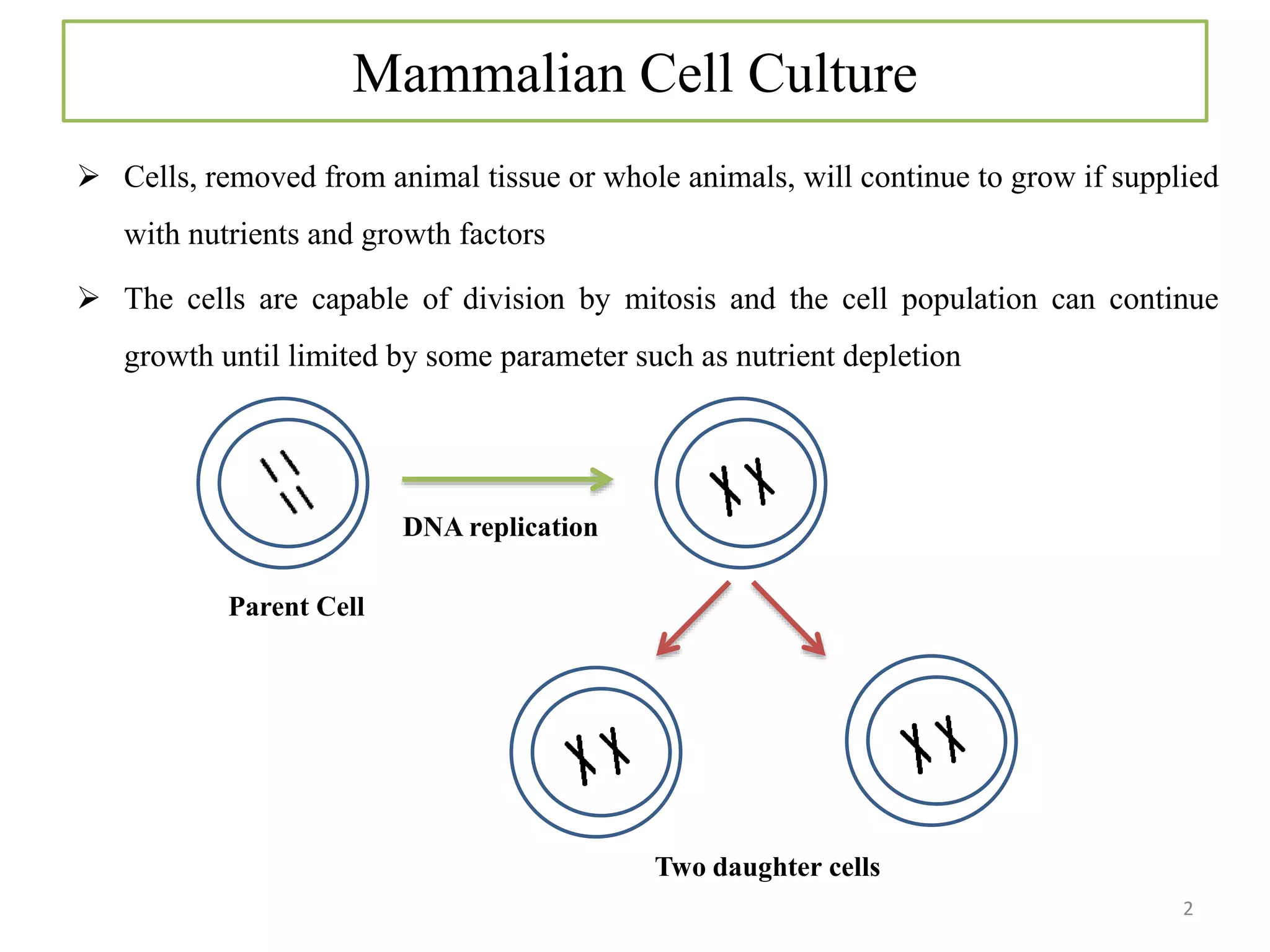
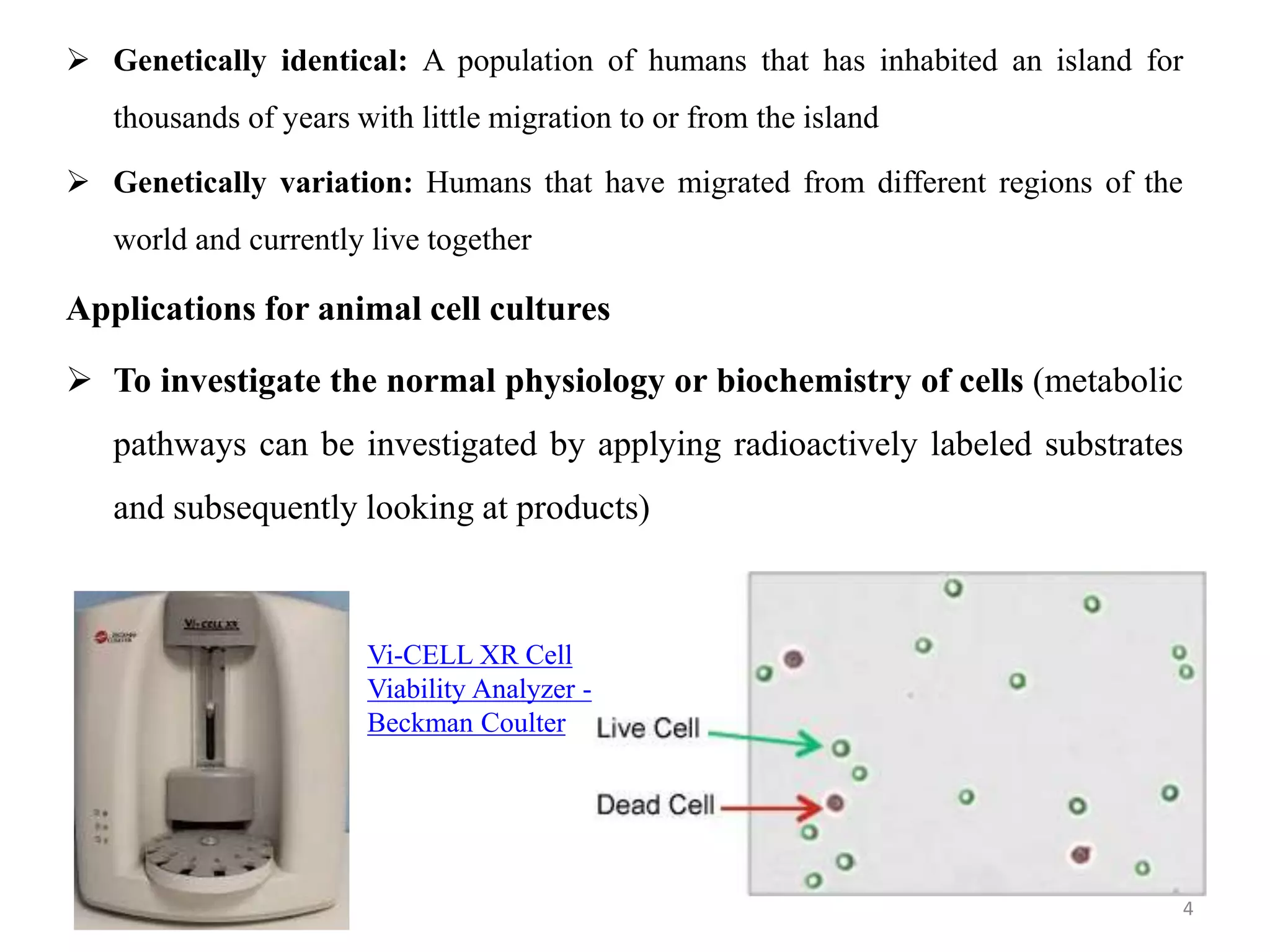
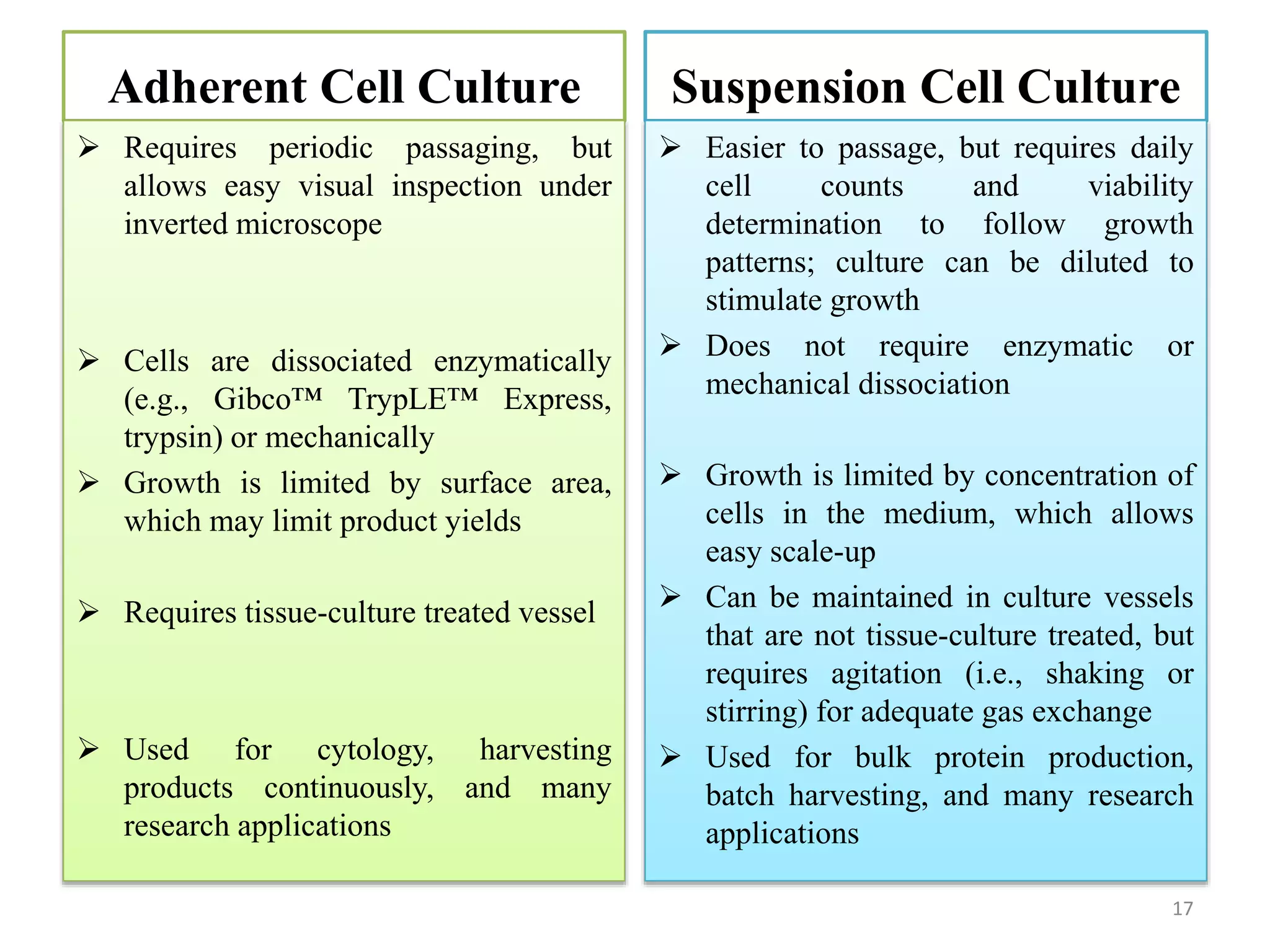
The document provides an overview of mammalian cell culture, explaining its principles, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. It discusses the importance of cell types like fibroblasts, the effects of nutrient variations on cell characteristics, and the significance of telomere shortening on cell growth. Additionally, it highlights the historical development of animal cell technology and different culture methods such as adherent and suspension cell cultures.