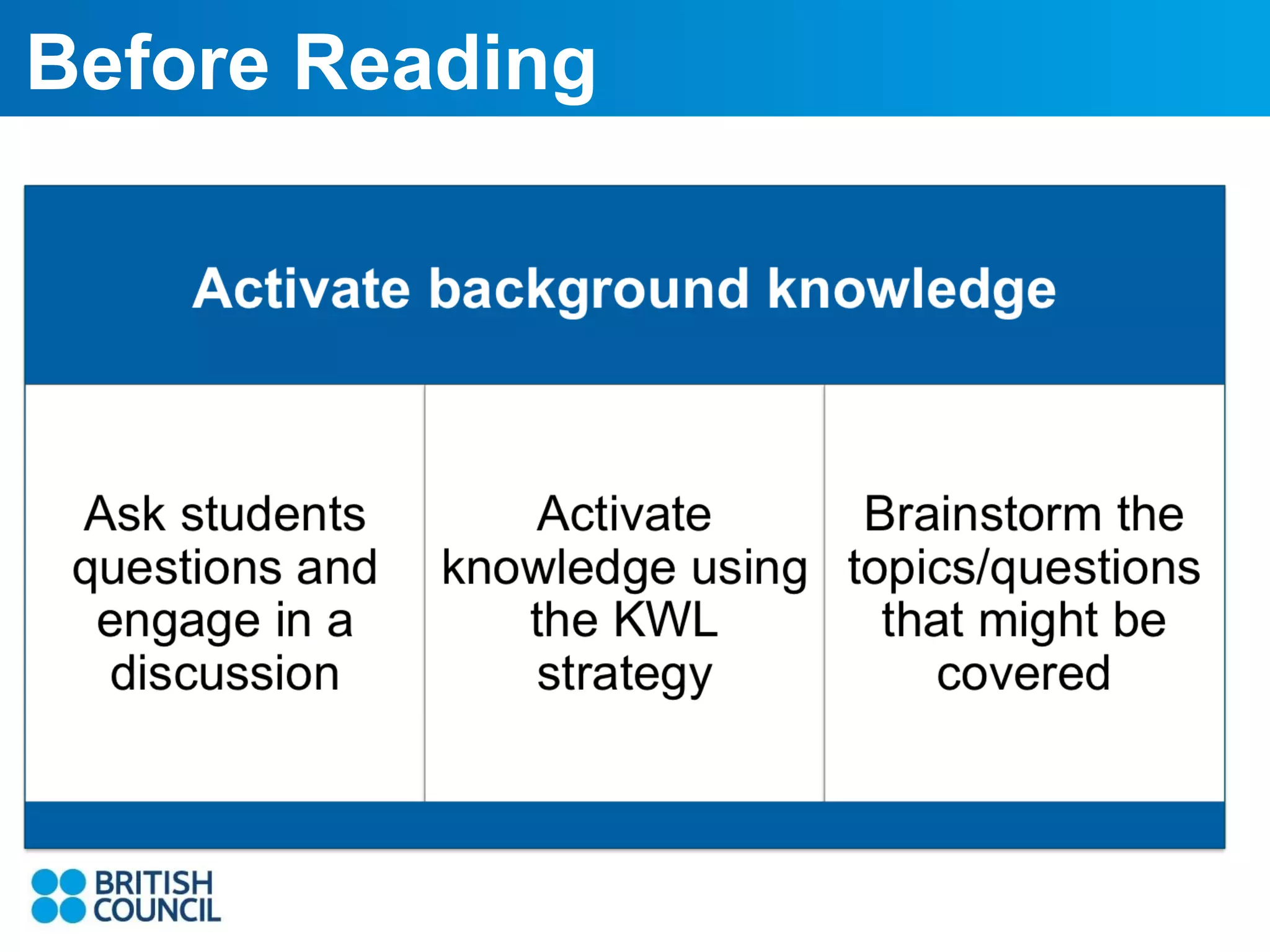
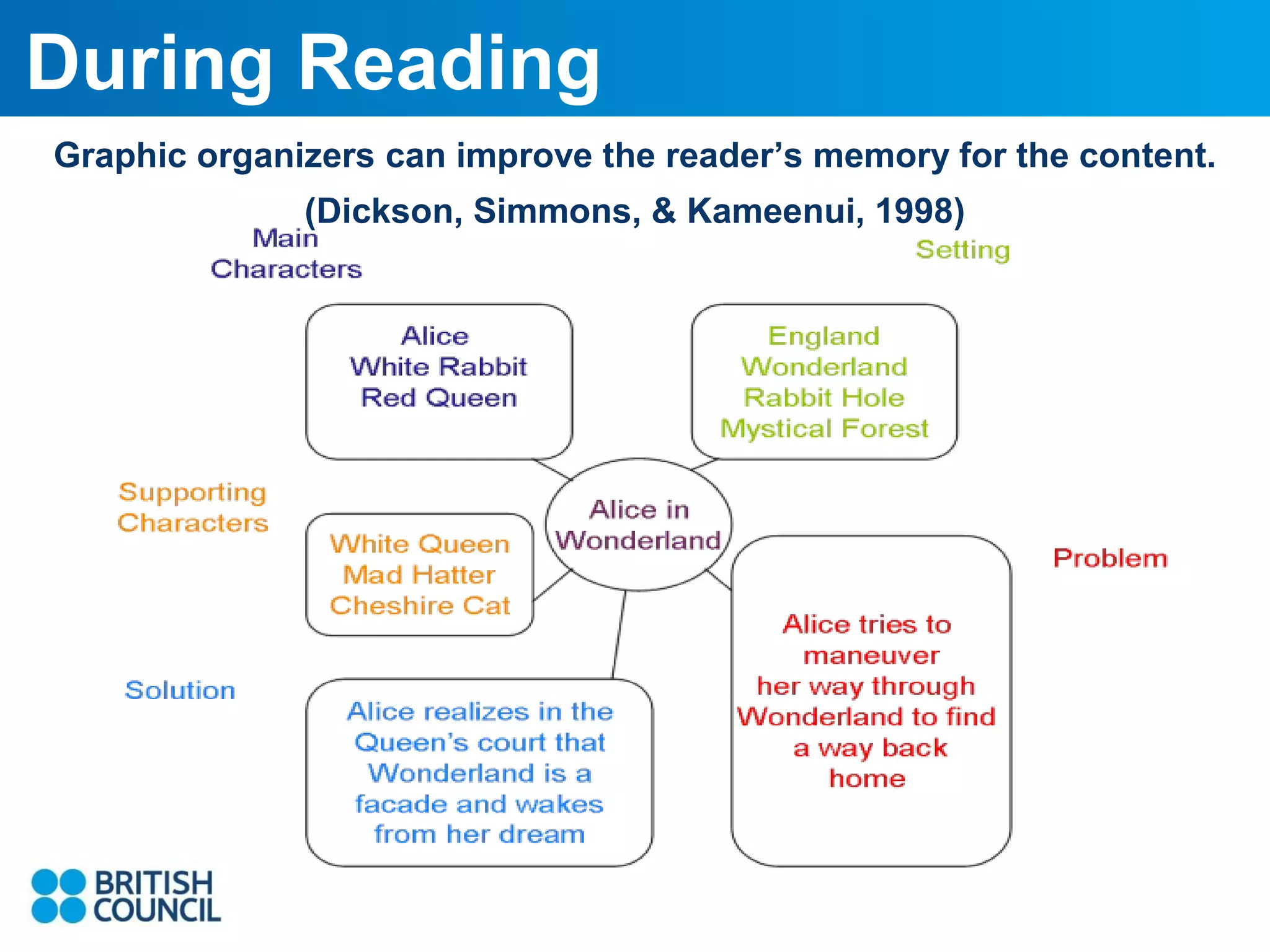
The document summarizes strategies for scaffolding reading experiences to ease the trauma of tackling English literature. It provides suggestions for activities to do before, during, and after reading to improve comprehension. Specifically, it recommends introducing key vocabulary before reading, asking questions while reading to encourage engagement, and having students write or discuss after reading to help organize and express their understanding. The overall goal is to use scaffolding techniques to assist students in comprehending texts through a gradual release of responsibility.