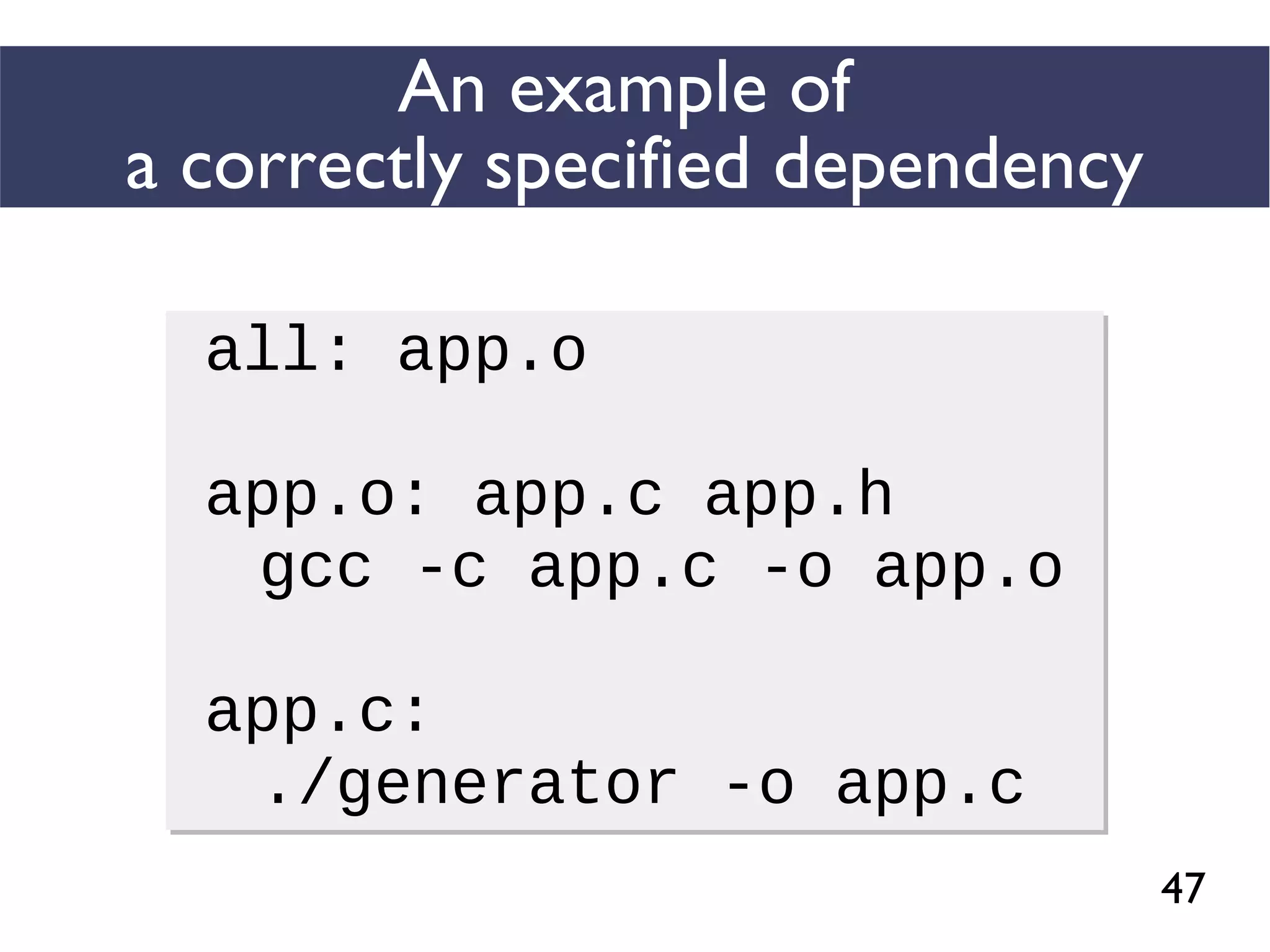
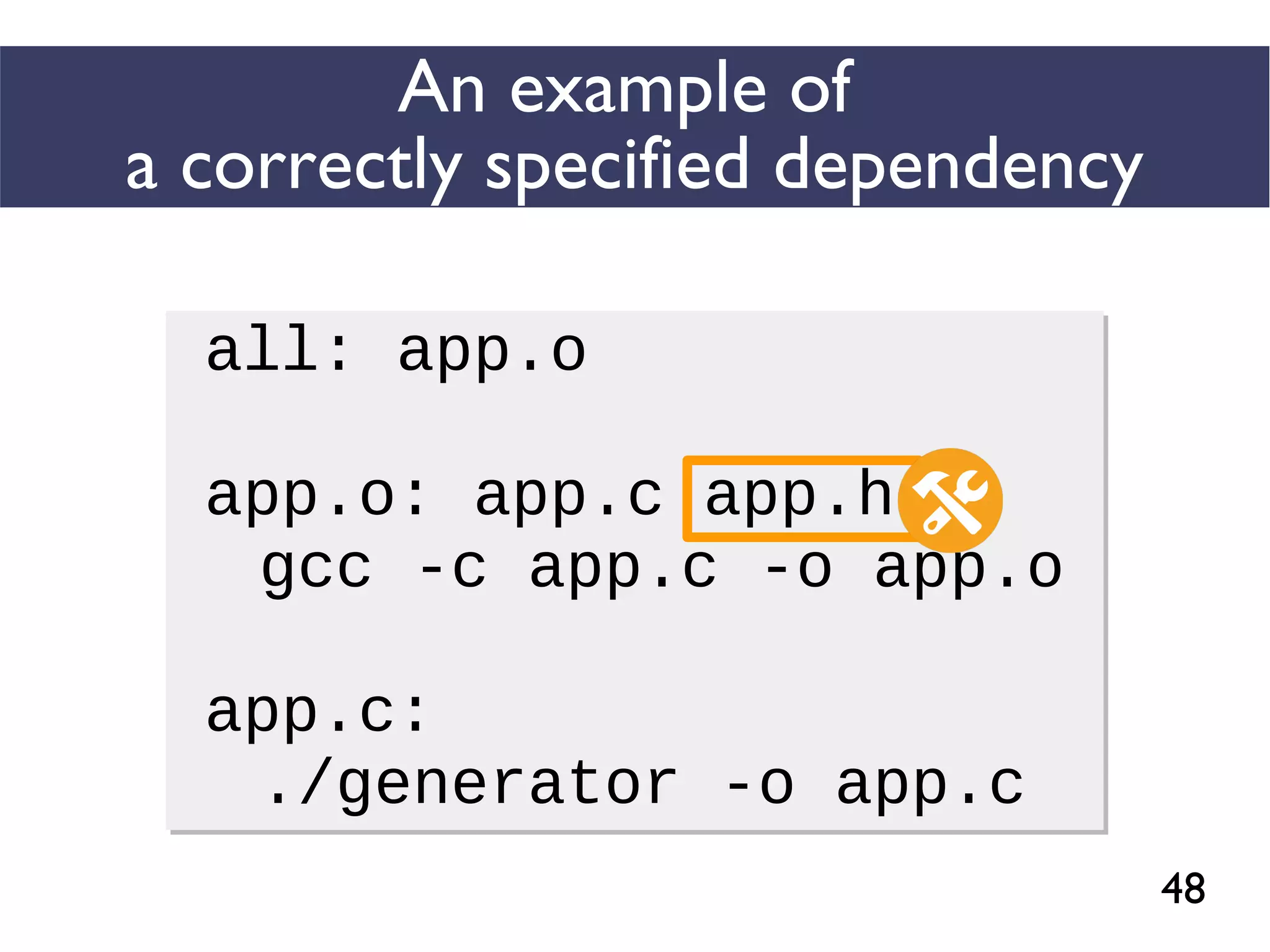
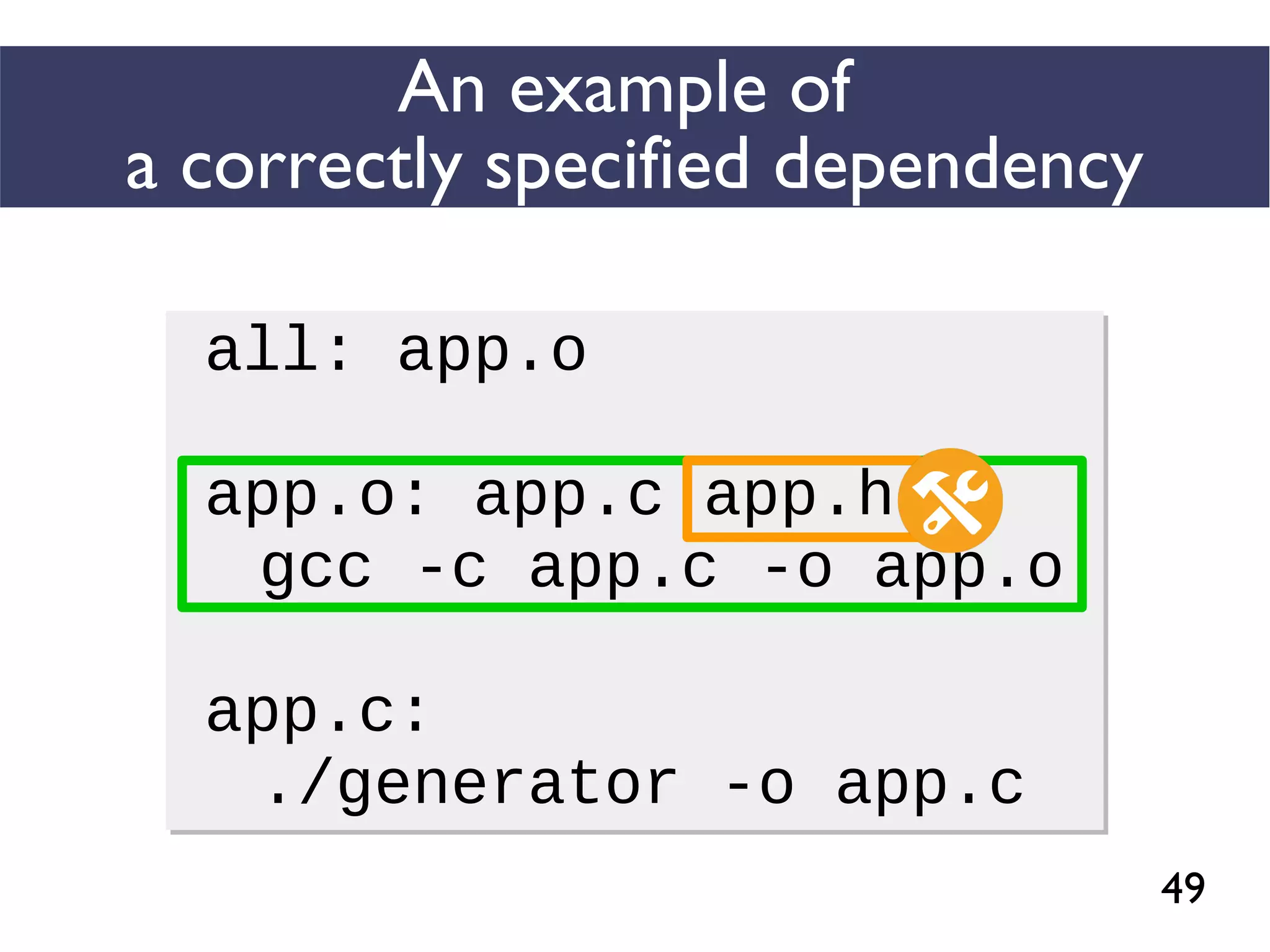
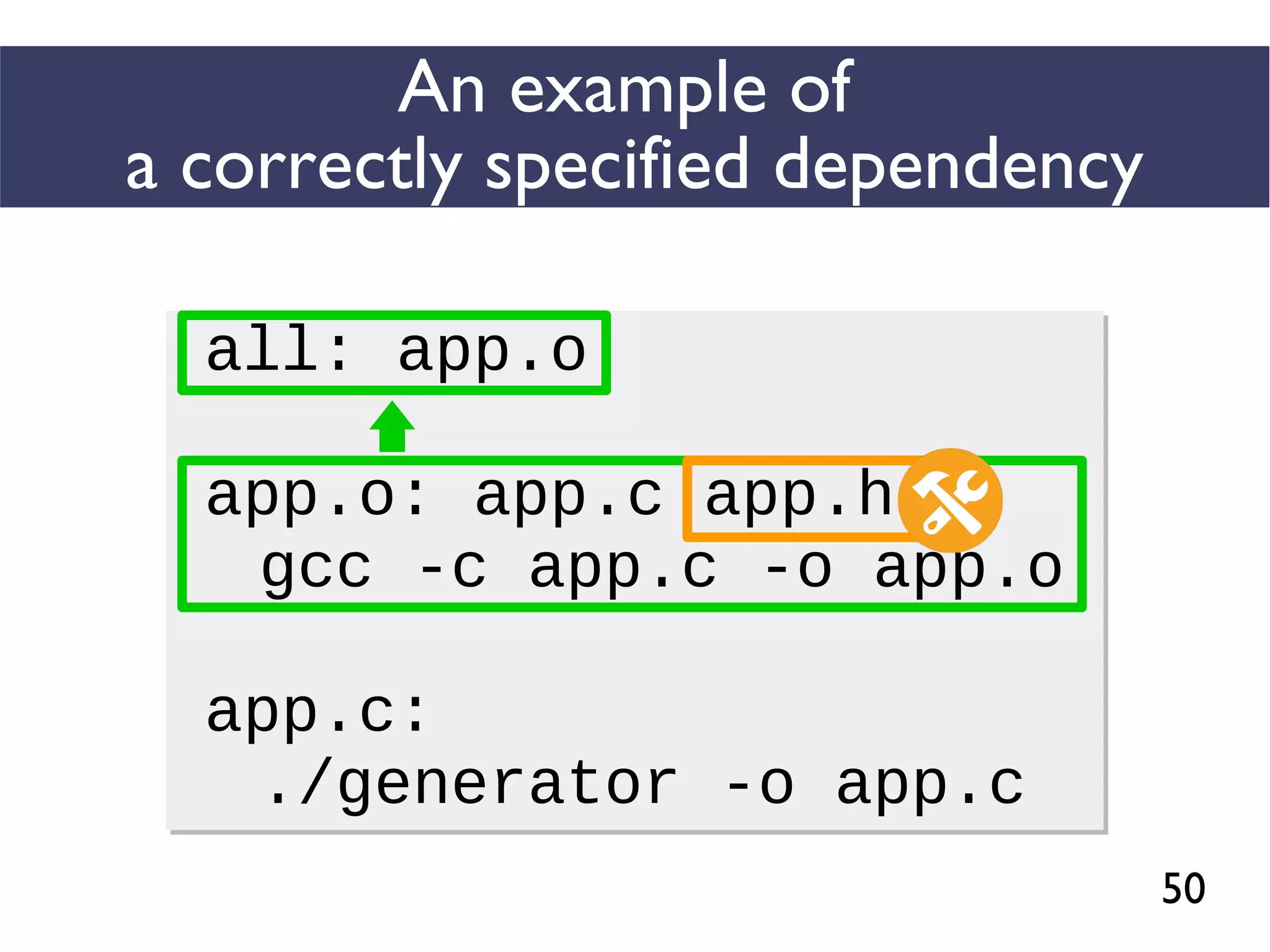
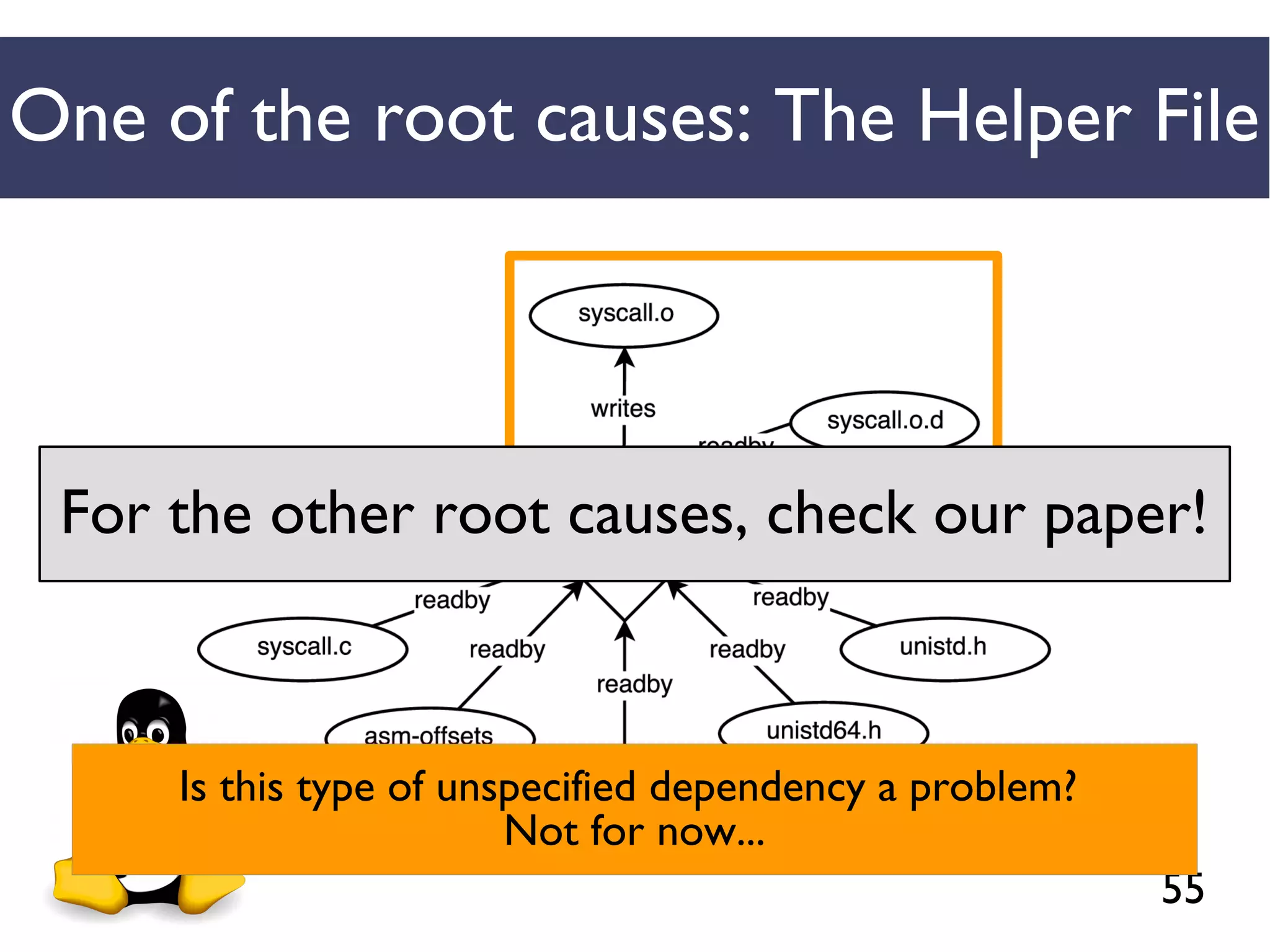
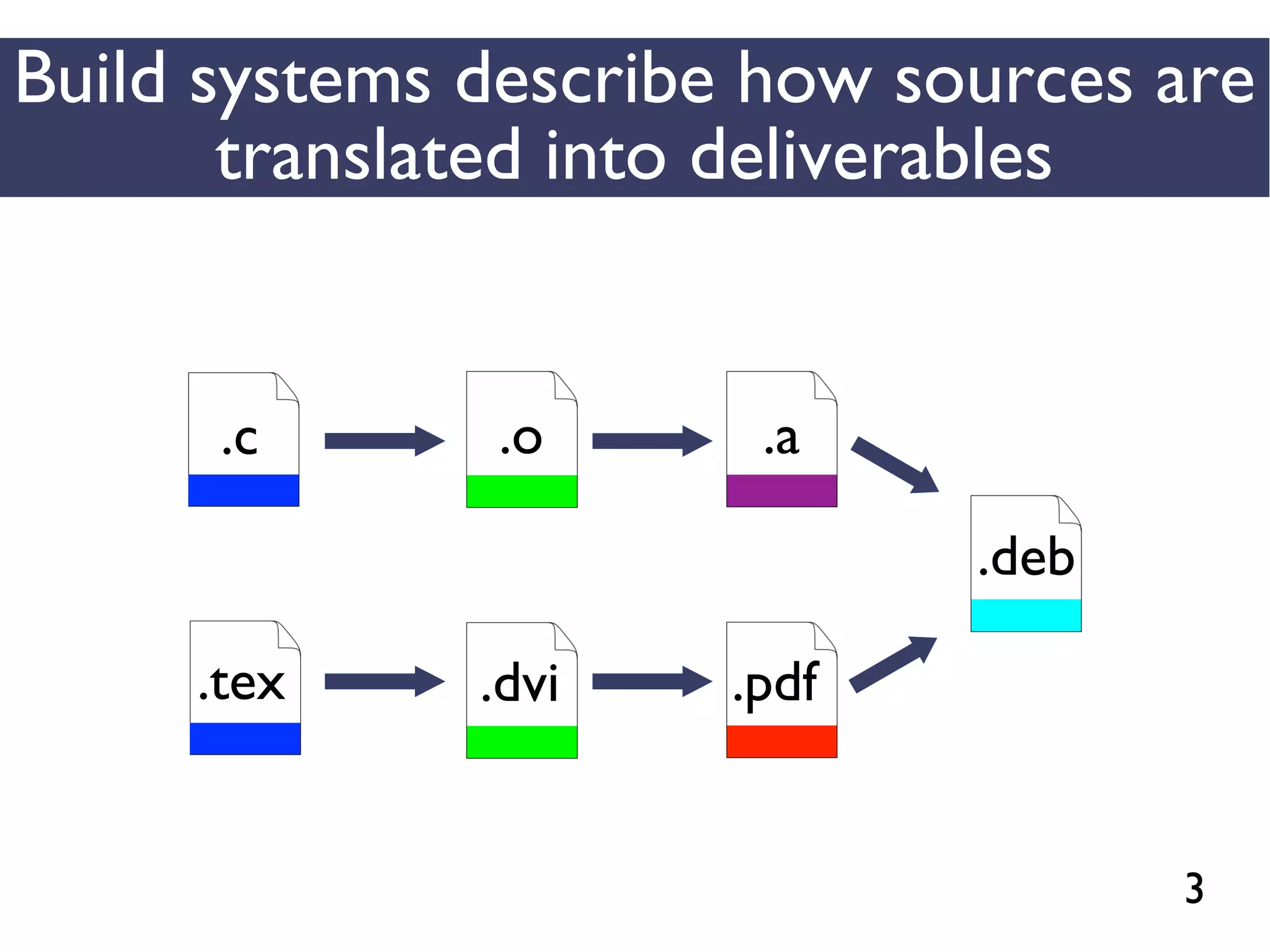
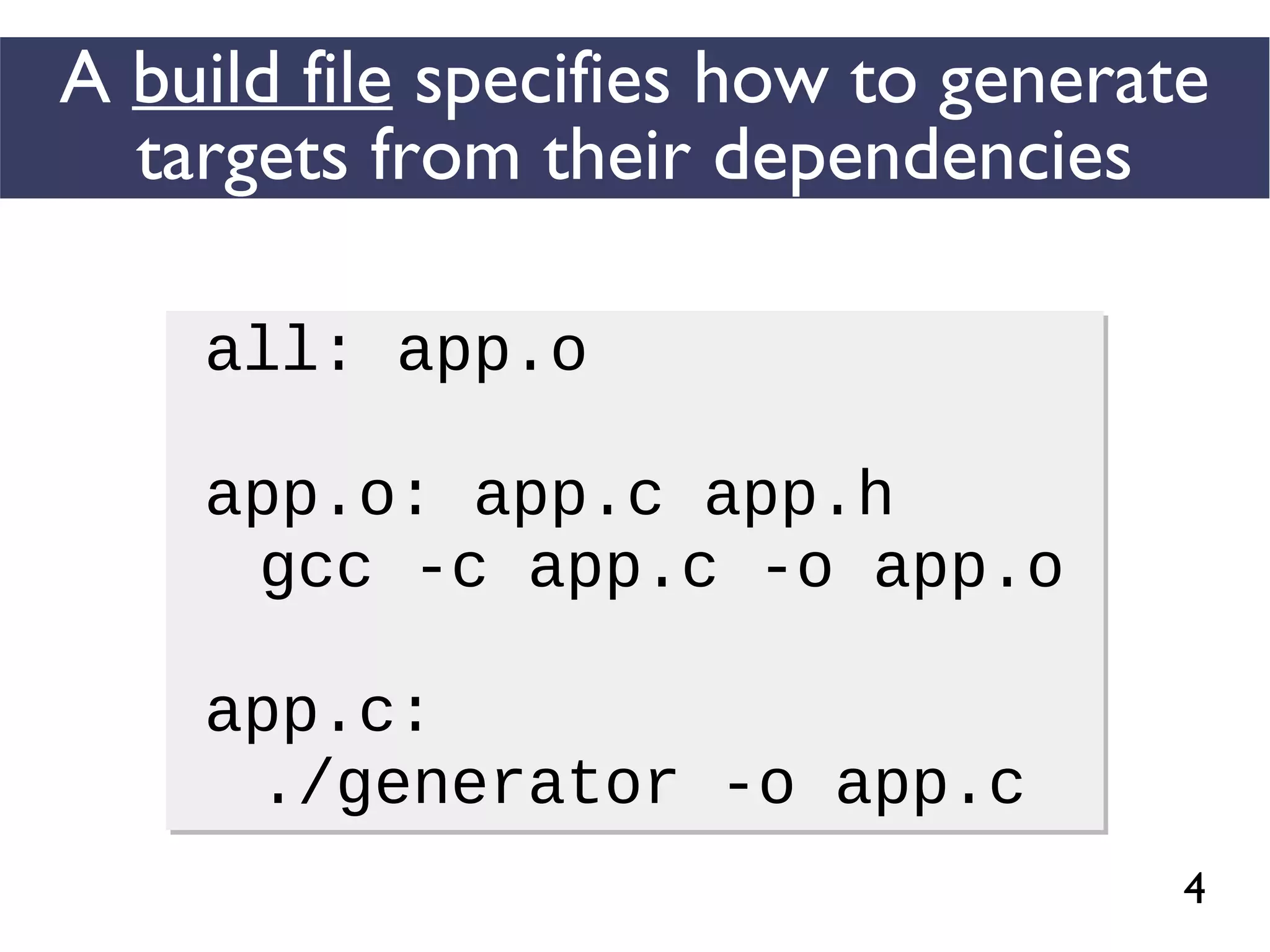
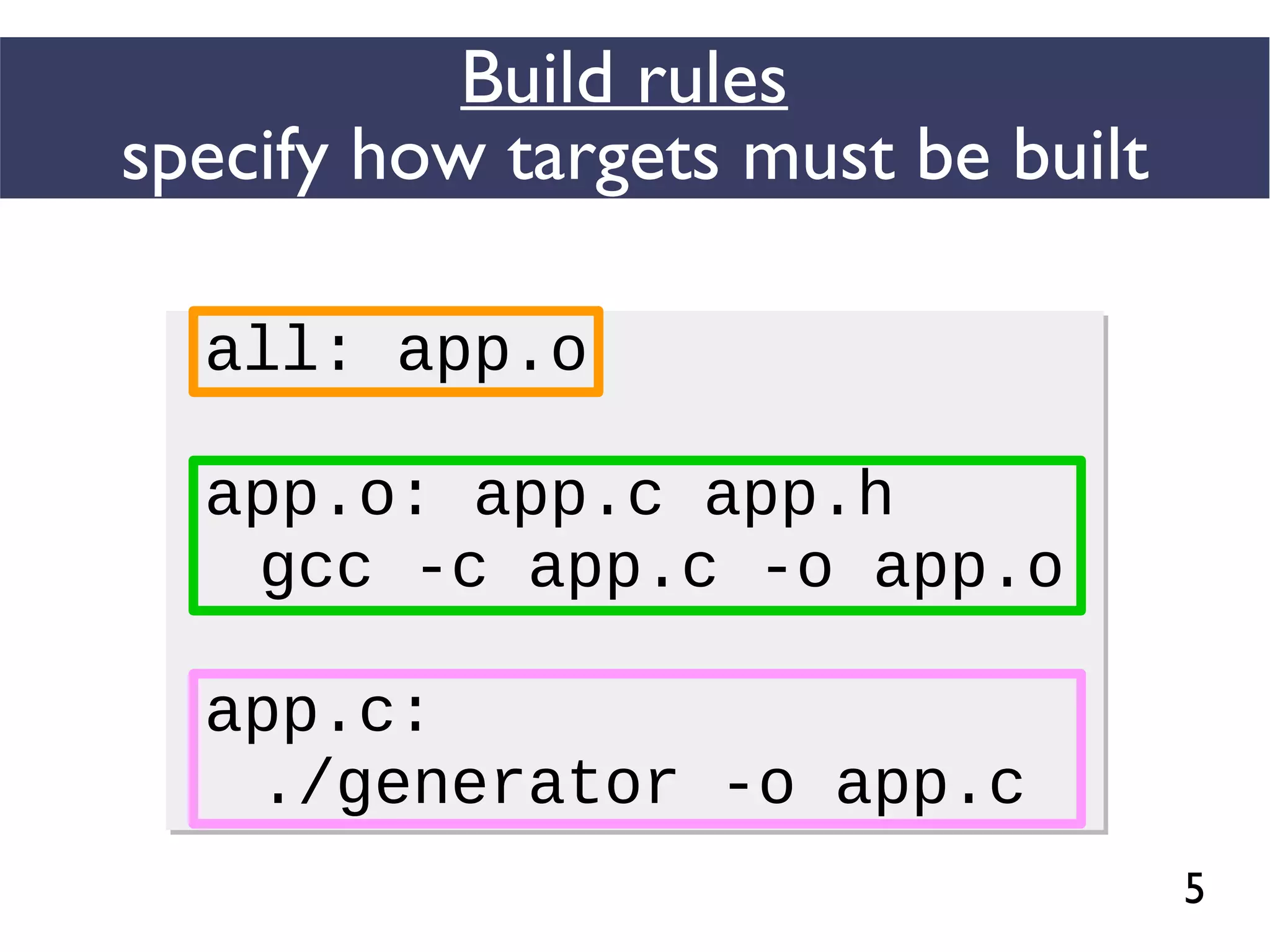
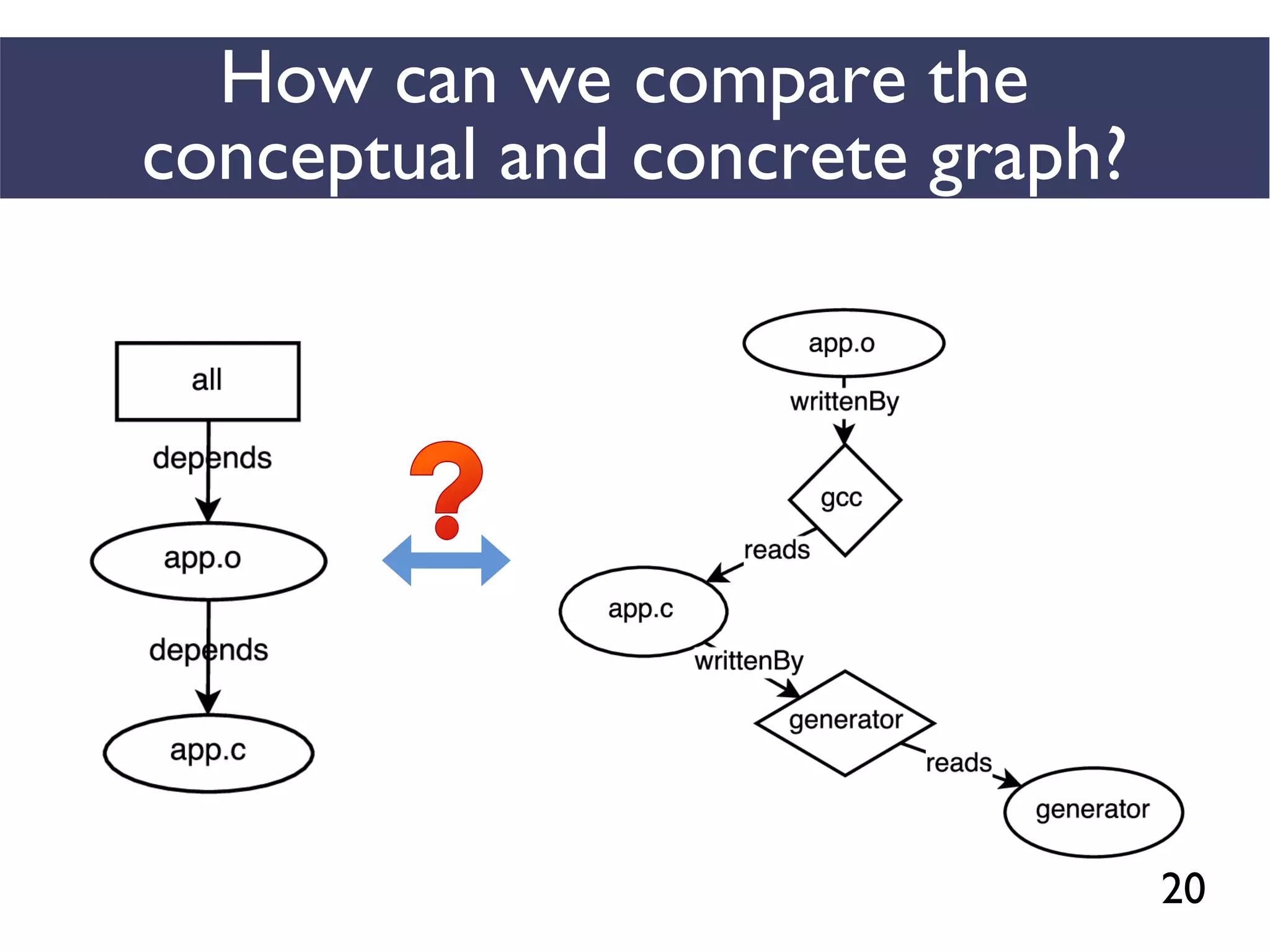
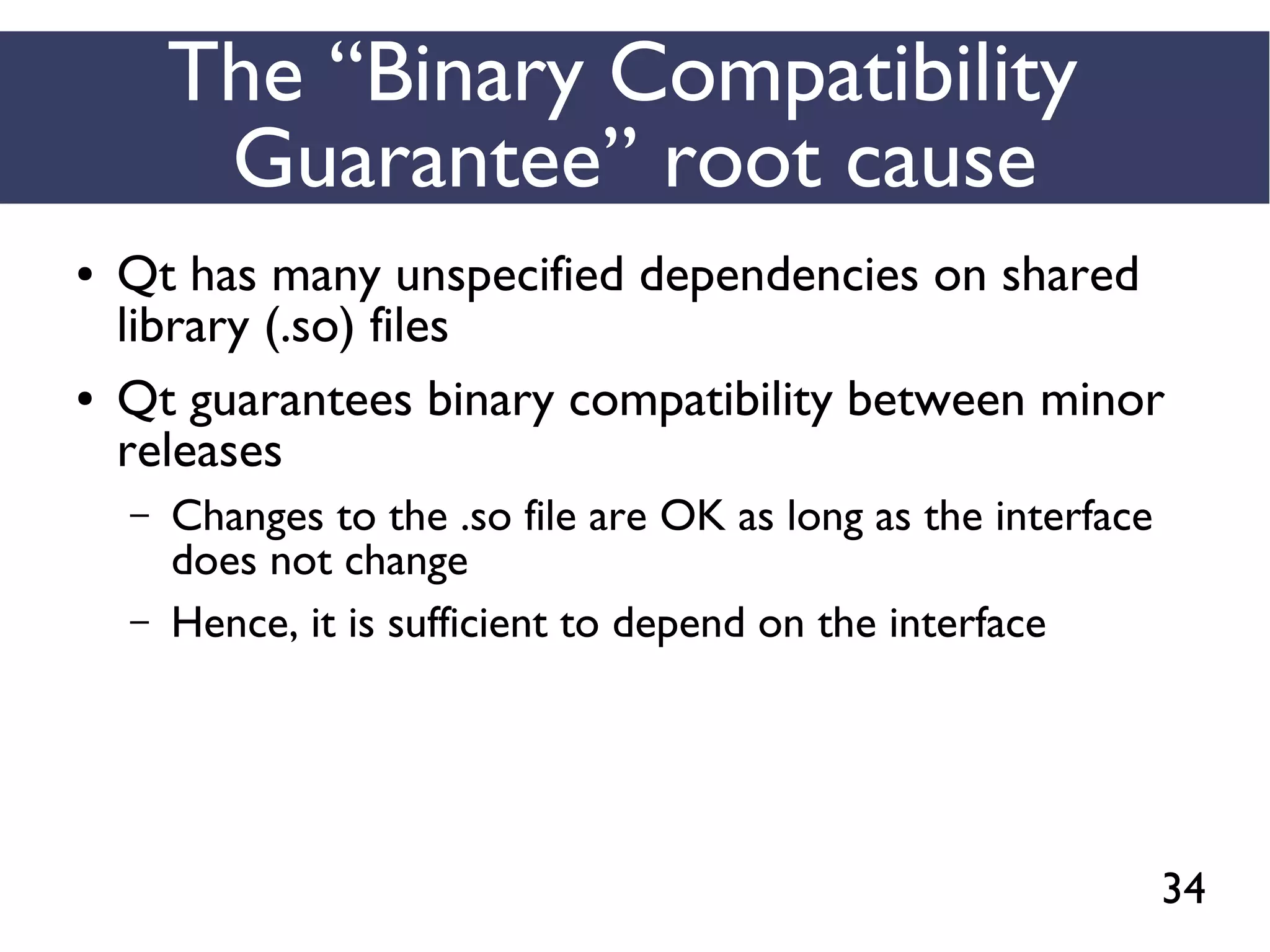
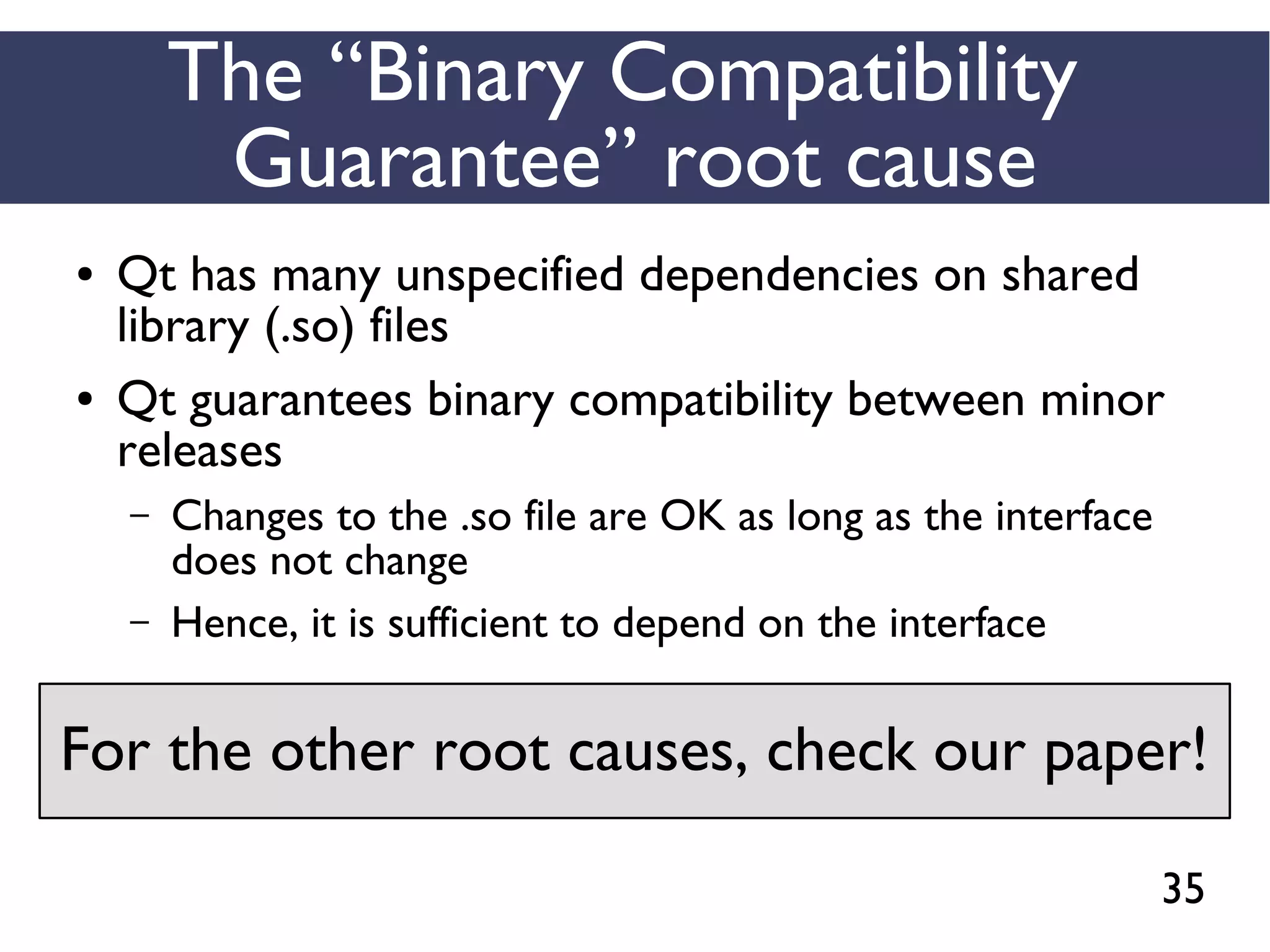
This document presents an empirical study of unspecified dependencies in make-based build systems, exploring how these can lead to significant issues in the build process. It discusses the prevalence of such dependencies in various projects and introduces a prototype tool designed to compare conceptual and concrete build graphs to identify problems. The findings reveal that developers often prefer to omit certain dependencies to expedite builds, despite the potential for future complications.













![44
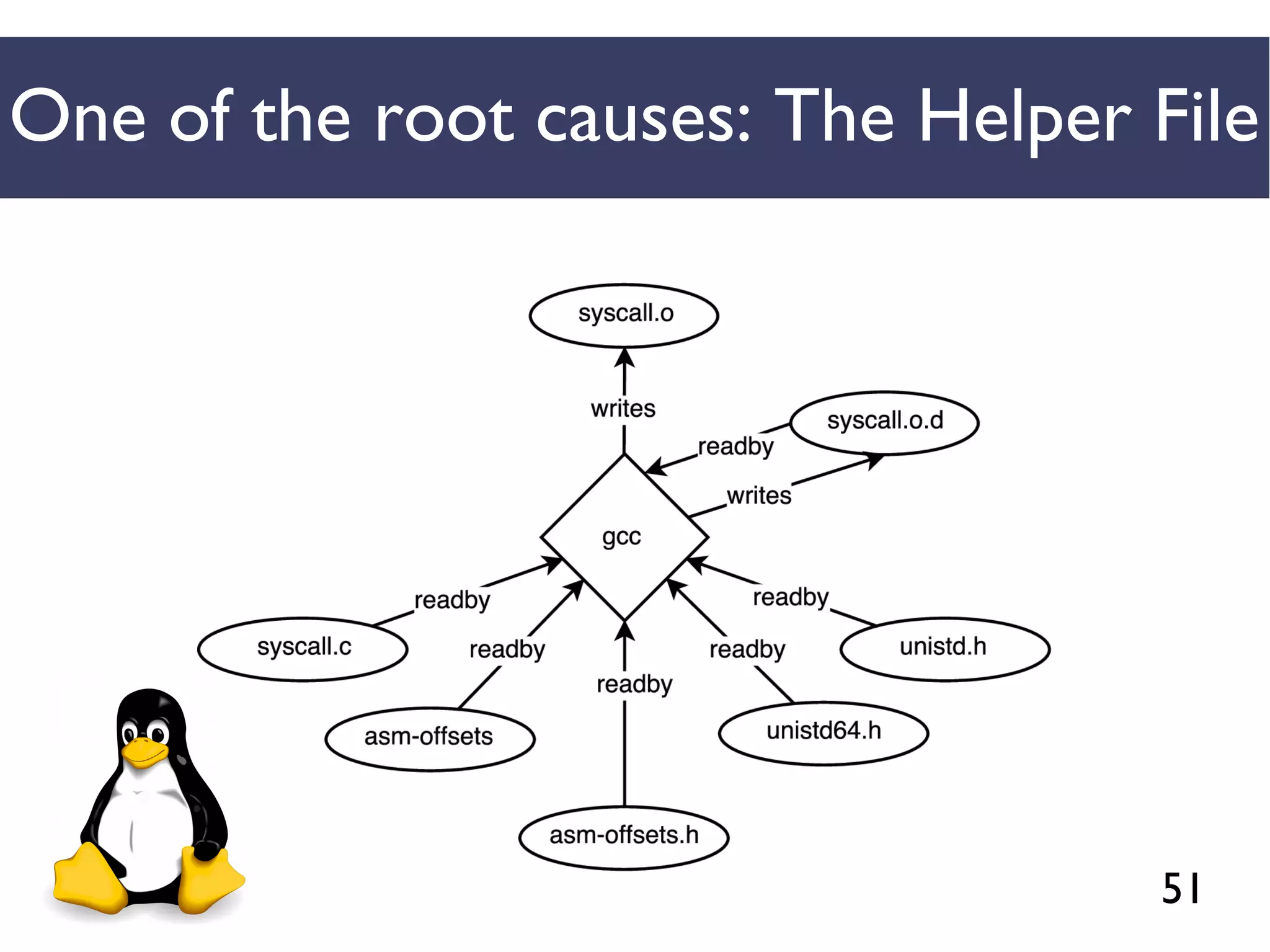
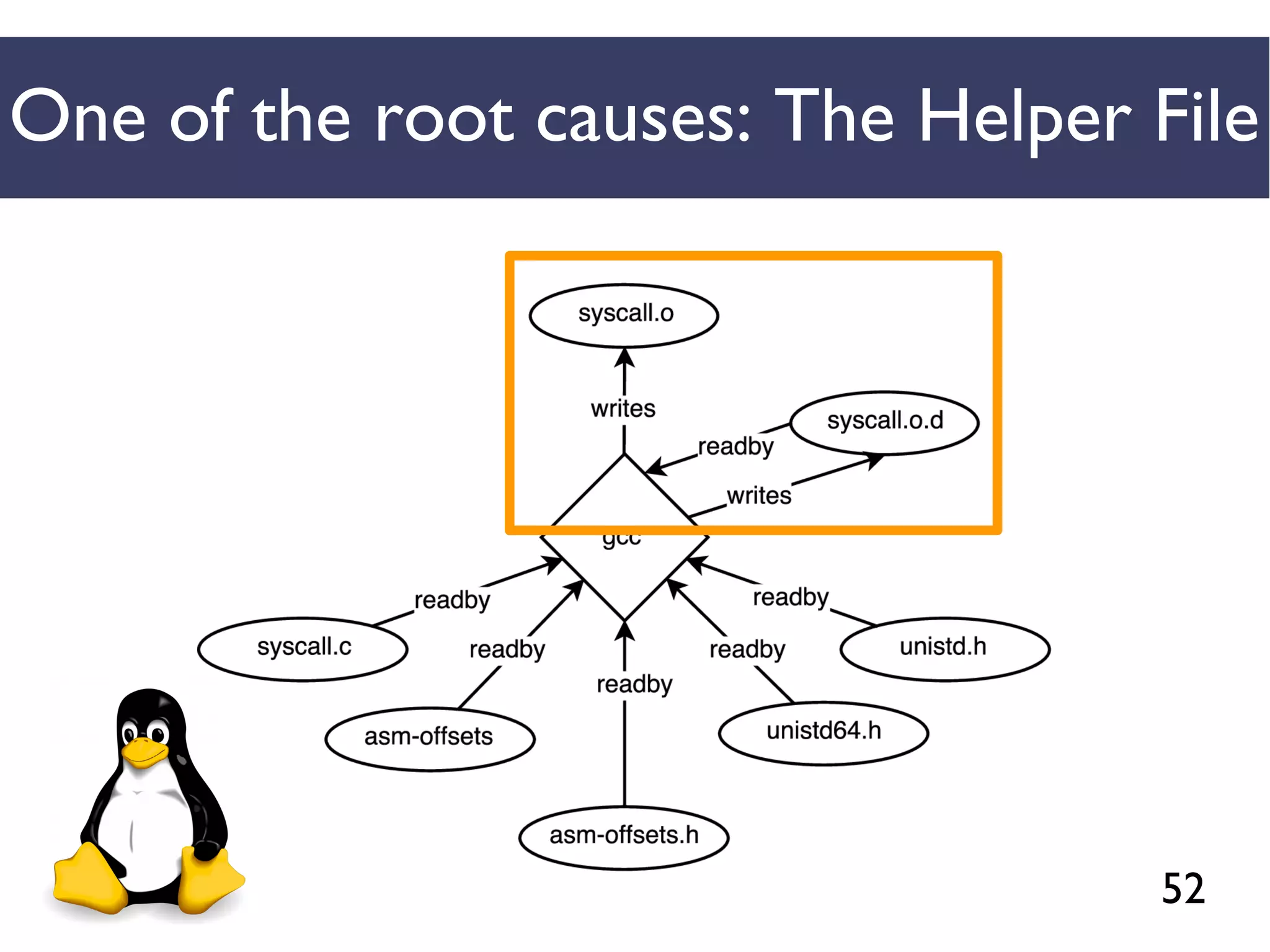
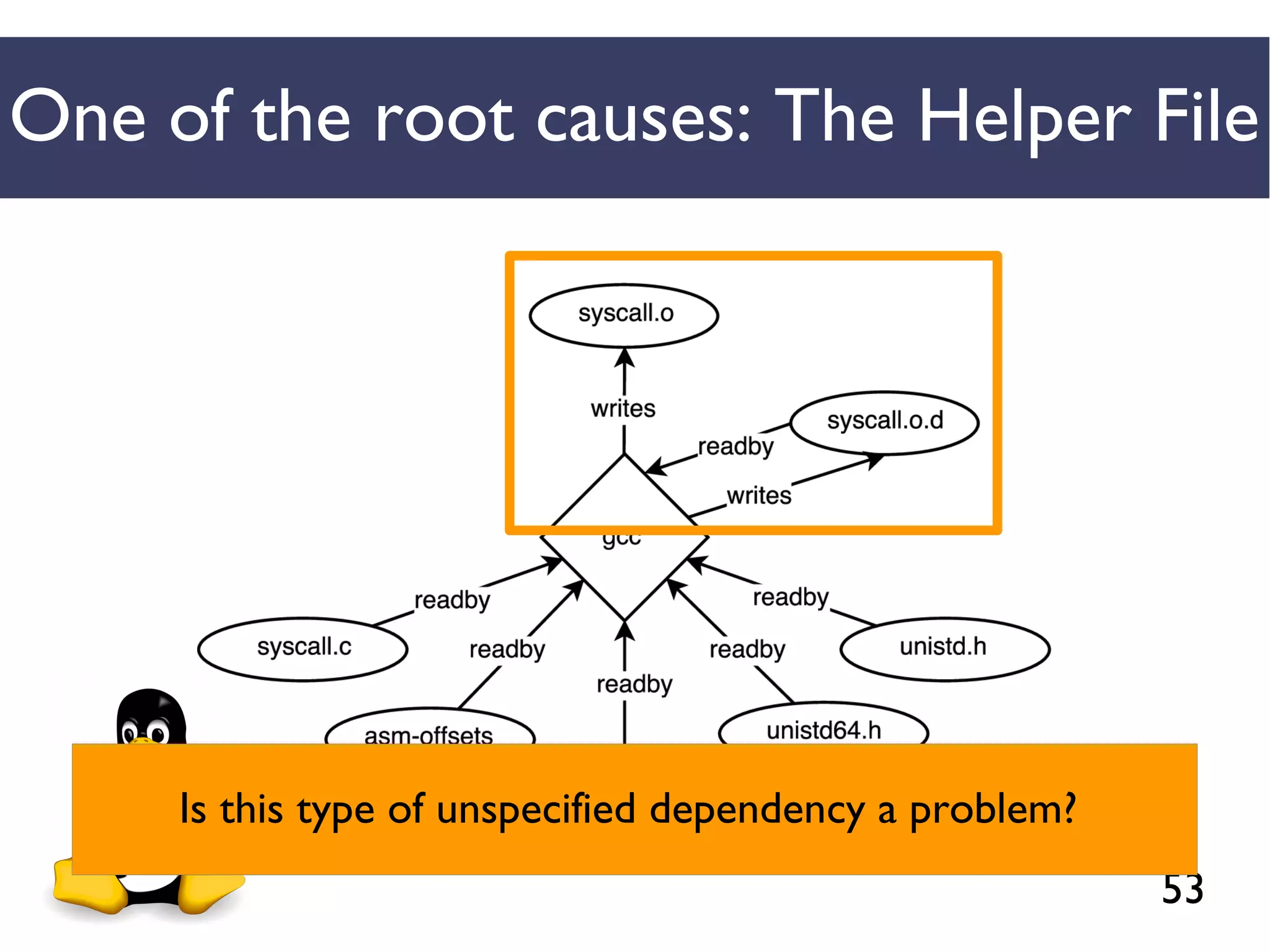
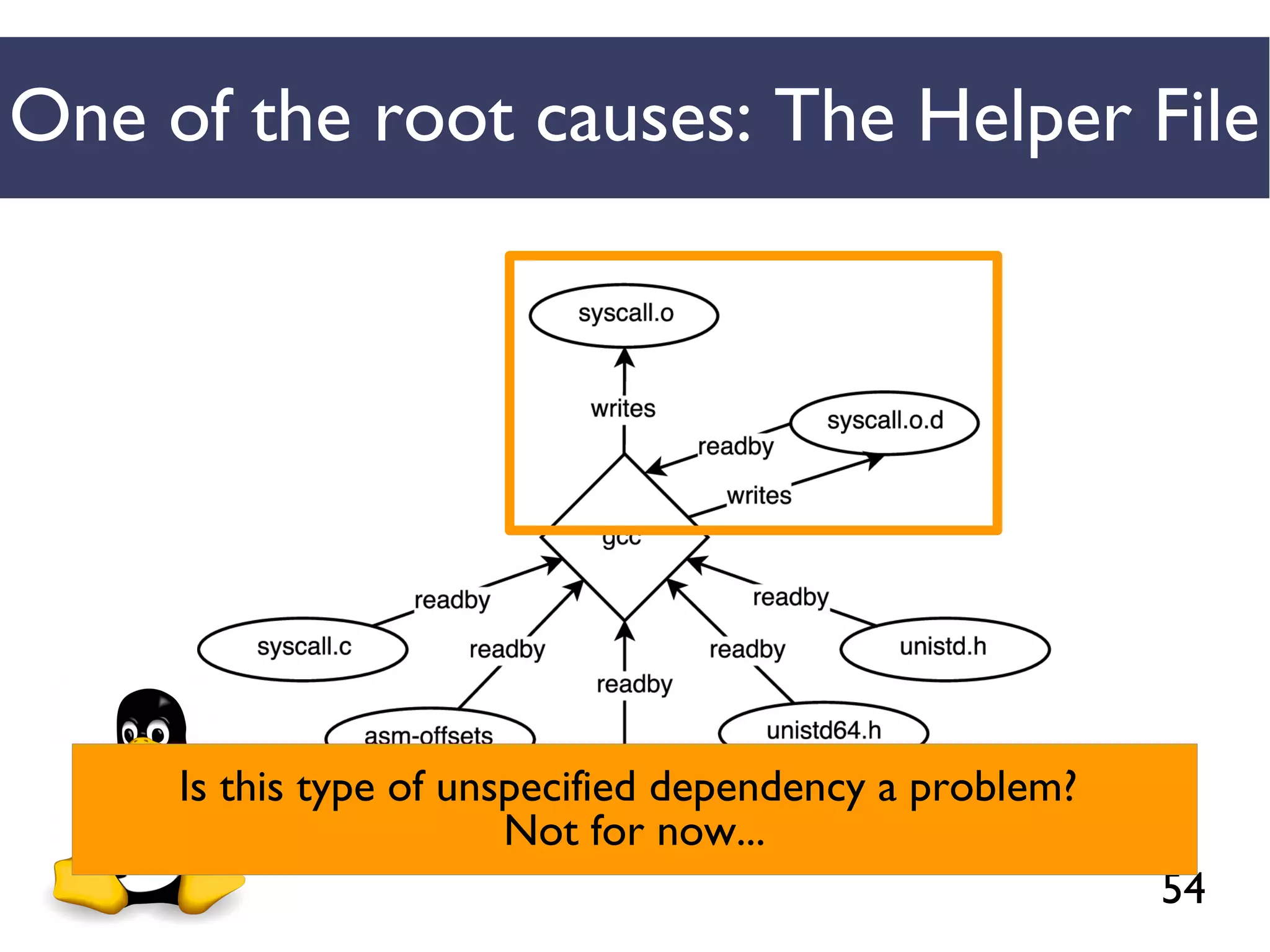
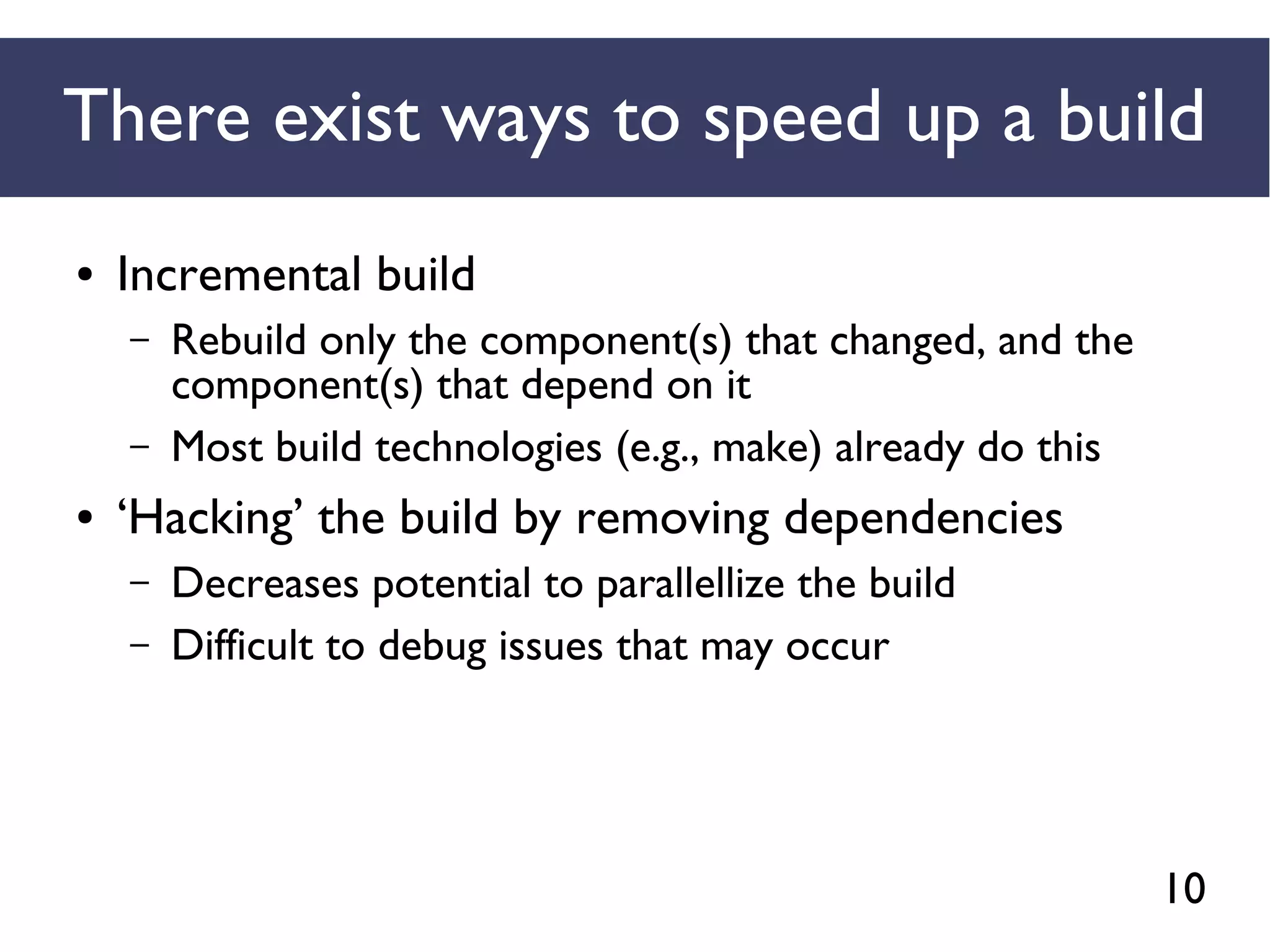
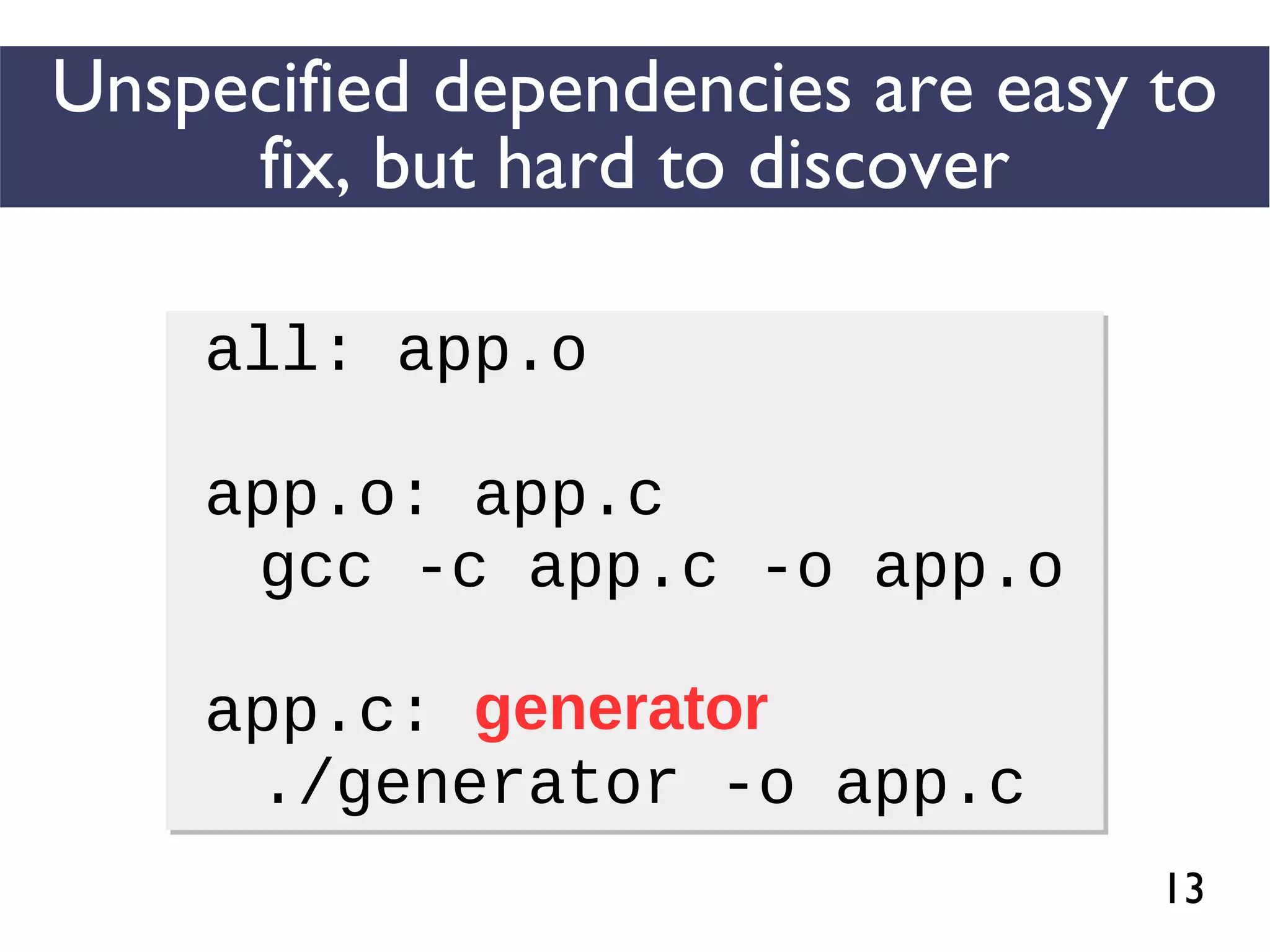
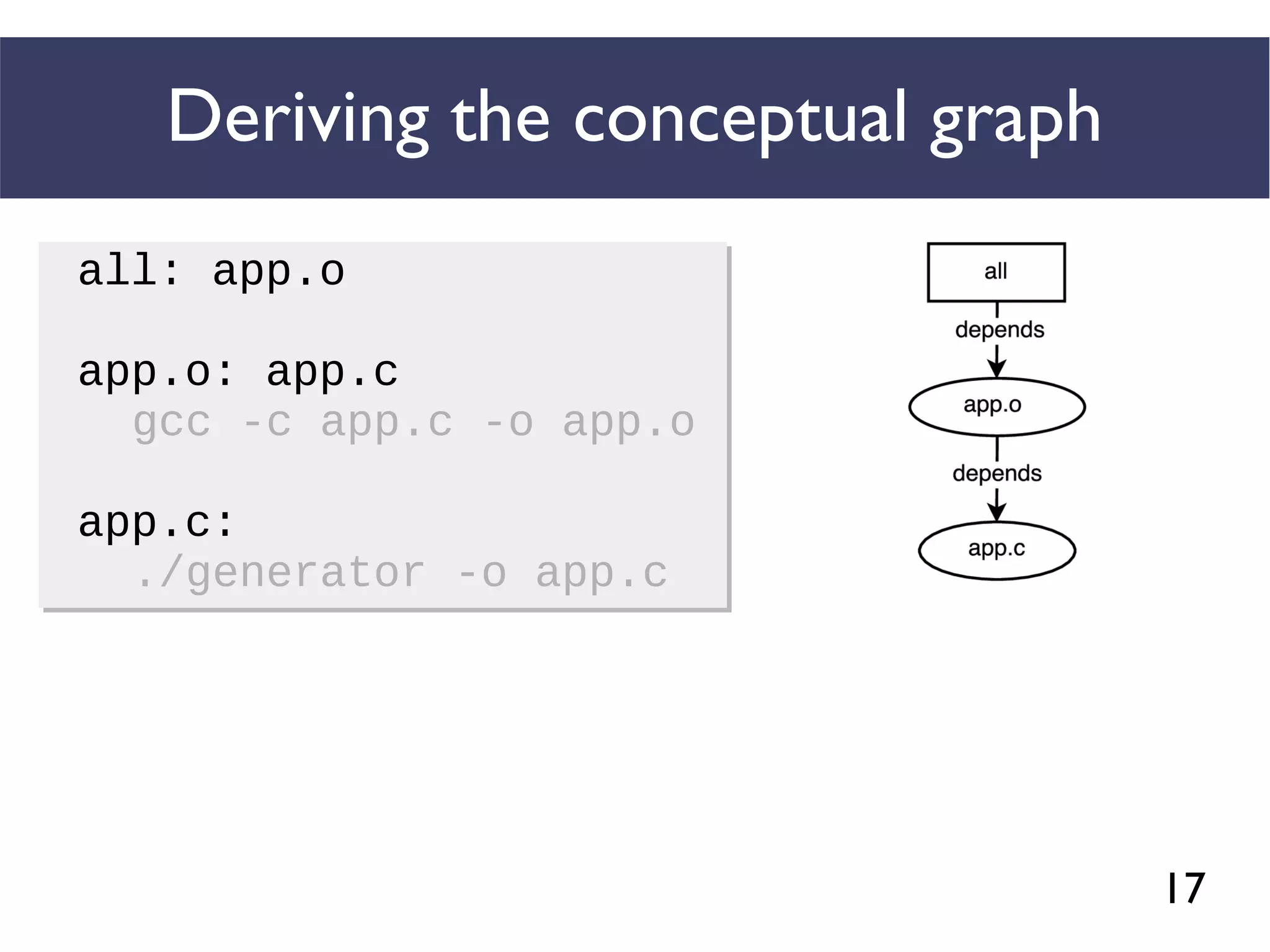
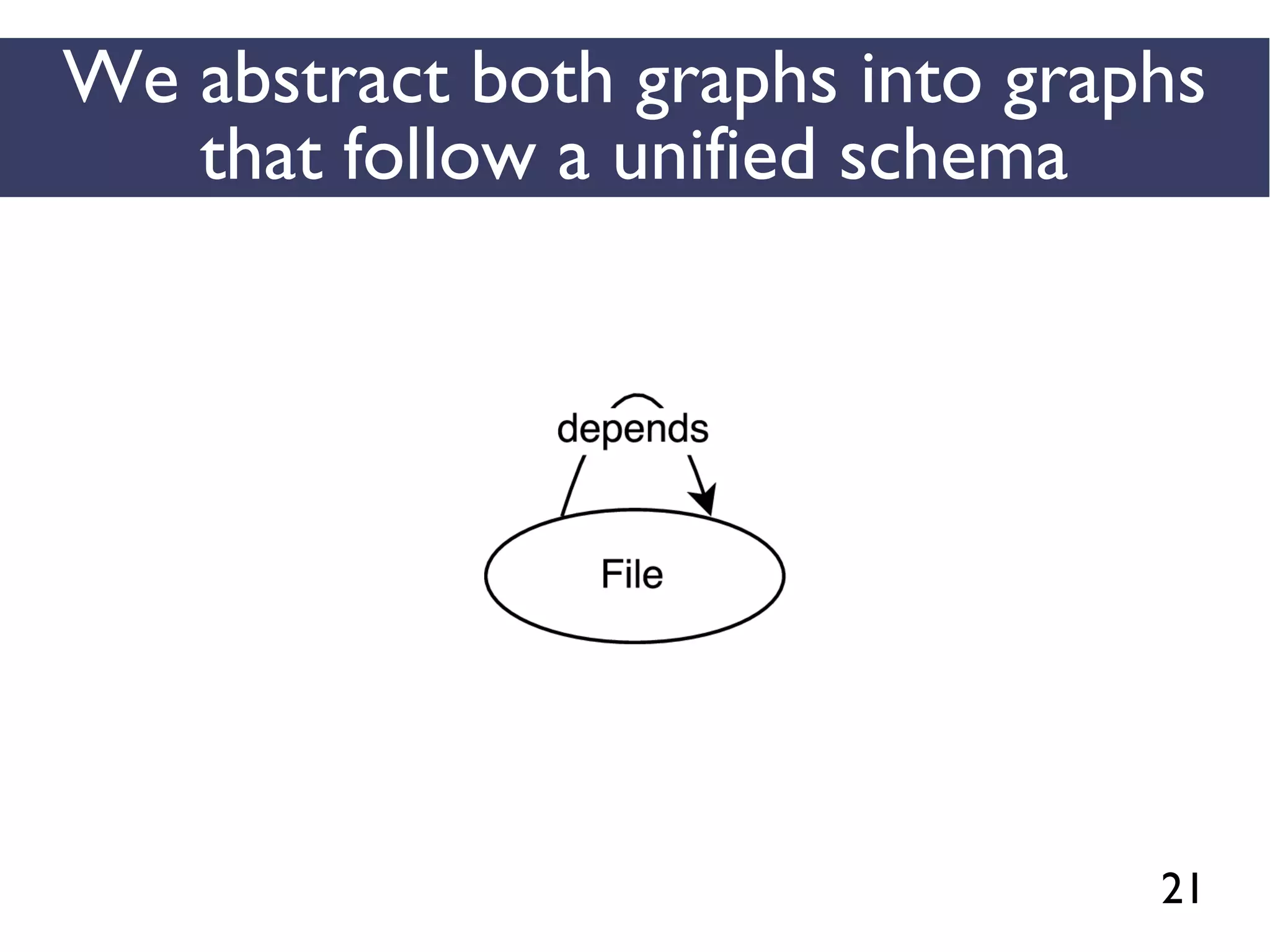
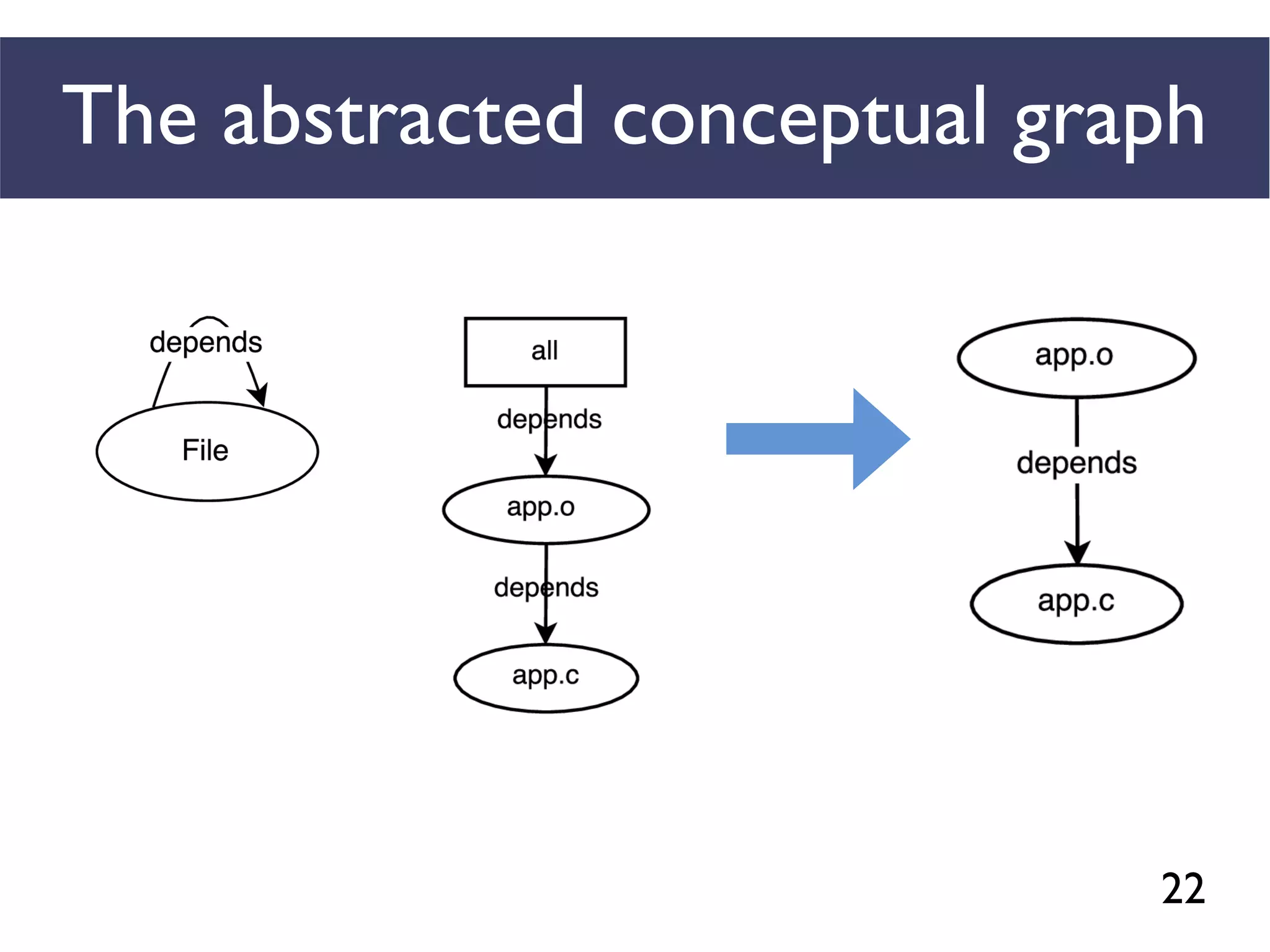
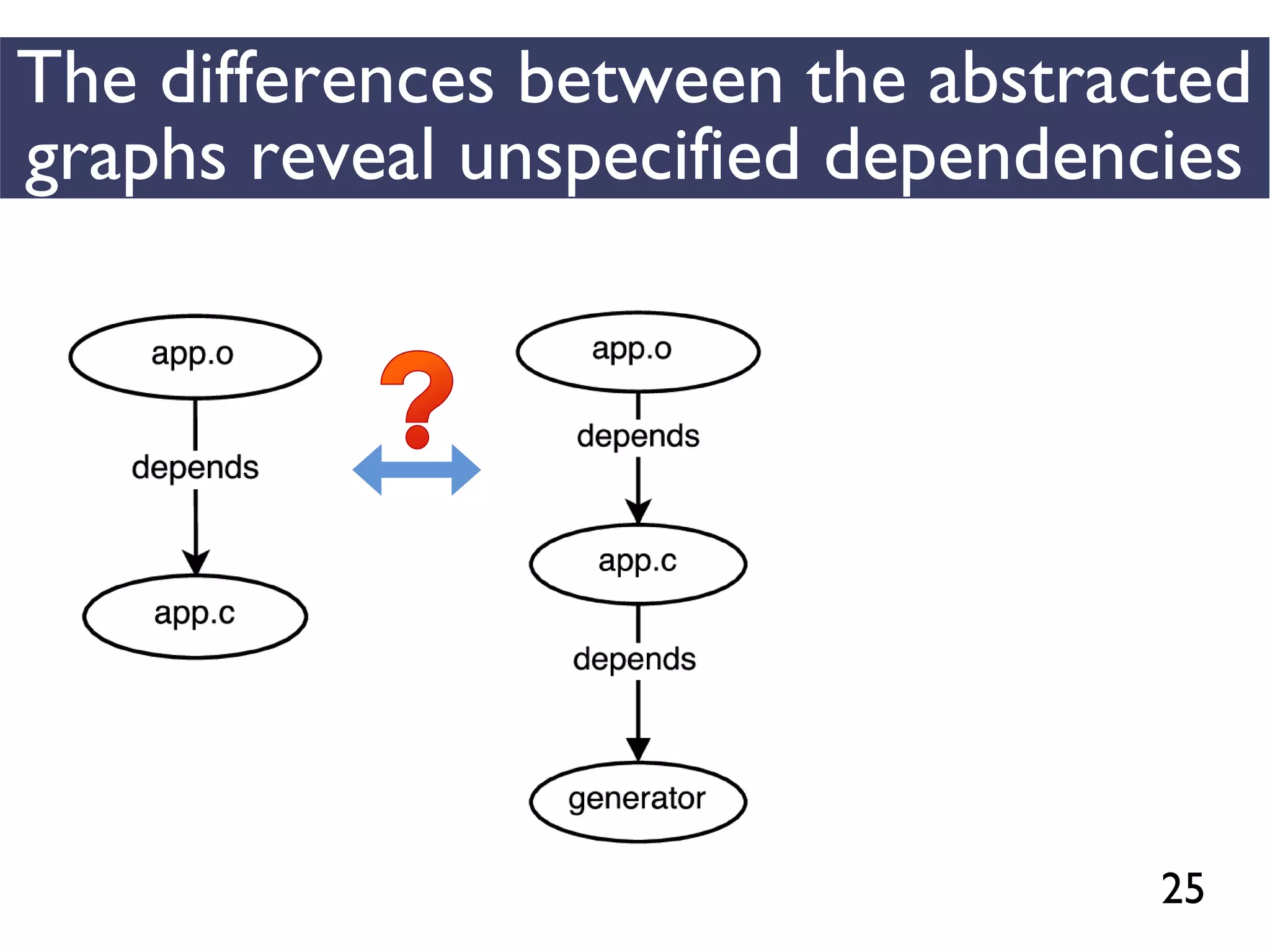
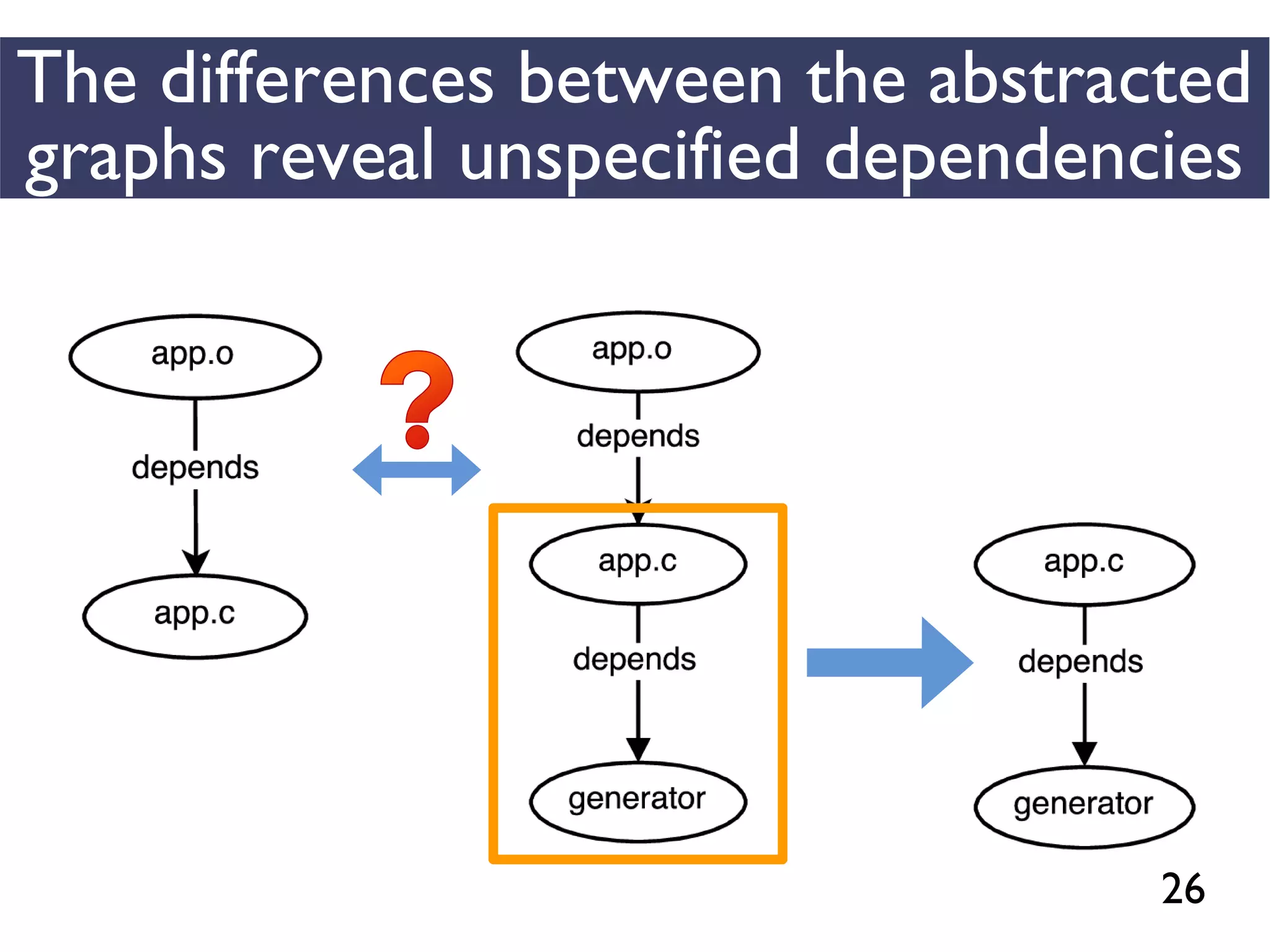
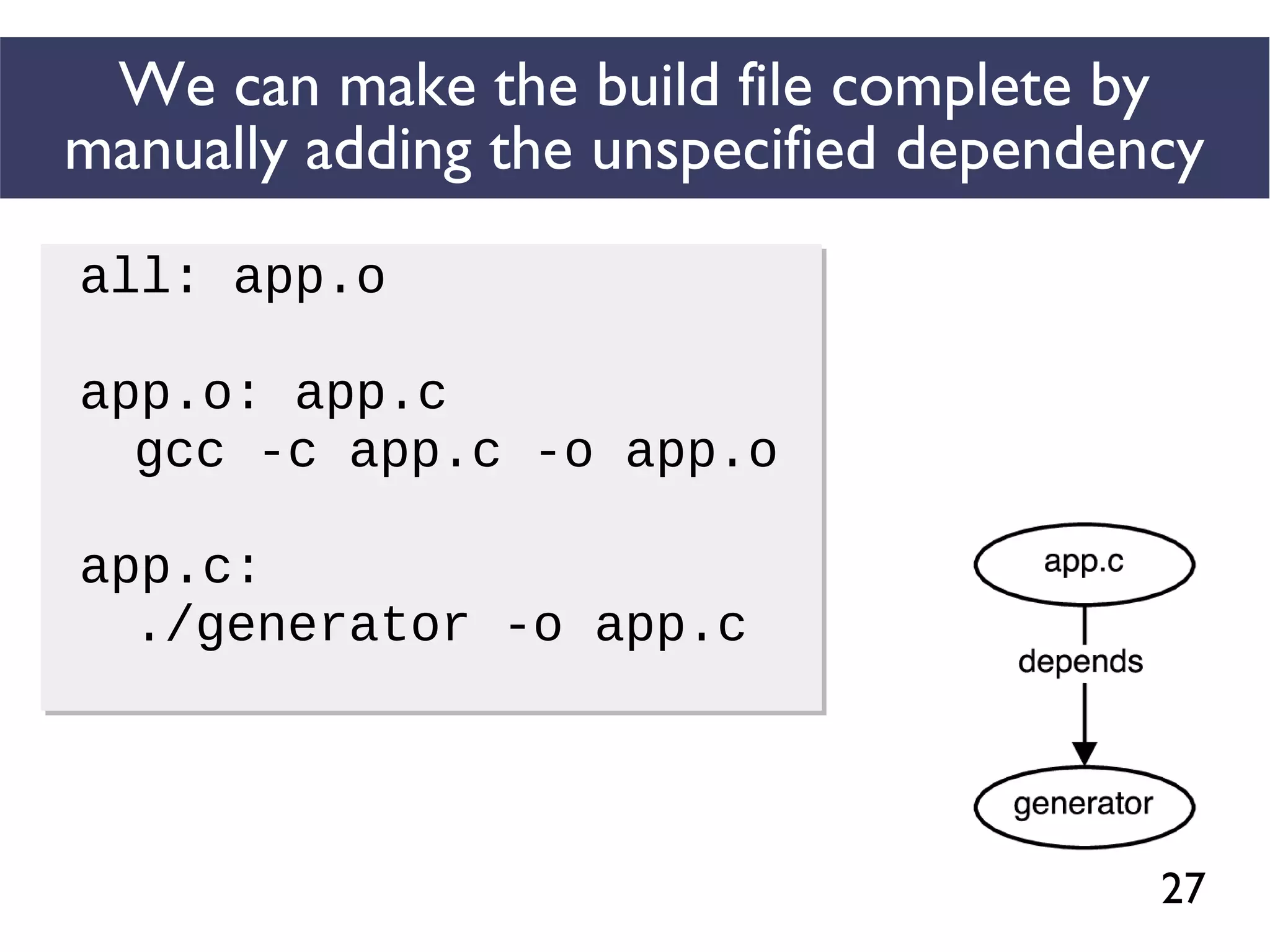
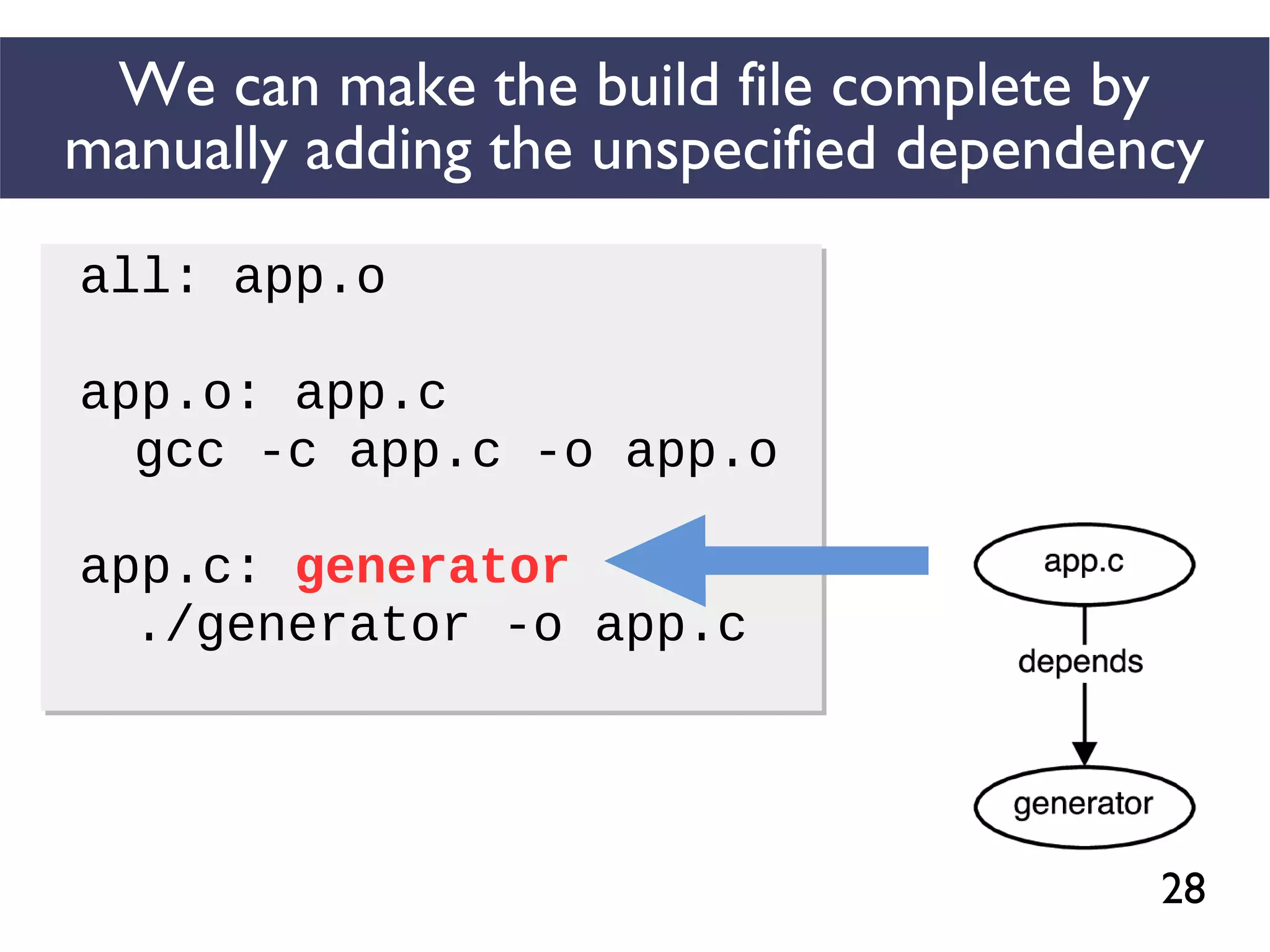
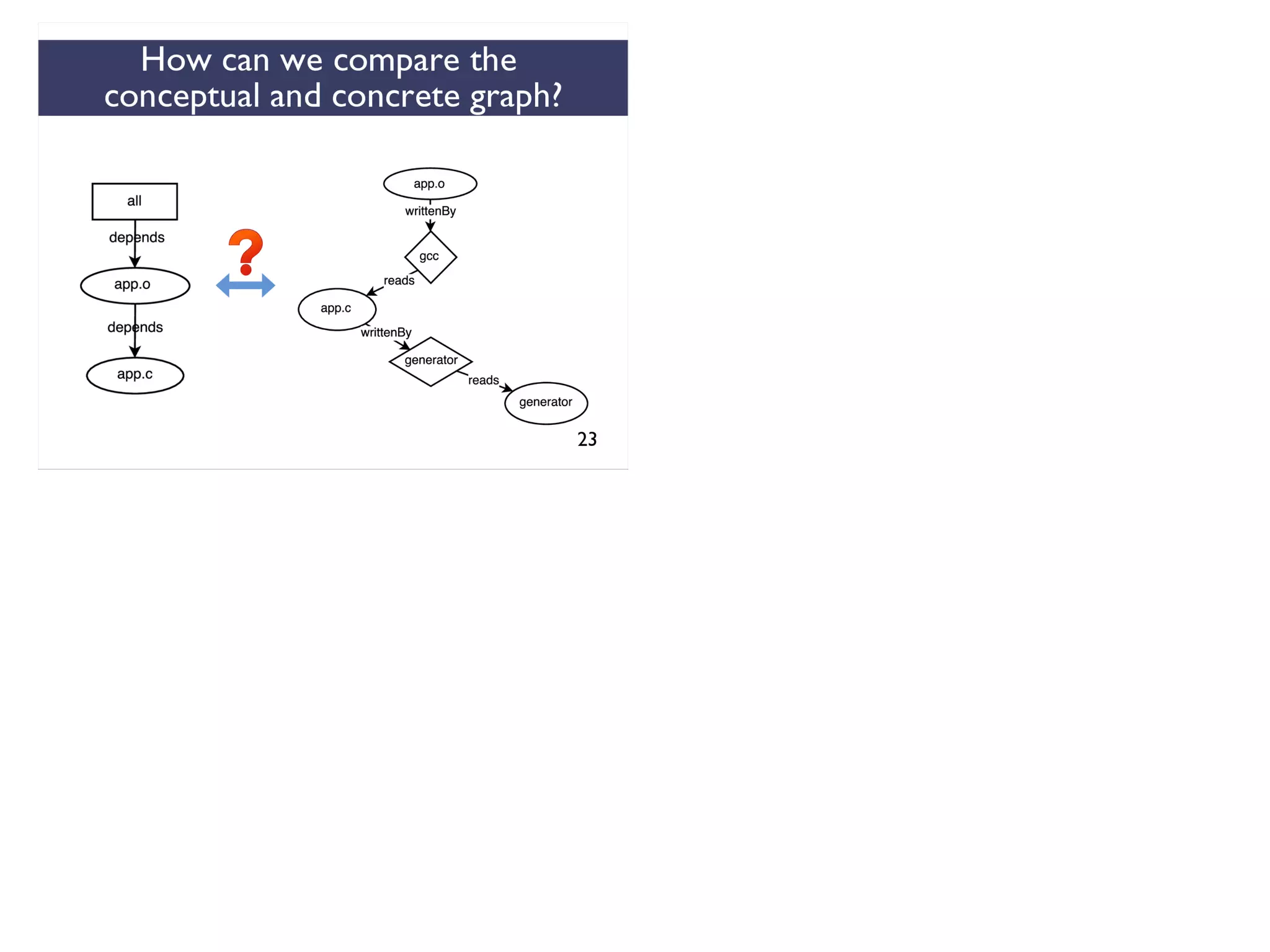
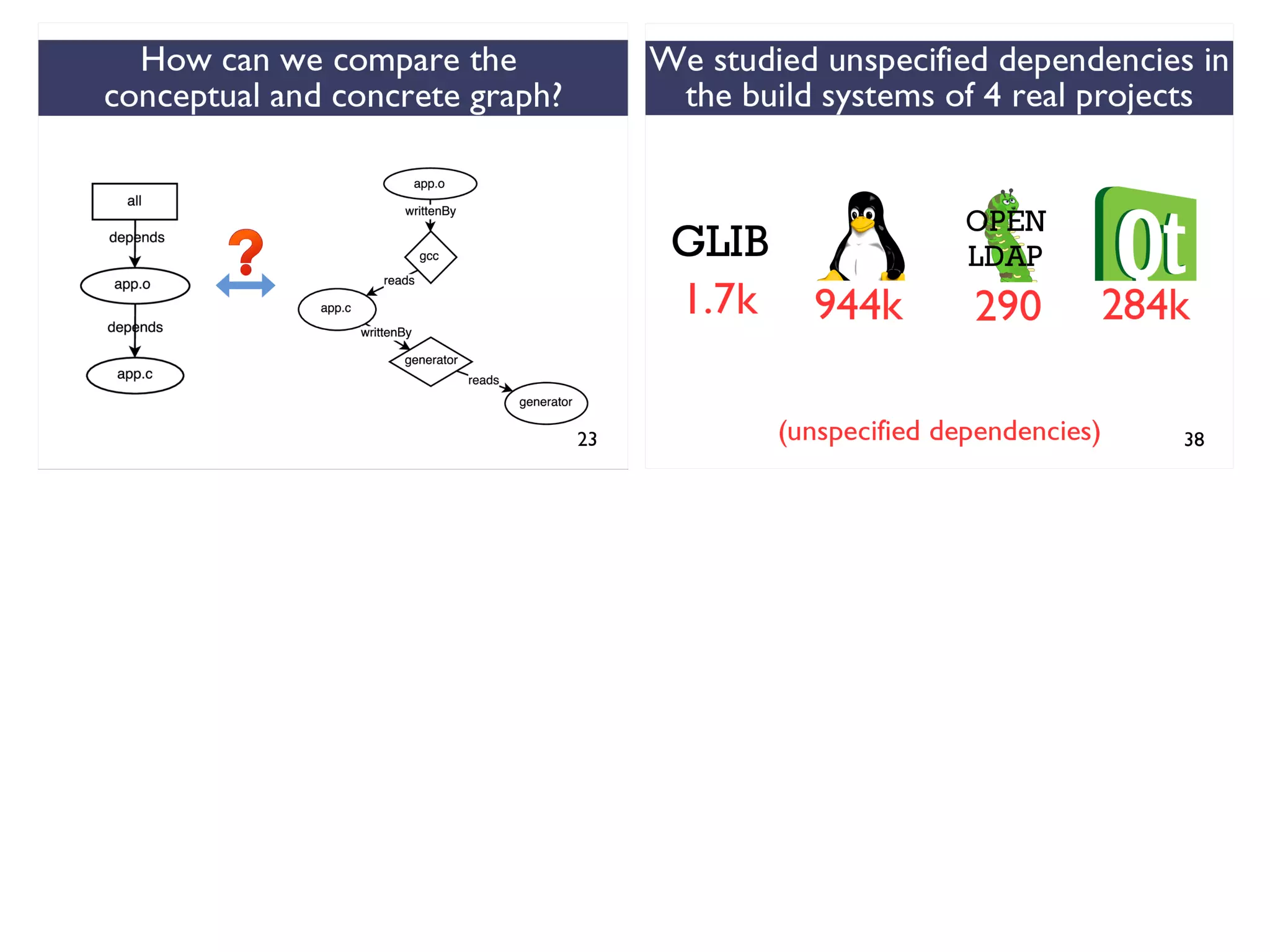
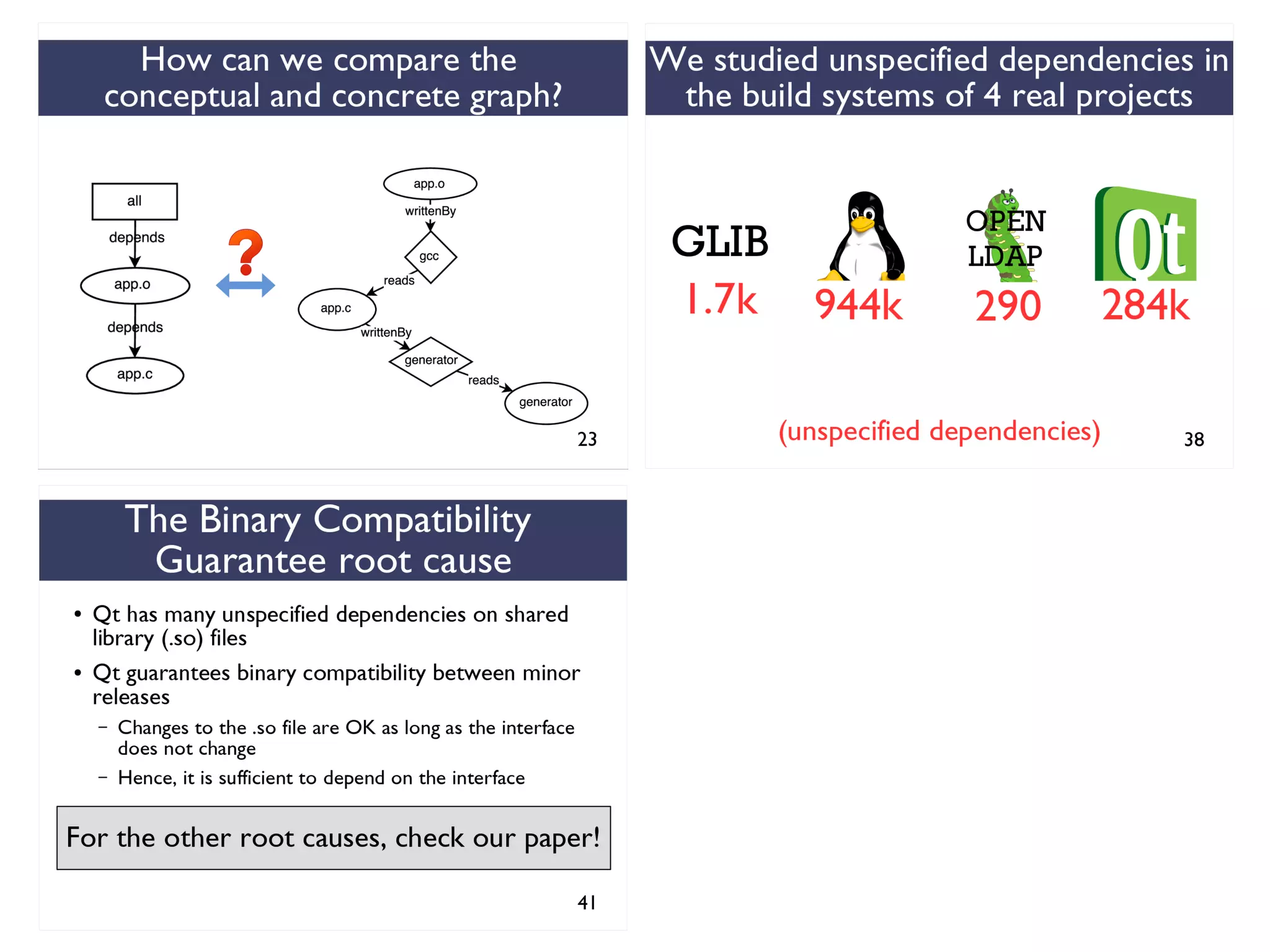
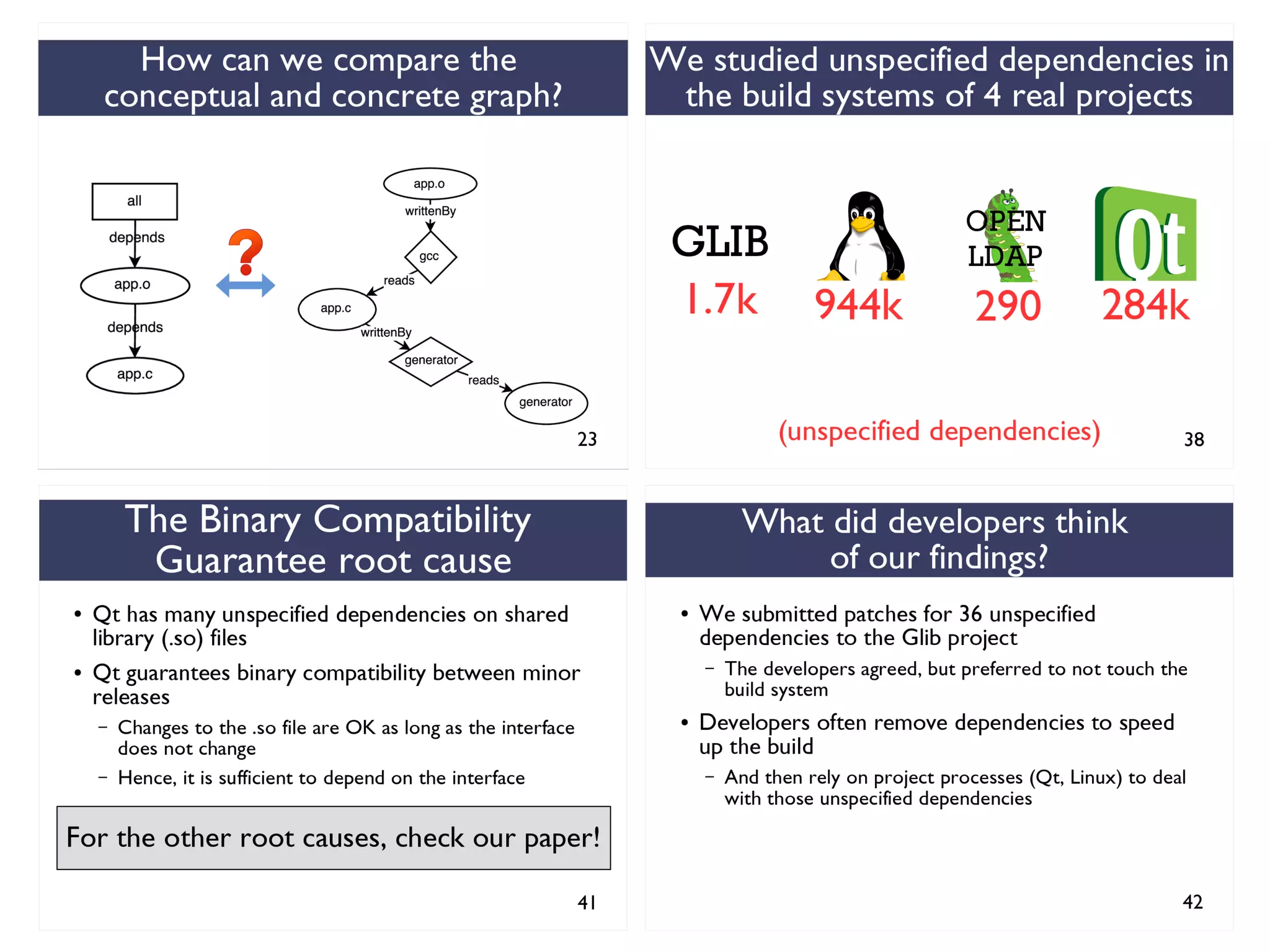
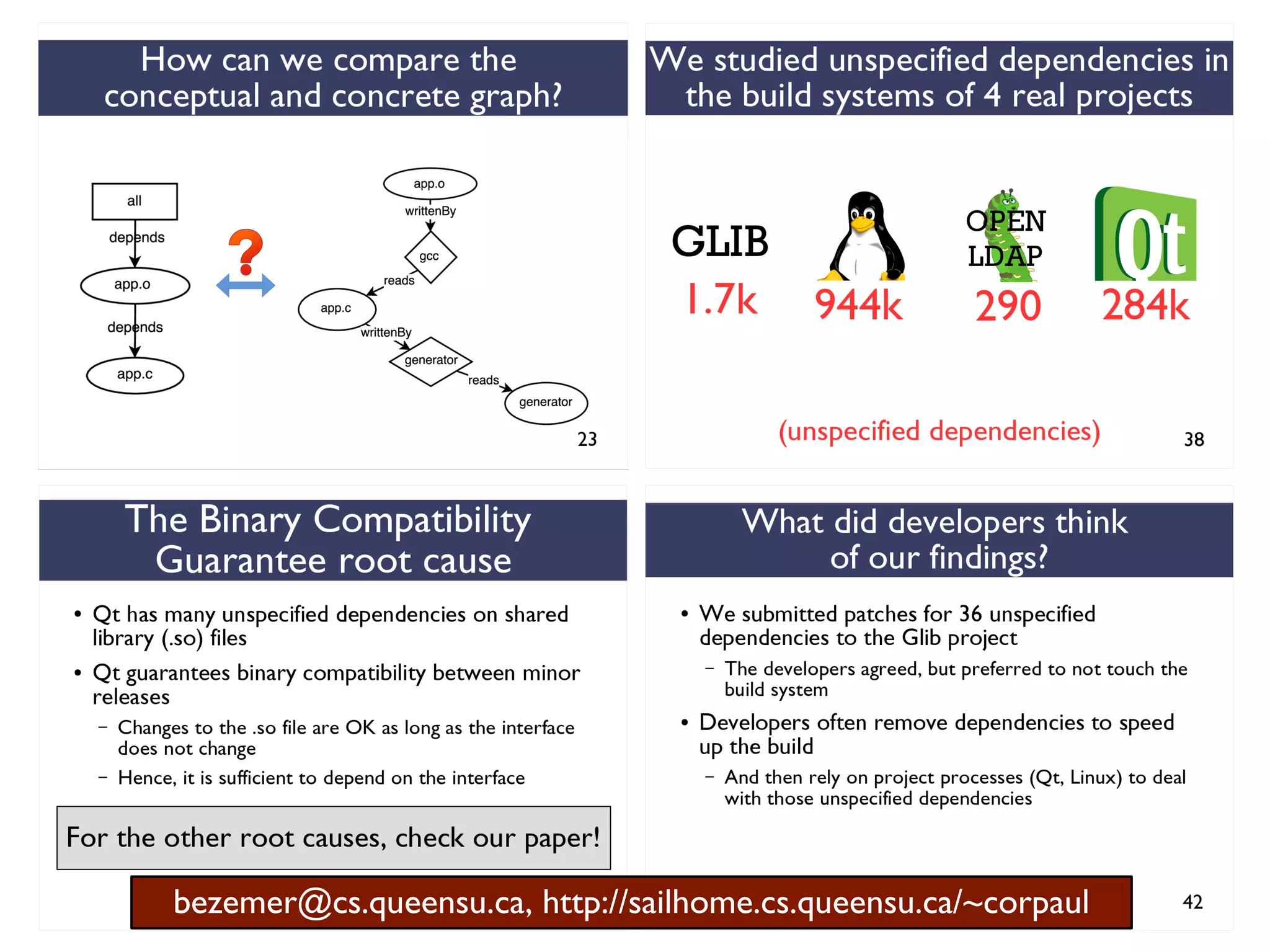
We combined several tools to reveal unspecified
dependencies in make-based build systems
MAKAO
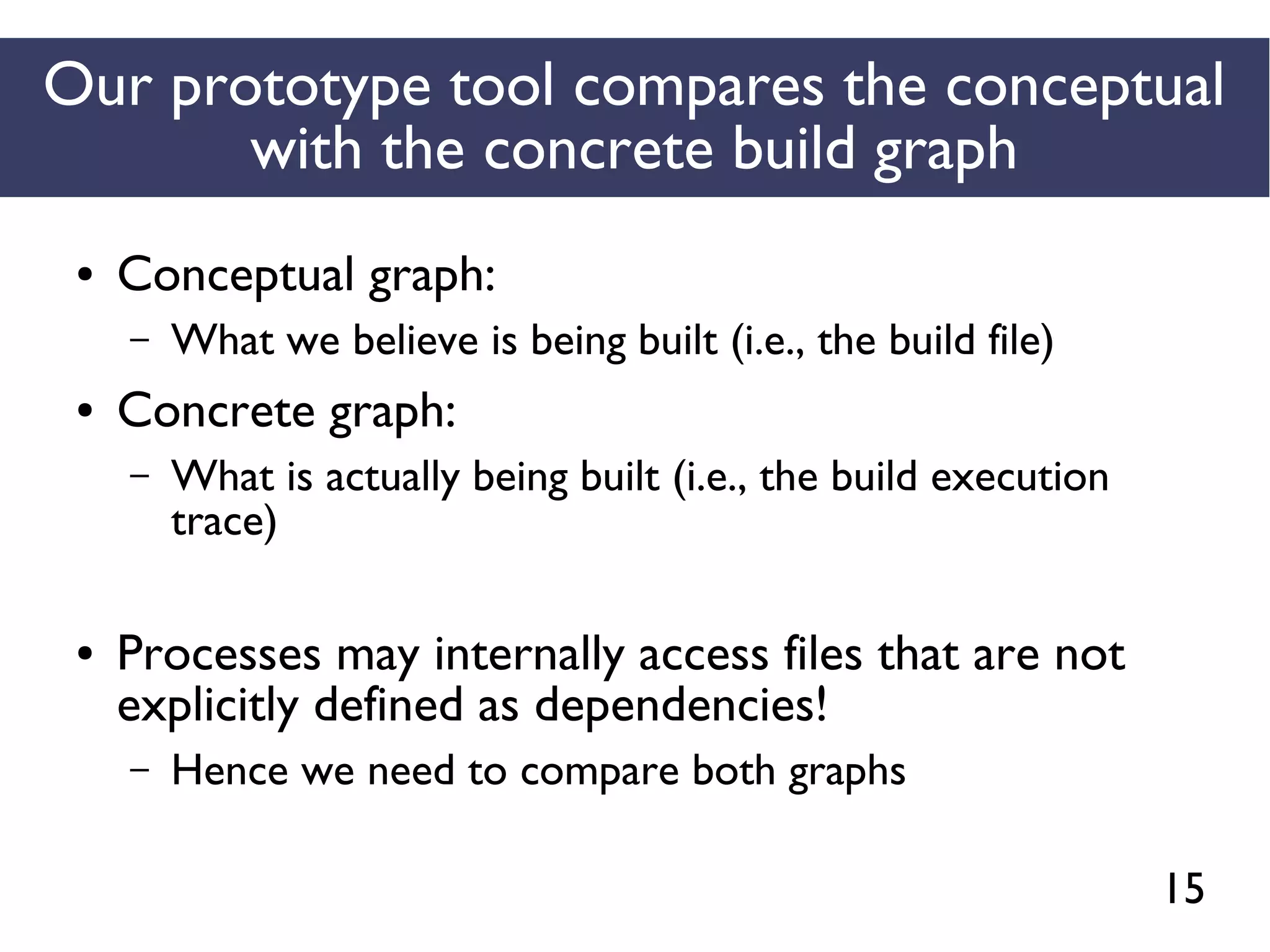
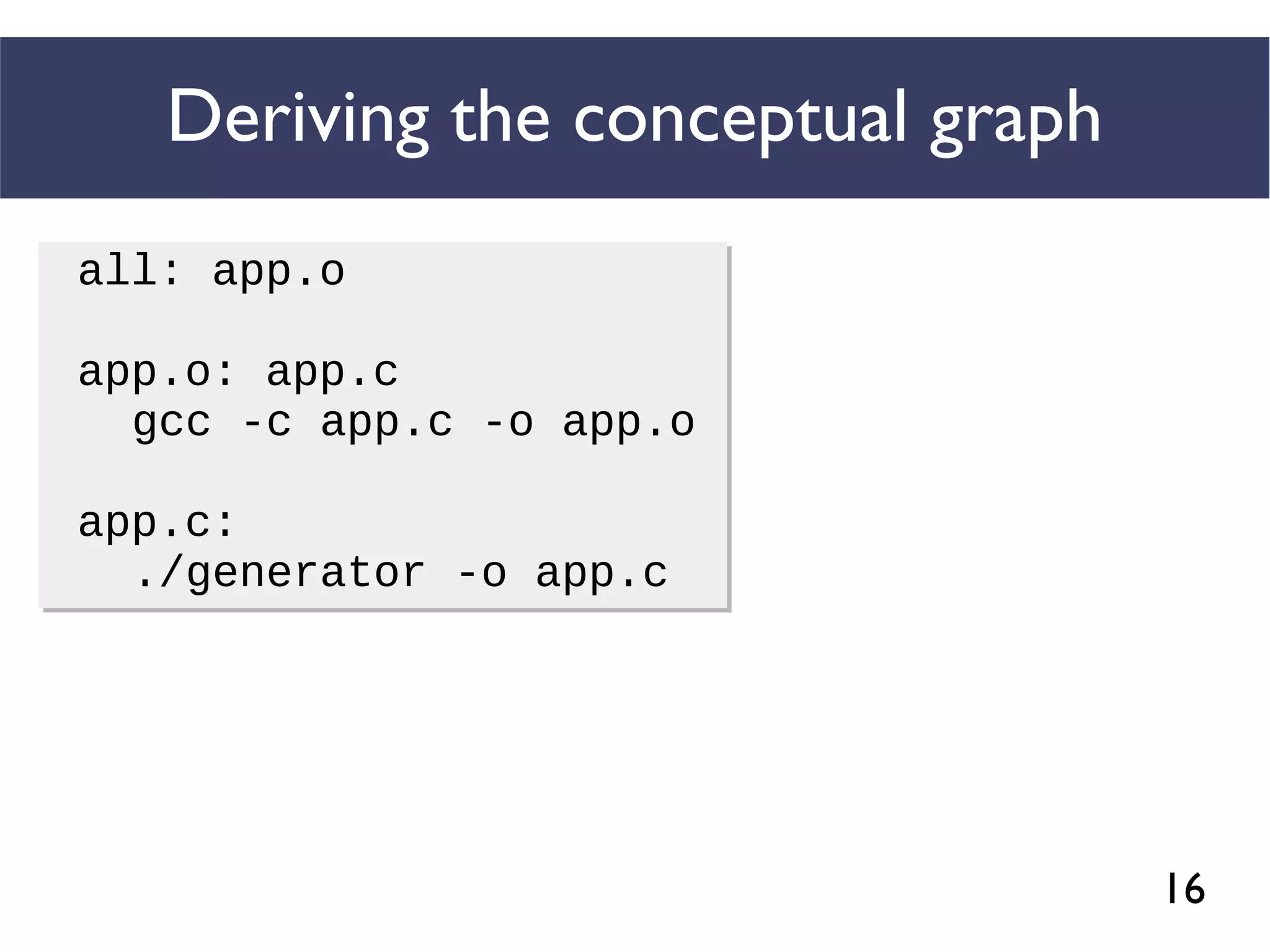
Conceptual graphs are
extracted using
[Adams et al., ICSM 2007]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uncoveringunspecifieddependenciestalk-170918131535/75/An-Empirical-Study-of-Unspecified-Dependencies-in-Make-Based-Build-Systems-44-2048.jpg)
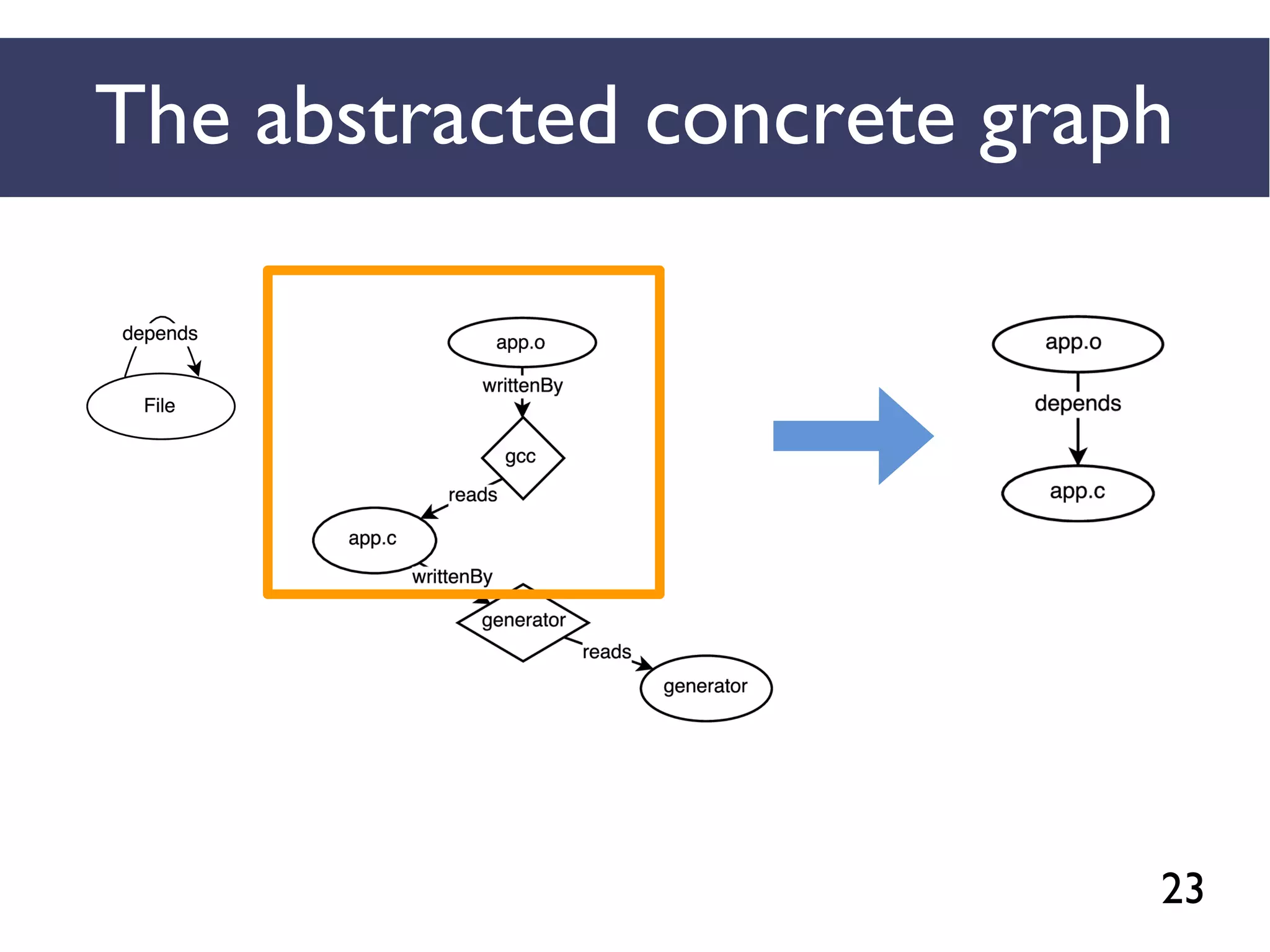
![45
We combined several tools to reveal unspecified
dependencies in make-based build systems
MAKAO
Conceptual graphs are
extracted using
[Adams et al., ICSM 2007]
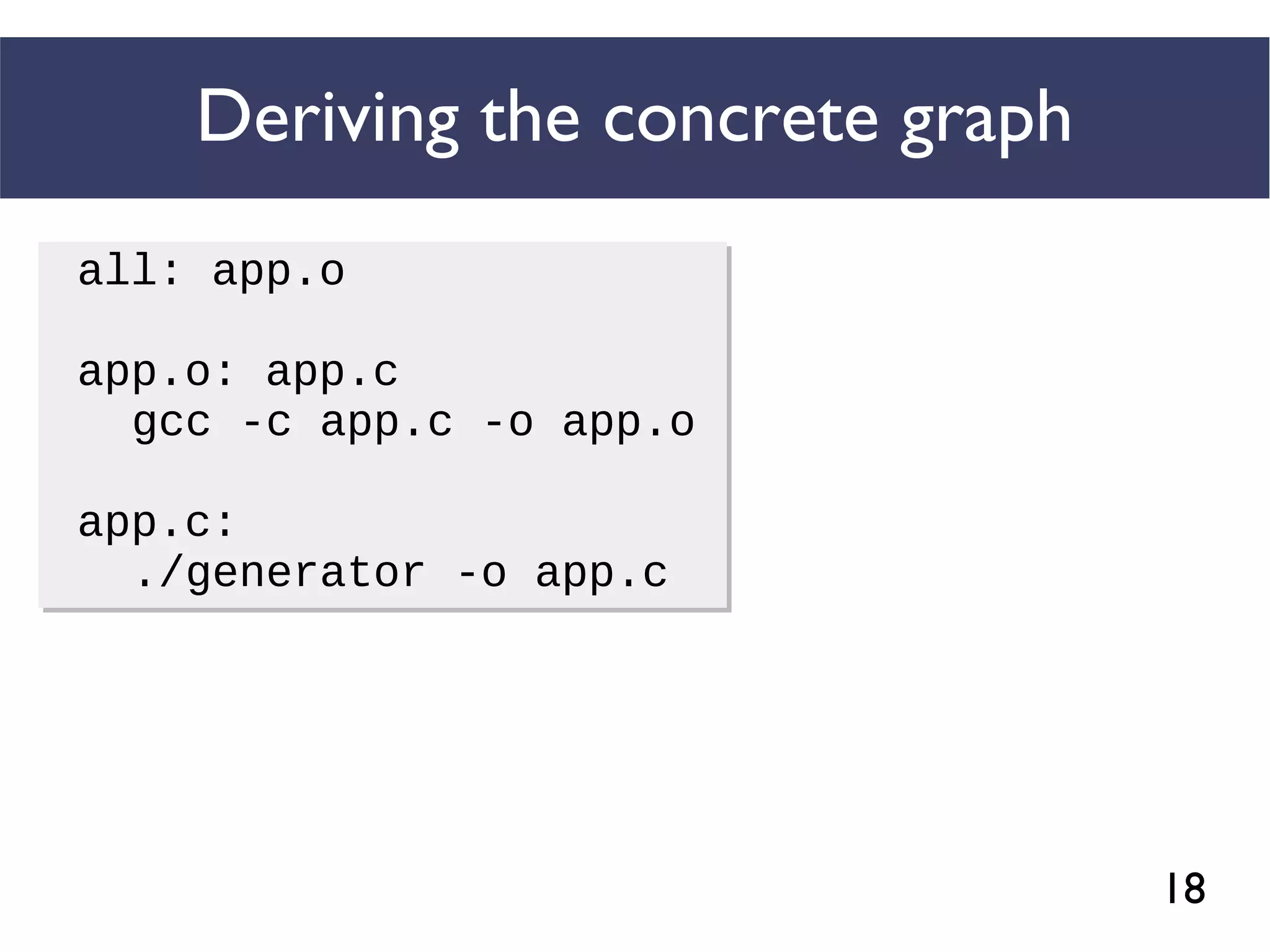
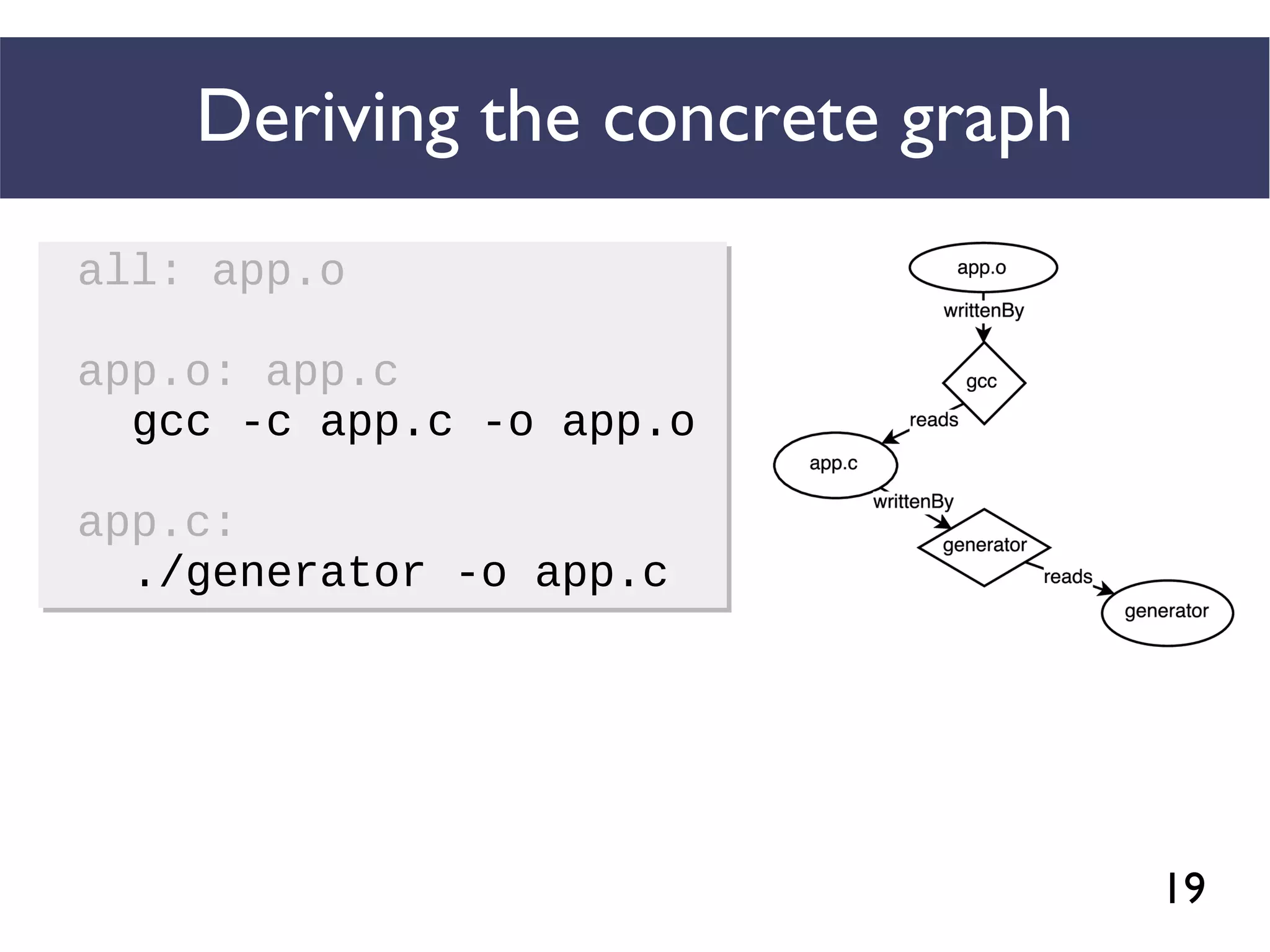
STRACE
Concrete graphs are
extracted from
execution logs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uncoveringunspecifieddependenciestalk-170918131535/75/An-Empirical-Study-of-Unspecified-Dependencies-in-Make-Based-Build-Systems-45-2048.jpg)
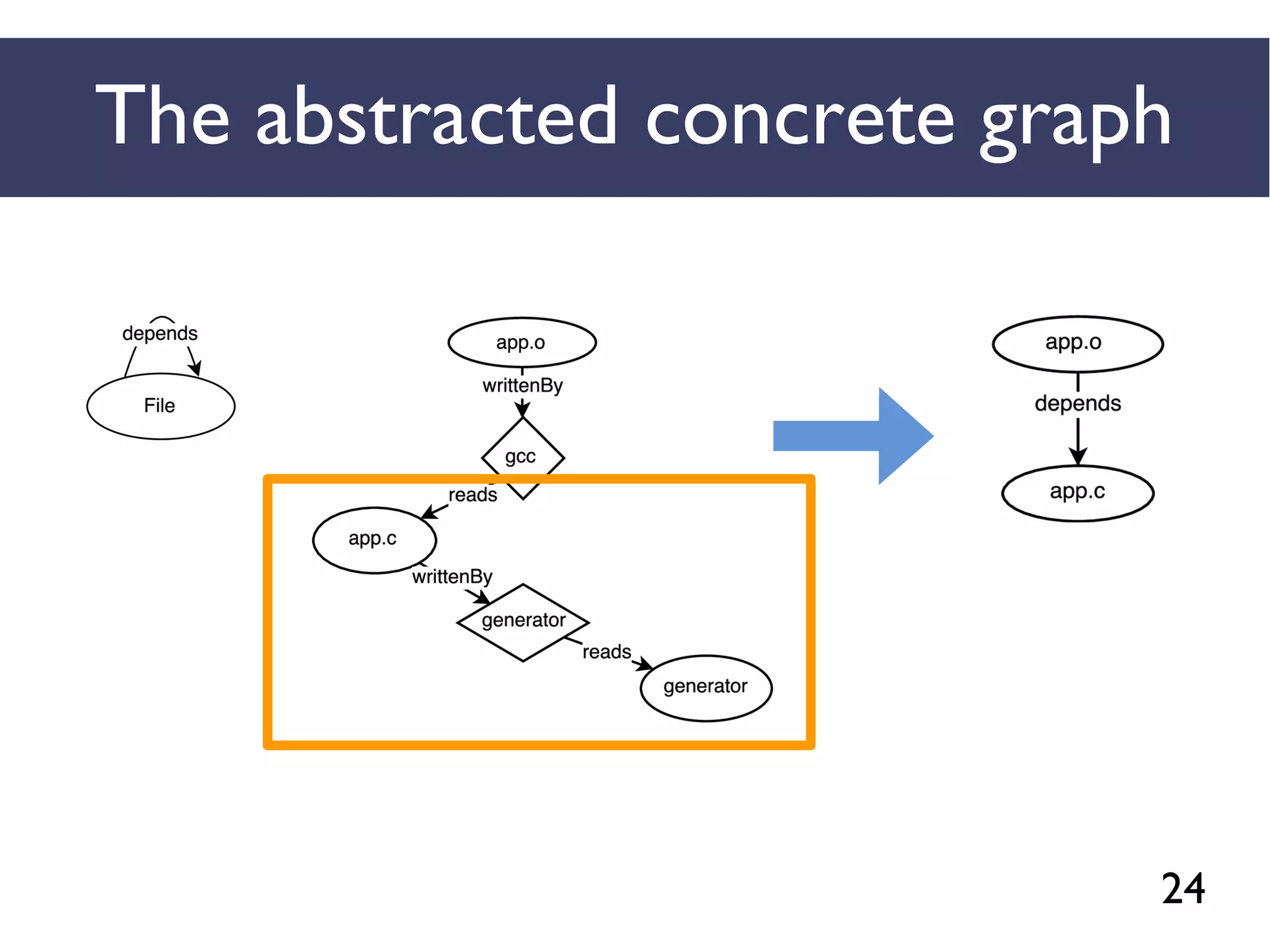
![46
We combined several tools to reveal unspecified
dependencies in make-based build systems
MAKAO
Conceptual graphs are
extracted using
[Adams et al., ICSM 2007]
STRACE
Concrete graphs are
extracted from
execution logs
Graphs are represented
and analyzed using](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uncoveringunspecifieddependenciestalk-170918131535/75/An-Empirical-Study-of-Unspecified-Dependencies-in-Make-Based-Build-Systems-46-2048.jpg)