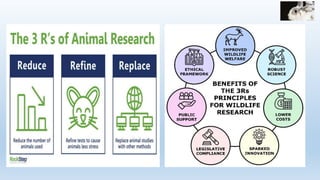
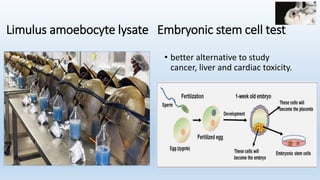
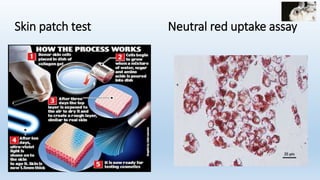
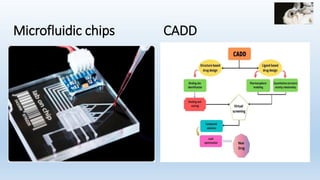
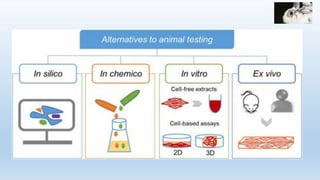
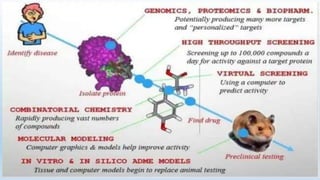
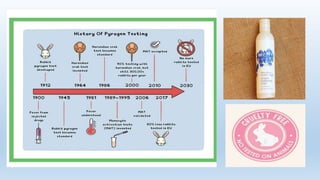
The document discusses alternatives to animal testing in research. It notes that while animals have traditionally been used for testing, this method is cruel, time-consuming, and not predictive of human outcomes. New alternative methods include in vitro, in silico, in chemico techniques using cells, tissues, organs-on-chips and computer modeling that can replace many animal tests in a more humane, effective and predictive way. Widespread adoption of alternative methods can improve both the ethics and accuracy of medical research.