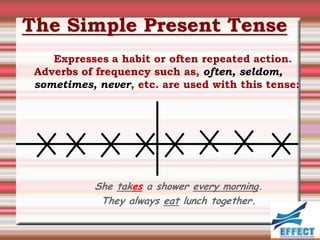
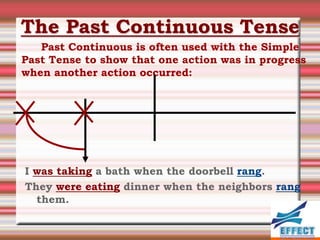
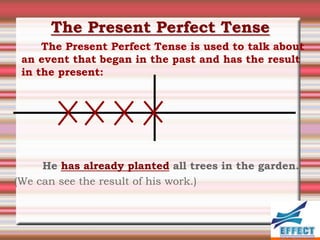
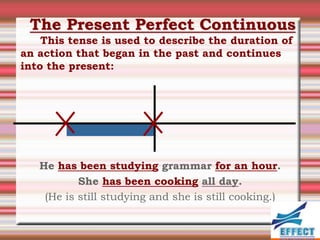
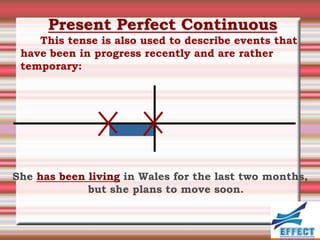
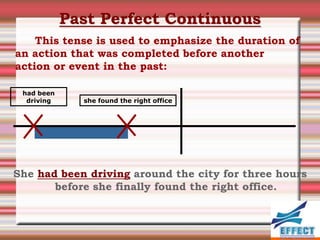
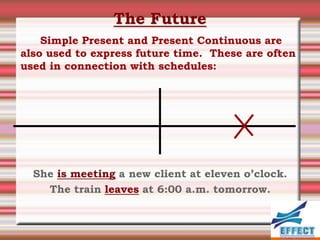
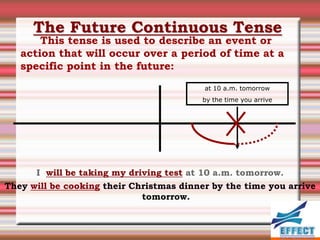
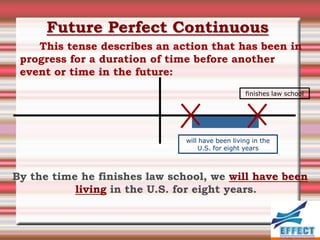
The document discusses the different verb tenses in English. It provides examples and explanations of 12 verb tenses: simple present, present continuous, simple past, past continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future, future continuous, future perfect, and future perfect continuous. Each tense expresses time and duration of events in different ways.