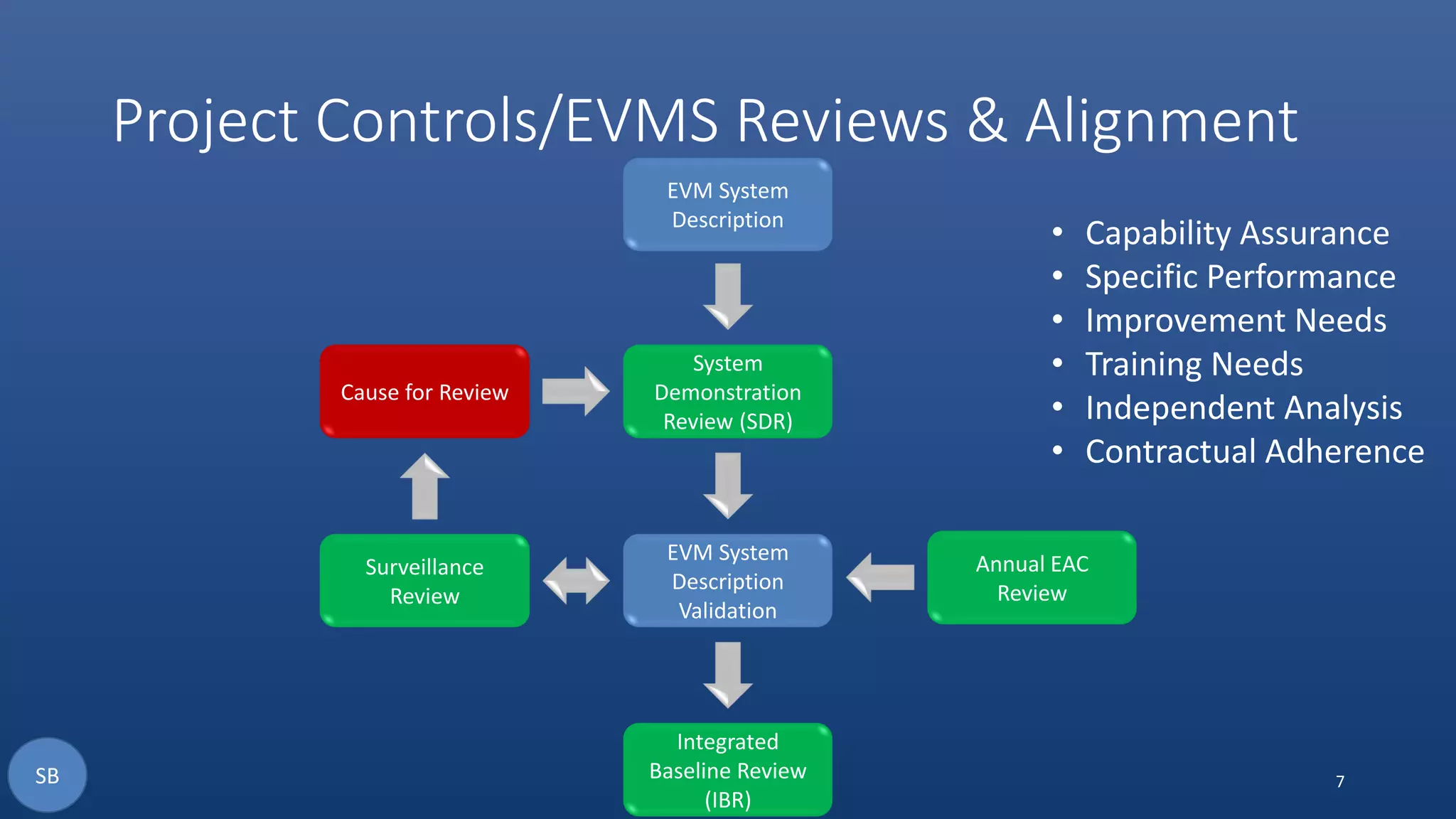
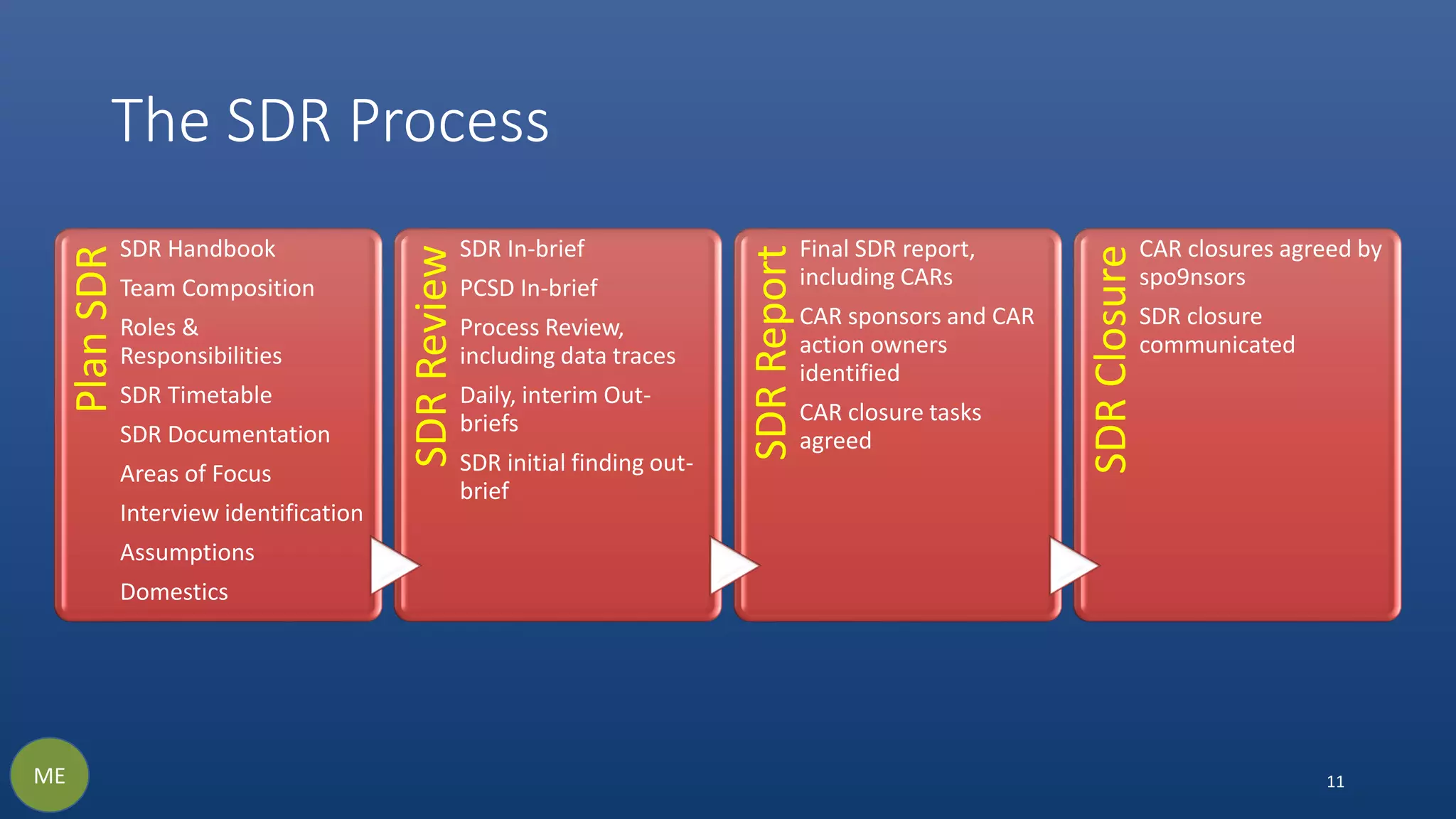
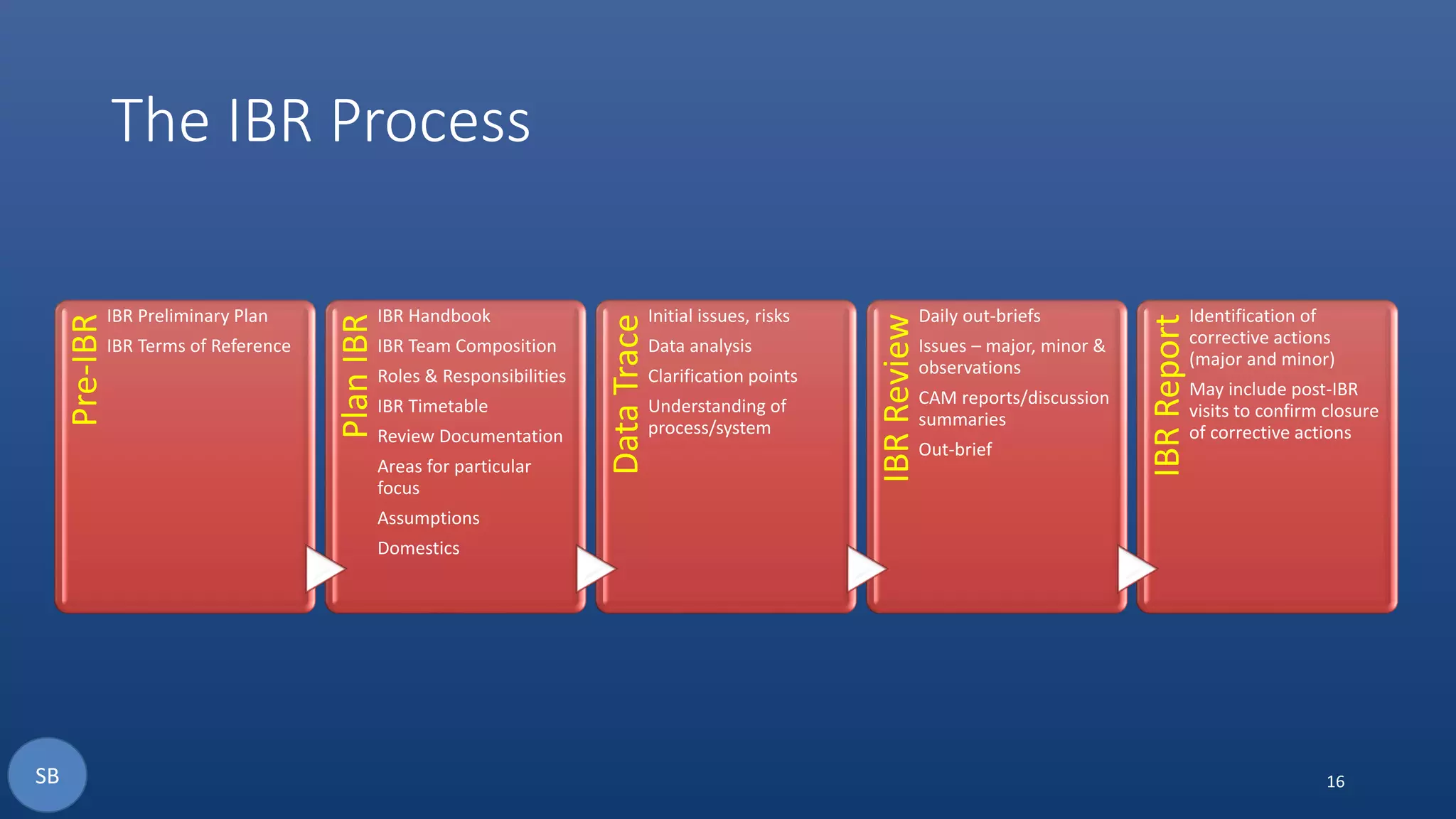
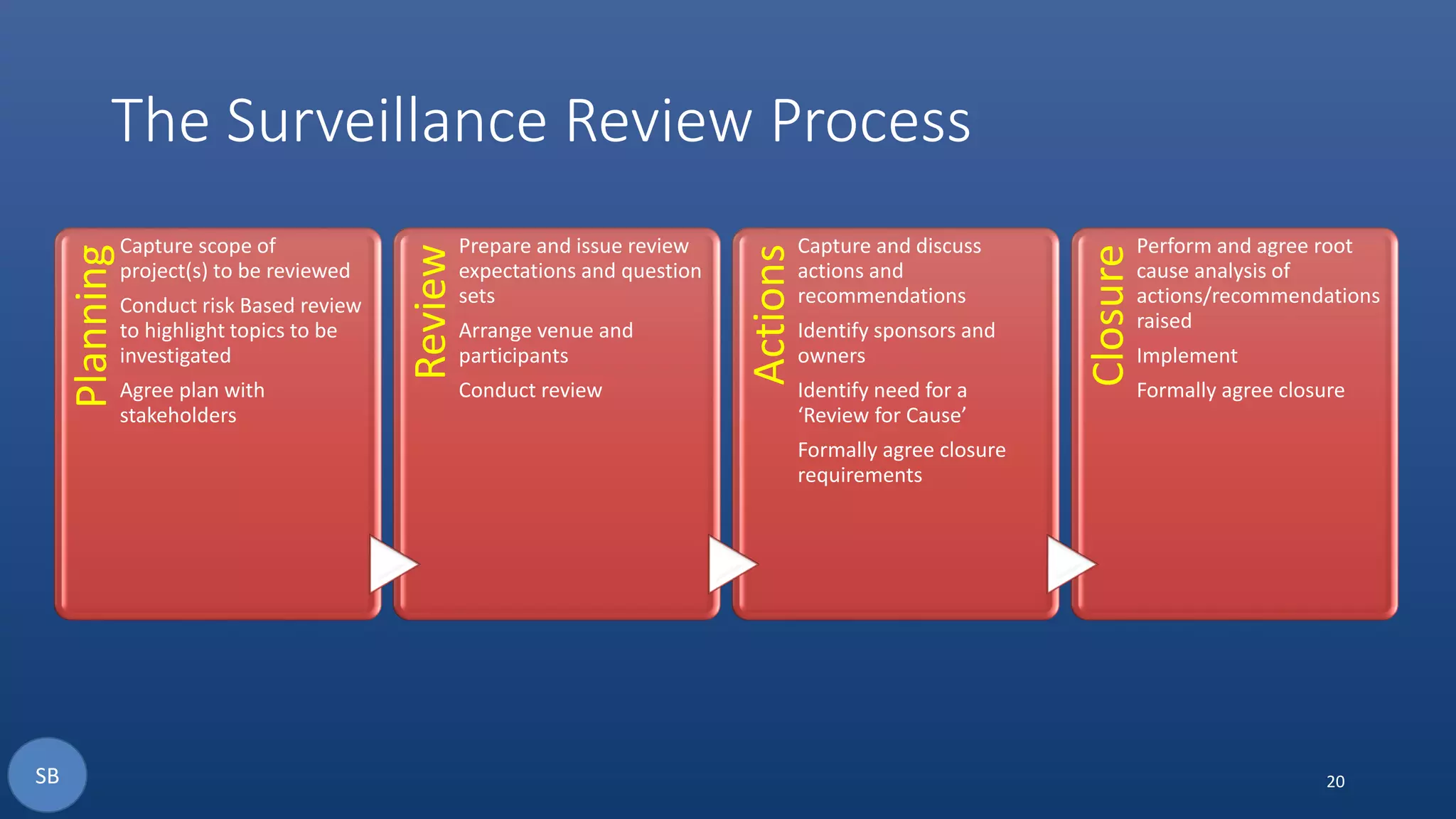
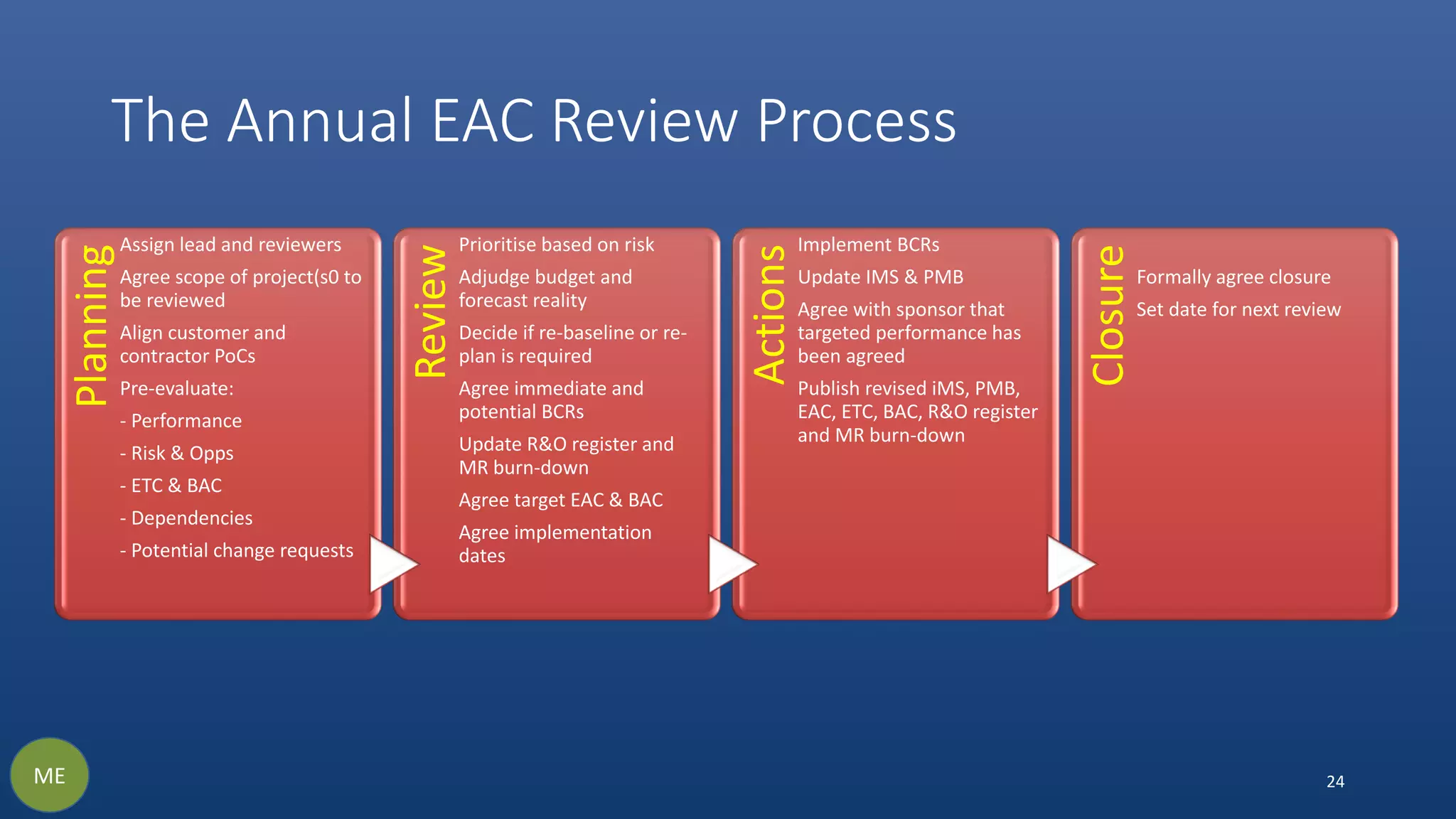
The document discusses the necessity and structure of an effective Earned Value Management System (EVMS), emphasizing the importance of understanding project controls, EVMS, and Earned Value Analysis. It outlines the objectives, content, and processes of various assurance reviews including System Demonstration Reviews (SDR), Integrated Baseline Reviews (IBR), Surveillance Reviews (SR), and Annual Estimate at Completion Reviews (AEAC). The aim is to clarify misconceptions and ensure credible implementation and adherence to EVMS in project management.