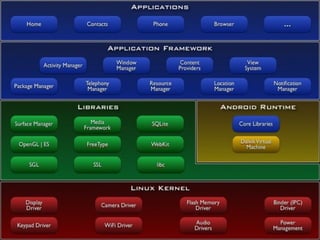
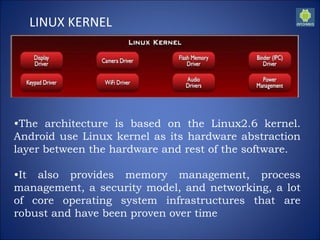
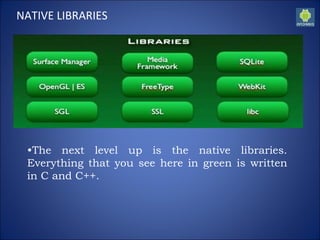
Android is an open-source software stack that includes an operating system, middleware, and key applications for mobile devices. It was developed by the Open Handset Alliance led by Google. The Android architecture consists of four layers - the application layer, application framework, libraries/runtime, and Linux kernel. It uses the Linux kernel as its core and a custom virtual machine called Dalvik for running applications. This allows Android to be used across a wide range of devices. While Android offers customization and a variety of applications, it also has some limitations like requirements to use Java and SDK tools for development.