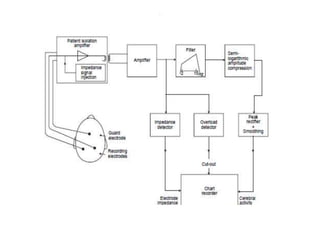
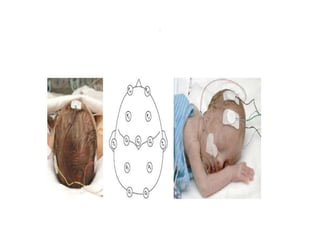
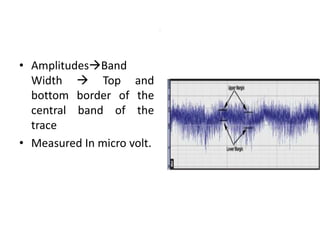
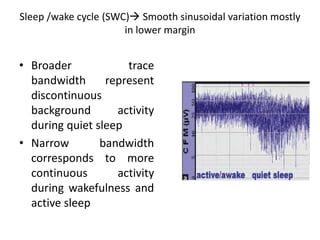
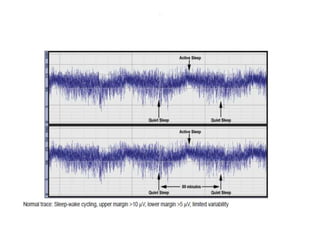
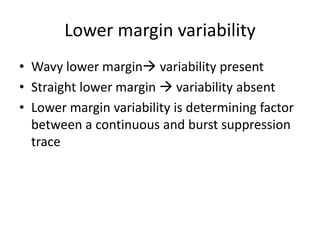
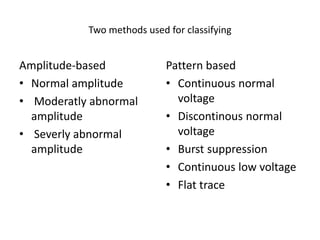
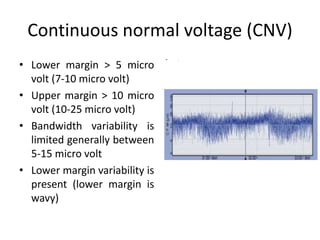
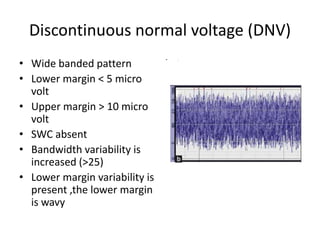
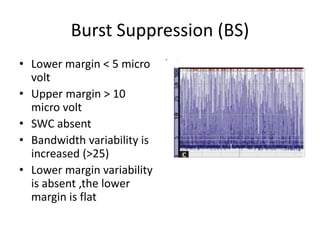
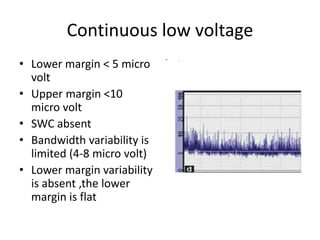
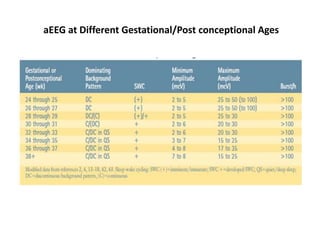
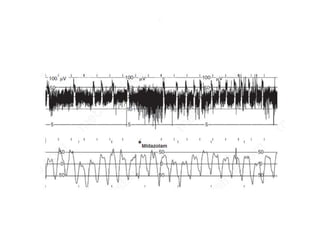
1. Amplitude integrated EEG (aEEG) is a device that measures background brain activity through electrodes placed on the scalp. It provides information on global brain function through a compressed timescale display.
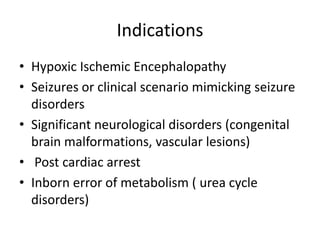
2. aEEG is useful for predicting outcomes in conditions like hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy, seizures, and neurological disorders. Abnormal aEEG patterns correlate with adverse outcomes while return of normal patterns indicates better prognosis.
3. aEEG can help identify infants who benefit most from therapeutic hypothermia for hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. More severe abnormalities on aEEG, like burst suppression, are associated with poorer response to cooling therapies.