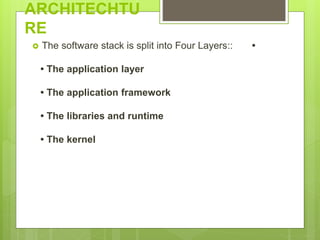
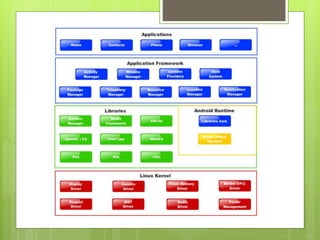
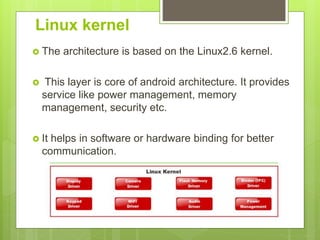
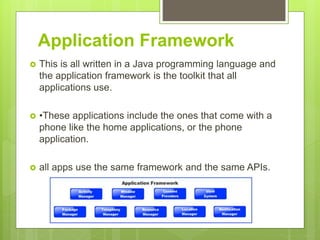
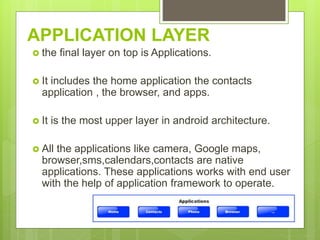
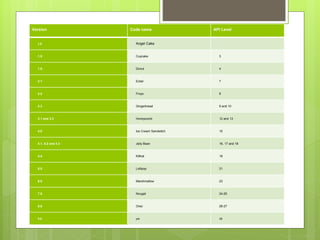
The document discusses the history and architecture of the Android operating system. It describes how Android was developed by Android Inc. which was later acquired by Google. It formed the Open Handset Alliance with other companies to develop Android as an open source platform. The architecture is based on the Linux kernel and has four layers - the application layer, application framework, native libraries/runtime, and kernel. It also lists the major versions of Android from 1.0 to the current 9.0.