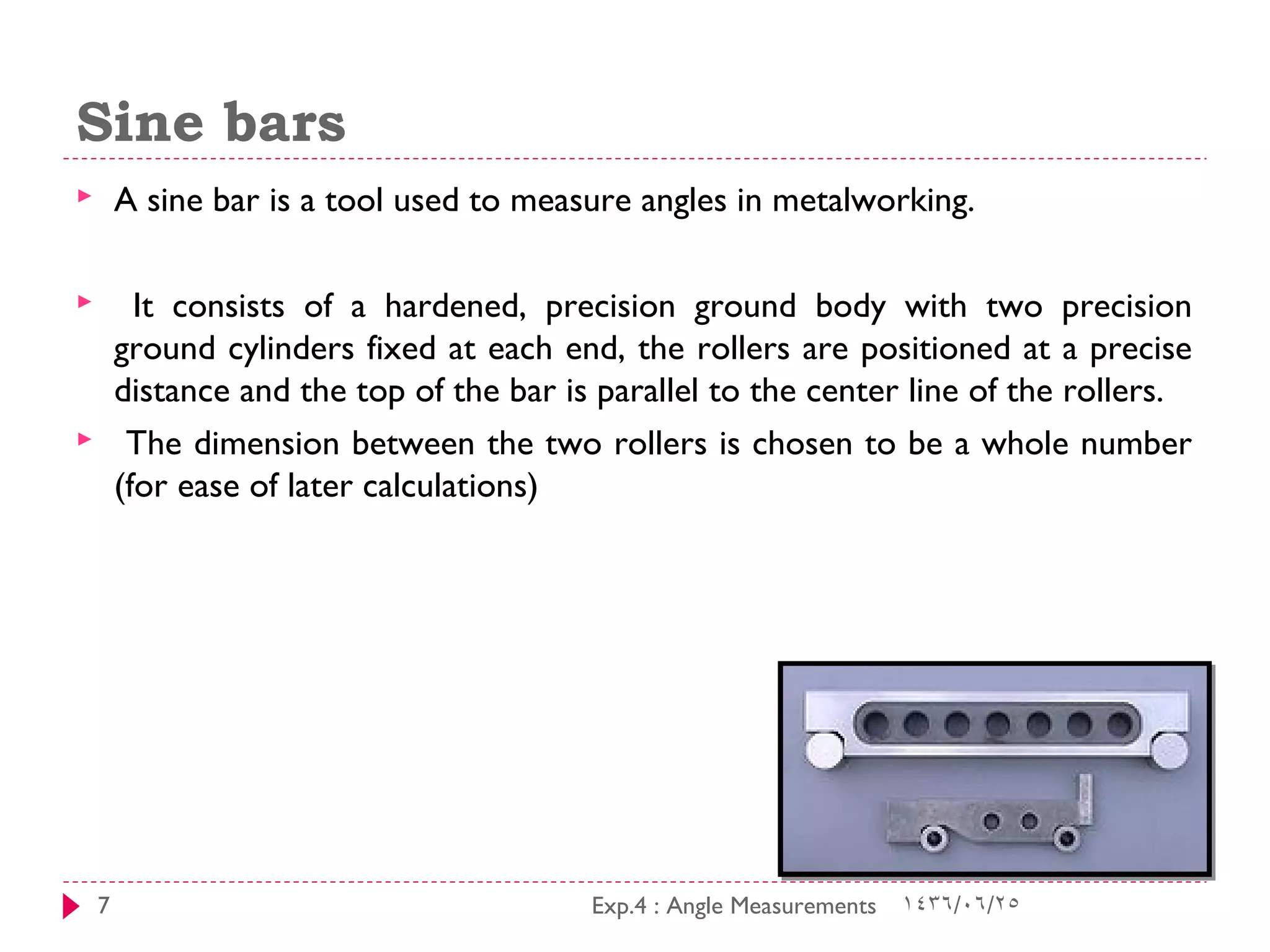
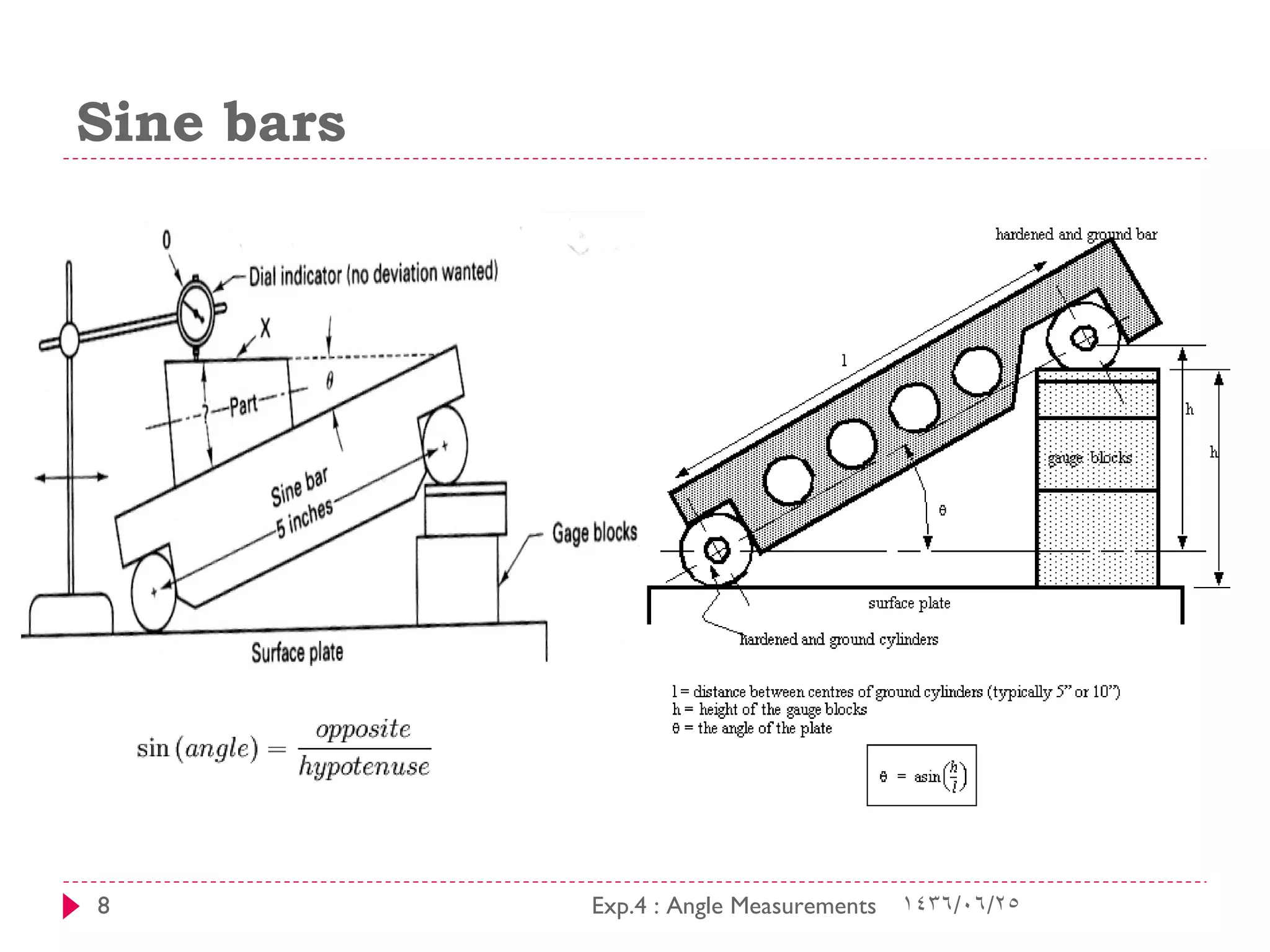
This document discusses tools for measuring angles, including block gauges, sine bars, combination sets, and protractors. Block gauges are made of materials that are hard, stable with temperature changes, resistant to corrosion, and have a smooth finish. Their parallel faces and precise dimensions make them useful for calibrating measurement tools and providing known lengths. Sine bars contain two precisely placed rollers used to measure angles in metalworking. Combination sets can measure common angles and be used as a square, level, and rule. Protractors can precisely measure angles to within one degree or five minutes and have rotating heads for direct reading in both directions.