The document provides an overview of object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts as applied in Android programming, including key principles such as classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction, and encapsulation. It explains these concepts through definitions and examples, emphasizing naming conventions, method overloading, constructors, abstract classes, and the use of keywords like 'super' and 'this'. The document aims to facilitate understanding of OOP to enhance software development and maintenance.





![ClassDeclaration
class Student1{
int id; // data member (also instance variable)
String name; // data member(also instance variable)
public static void main(String args[]){
Student1 s1 = new Student1(); // creating an object of Student
System.out.println(s1.id); // accessing class data member
System.out.println(s1.name);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopsconcepts-160119122611/85/OOPs-Concepts-Android-Programming-6-320.jpg)

![Methodoverloading - Example
Example-1 Different No of Parameters
class Calculation{
void sum(int a,int b)
{System.out.println(a+b);}
void sum(int a,int b,int c)
{System.out.println(a+b+c);}
public static void main(String args[]){
Calculation obj=new Calculation();
obj.sum(10,10,10);
obj.sum(20,20);
} }
Example -2 Changing Data type
class Calculation2{
void sum(int a,int b)
{System.out.println(a+b);}
void sum(double a,double b)
{System.out.println(a+b);}
public static void main(String args[]){
Calculation2 obj=new Calculation2();
obj.sum(10.5,10.5);
obj.sum(20,20);
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopsconcepts-160119122611/85/OOPs-Concepts-Android-Programming-8-320.jpg)

![Constructor - example
class Student5{
int id;
String name;
int age;
Student5() { } // default
Student5(int i,String n){
id = i;
name = n; }
Student5(int i,String n,int a){
id = i;
name = n;
age=a;
}
void display(){
System.out.println(id+" "+name+" "+age);}
public static void main(String args[]){
Student5 s1 = new Student5(111,"Karan");
Student5 s2 = new Student5(222,"Aryan",25);
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopsconcepts-160119122611/85/OOPs-Concepts-Android-Programming-10-320.jpg)

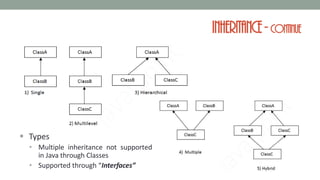
![Inheritance- example
class Employee{
float salary=40000;
}
class Programmer extends Employee{
int bonus=10000;
public static void main(String args[]){
Programmer p=new Programmer();
System.out.println("Programmer salary is:"+p.salary);
System.out.println("Bonus of Programmer is:"+p.bonus);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopsconcepts-160119122611/85/OOPs-Concepts-Android-Programming-13-320.jpg)




![Abstractclass - CONTINUE
Example
abstract class Bike{
abstract void run();
}
class Honda4 extends Bike{
void run(){System.out.println("running safely..");}
public static void main(String args[]){
Bike obj = new Honda4();
obj.run();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopsconcepts-160119122611/85/OOPs-Concepts-Android-Programming-18-320.jpg)

![Interface-example-1
Understand Relationship
Example:
interface printable{
void print();
}
class A6 implements printable{
public void print()
{System.out.println("Hello");}
public static void main(String args[]){
A6 obj = new A6();
obj.print();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopsconcepts-160119122611/85/OOPs-Concepts-Android-Programming-20-320.jpg)
![Interface-example-2
interface Printable{
void print(); }
interface Showable{
void show(); }
class A7 implements Printable,Showable{
public void print(){System.out.println("Hello");}
public void show(){System.out.println("Welcome");}
public static void main(String args[]){
A7 obj = new A7();
obj.print();
obj.show();
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopsconcepts-160119122611/85/OOPs-Concepts-Android-Programming-21-320.jpg)

![Encapsulation- example
//save as Student.java
public class Student{
private String name;
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name=name
}
}
//save as Test.java
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Student s=new Student();
s.setname("vijay");
System.out.println(s.getName());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopsconcepts-160119122611/85/OOPs-Concepts-Android-Programming-23-320.jpg)

![Superkeyword- example
Example - 1
class Vehicle{
int speed = 50;
}
class Bike4 extends Vehicle{
int speed = 100;
void display(){
System.out.println(super.speed);
//will print speed of Vehicle now
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Bike4 b = new Bike4();
b.display();
} }
Example - 2
class Vehicle{
Vehicle()
{System.out.println("Vehicle is created");}
}
class Bike5 extends Vehicle{
Bike5(){
super();
//will invoke parent class constructor
System.out.println("Bike is created");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Bike5 b = new Bike5();
} }
Example – 3
class Person{
void message()
{System.out.println("welcome");}
}
class Student16 extends Person{
void message()
{System.out.println("welcome to java");}
void display(){
message();
//will invoke current class message() method
super.message();
//will invoke parent class message() method
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Student16 s=new Student16();
s.display();
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopsconcepts-160119122611/85/OOPs-Concepts-Android-Programming-25-320.jpg)

![Thiskeyword - example
Example - 1
class Student11{
int id;
String name;
Student11(int id,String name){
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
void display()
{ System.out.println(id+" "+name);}
public static void main(String args[]){
Student11 s1 = new Student11(111,"Karan");
Student11 s2 = new Student11(222,"Aryan");
s1.display();
s2.display();
} }
Example – 2
class Student13{
int id;
String name;
Student13()
{System.out.println("defaultconstructor is invoked");}
Student13(int id,String name){
this (); //it is used to invoked current class constructor.
this.id = id;
this.name = name; }
void display(){System.out.println(id+" "+name);}
public static void main(String args[]){
Student13 e1 = new Student13(111,"karan");
Student13 e2 = new Student13(222,"Aryan");
e1.display();
e2.display();
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopsconcepts-160119122611/85/OOPs-Concepts-Android-Programming-27-320.jpg)

