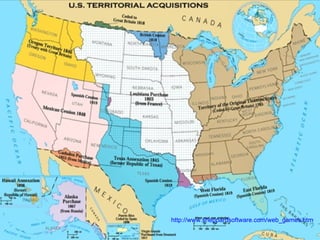
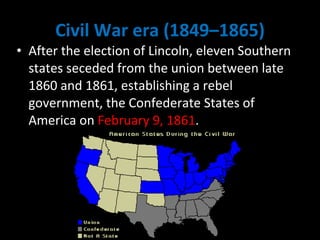
The document provides a detailed overview of American history from pre-colonial times to the present. It covers major periods and events including the arrival of indigenous peoples, European exploration and colonization, the American Revolution, formation of the US government, westward expansion, the Civil War, World Wars I and II, the Cold War, Civil Rights movement, 9/11 terrorist attacks, and recent presidencies. Key people and developments that shaped the country are discussed within the broader context of the economic, political, and social transformations of each historical period.