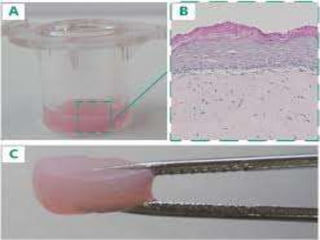
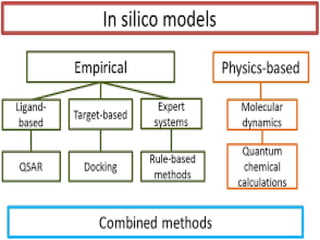
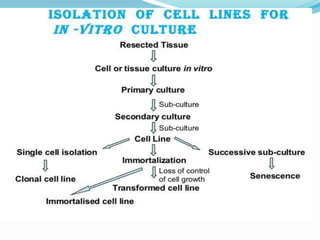
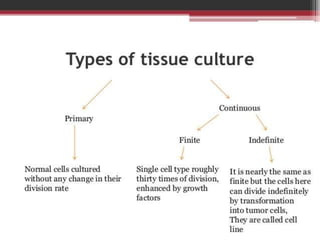
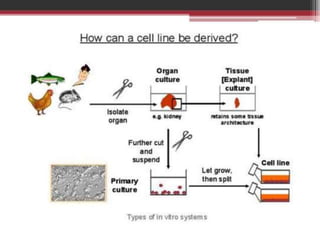
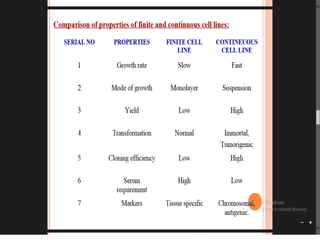
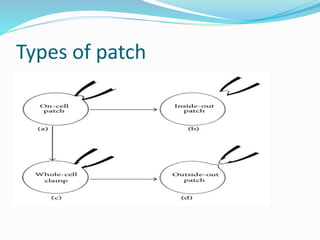
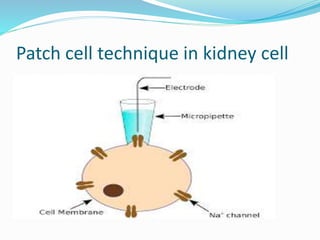
This document discusses several alternative methods that can be used instead of animal experiments for pharmacological and toxicological screening. It describes the full thickness skin model method which uses skin tissue to evaluate the effects of substances instead of live animals. It also mentions in silico methods which use computer programs and knowledge of similar substances to predict properties without testing. The document outlines the cell line technique using continuous cell lines to screen for effects like anticancer drugs. Finally, it explains the patch clamp technique which studies individual ion channels in isolated cells and kidney tubules as an alternative to testing on whole animals.