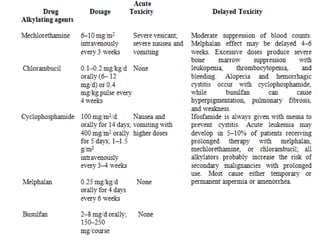
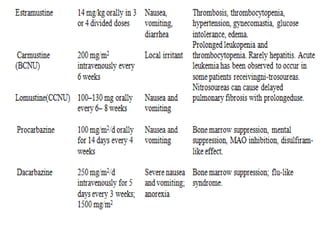
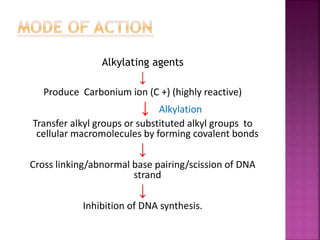
This document summarizes cancer chemotherapy drugs that act as alkylating agents. It describes how these drugs produce reactive carbonium ions that alkylate and cross-link DNA, inhibiting its replication and causing cell death. The major classes of alkylating agents discussed are nitrogen mustards, ethylenimines, alkyl sulfonates, nitrosoureas, and triazines. Specific drugs from these classes are mentioned along with their mechanisms of action, metabolism, uses, and dosages.










![ Have primary inhibitory action on RNA and Protein
synthesis.(KDT)
Undergo demethylation to active intermediate
(monomethyl triazeno-imidazole-carboxamide
[MTIC]) that interrupts DNA replication by causing
methylation of guanine.(DIPIRO)
Metabolised in liver .
Used in Malignant Melanoma and Hodgkin’s Disease.
Side effects – nausea and vomiting.
Dose – 3.5 mg/Kg/day IV for 10 days ; repeat after 4
weeks.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alkylatingagents-171030041341/85/Alkylating-agents-17-320.jpg)