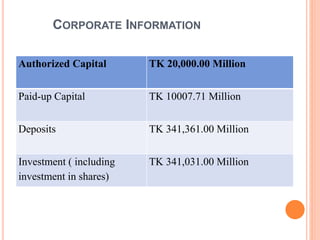
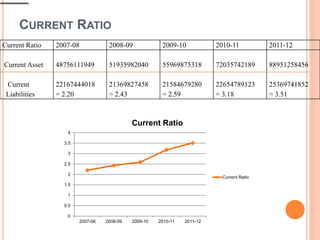
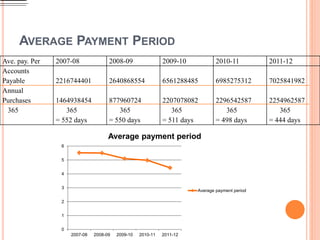
The document is a case analysis of e-banking application at Islami Bank Bangladesh Limited (IBBL) conducted by a group of 6 students. It provides an overview of IBBL, analyzes the bank using Porter's Five Forces model and SWOT analysis, describes the bank's products/services, and presents various financial ratios analyzing IBBL's liquidity, leverage, profitability, and efficiency over several years. The ratios generally show improving trends in IBBL's financial position and performance over time.