options:
-a, --all Show documentation for all modules
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-l, --list List available modules
-M MODULE_PATH, --module-path=MODULE_PATH
specify path(s) to module library (default=None)
-s, --snippet Show playbook snippet for specified module(s)
-v, --verbose verbose mode (-vvv for more, -vvvv to enable
connection debugging)
--version show program's version number and exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ansible101jtf2017-170827042739/85/Ansible101-29-320.jpg)

