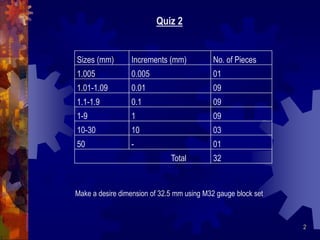
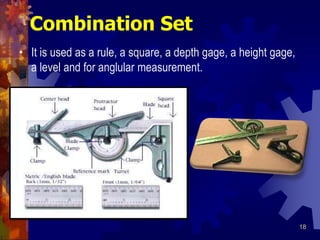
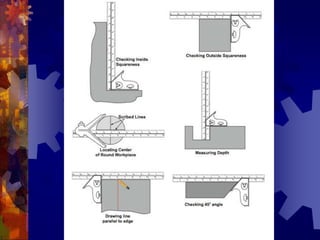
This document provides information about angular measurement tools and techniques. It discusses units of angular measurement such as degrees, minutes, and seconds. It also describes various tools used to measure angles, including protractors, combination sets, vernier protractors, universal bevel protractors, inclinometers, and sine bars. Examples are provided for converting between decimal degrees and degrees-minutes-seconds notation.