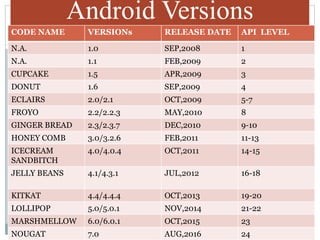
The document provides an overview of Android, detailing its origins, versions, software architecture, and the challenges and limitations faced in app development. Android, developed by Google as a Linux-based operating system, supports a robust application ecosystem with over 400,000 apps. Key challenges include performance optimization and security concerns, alongside a dependency on internet connectivity.