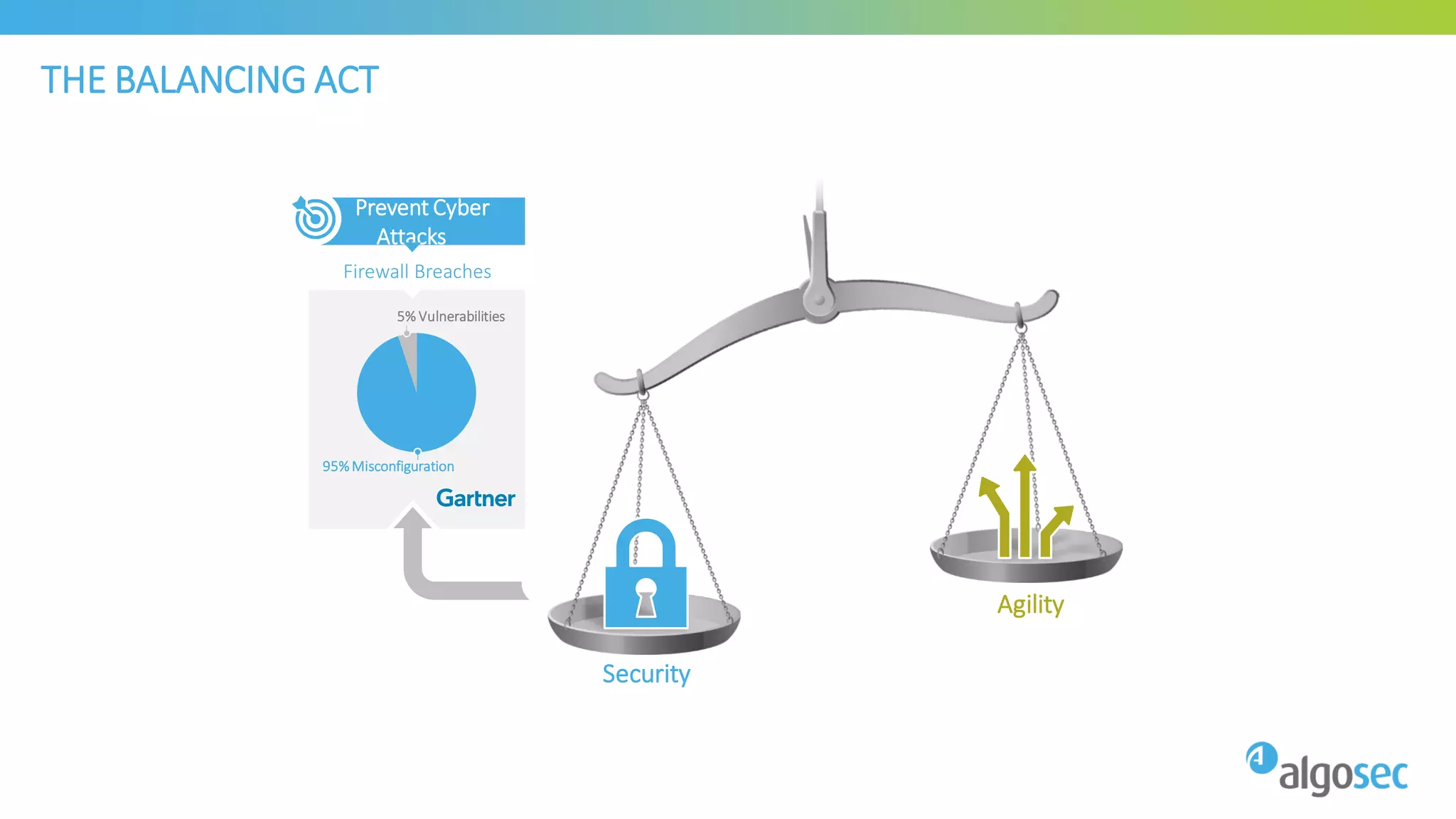
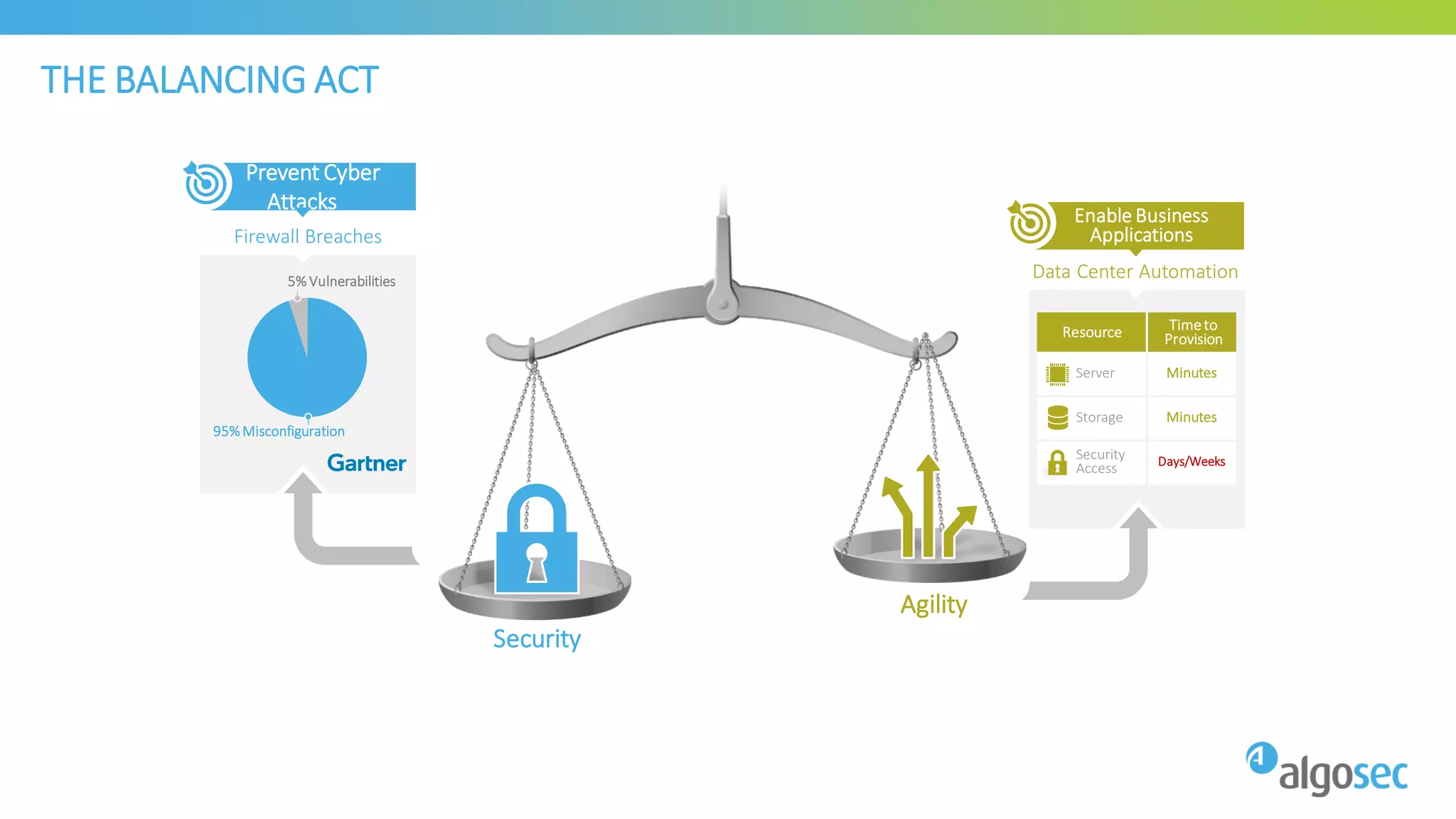
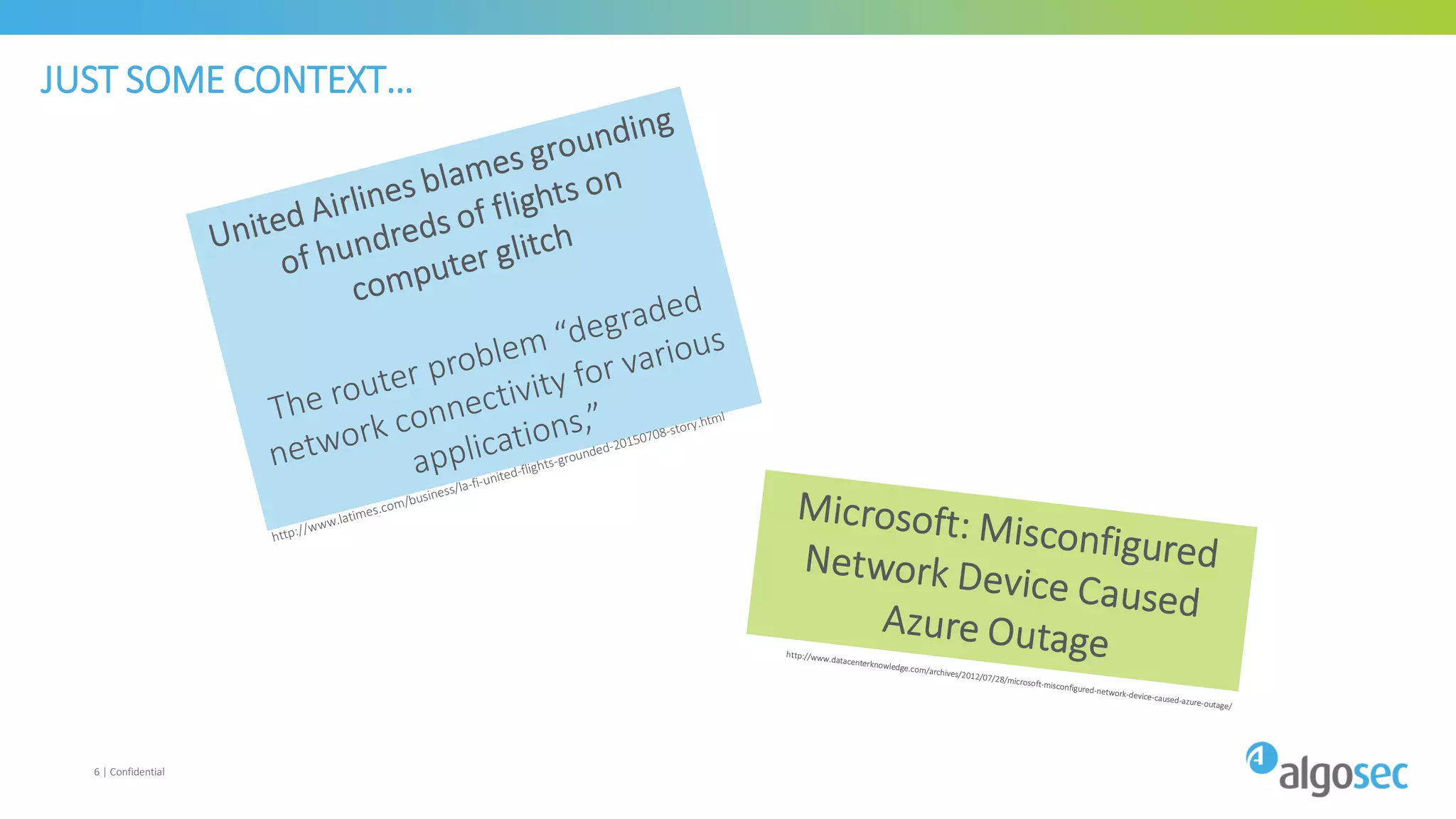
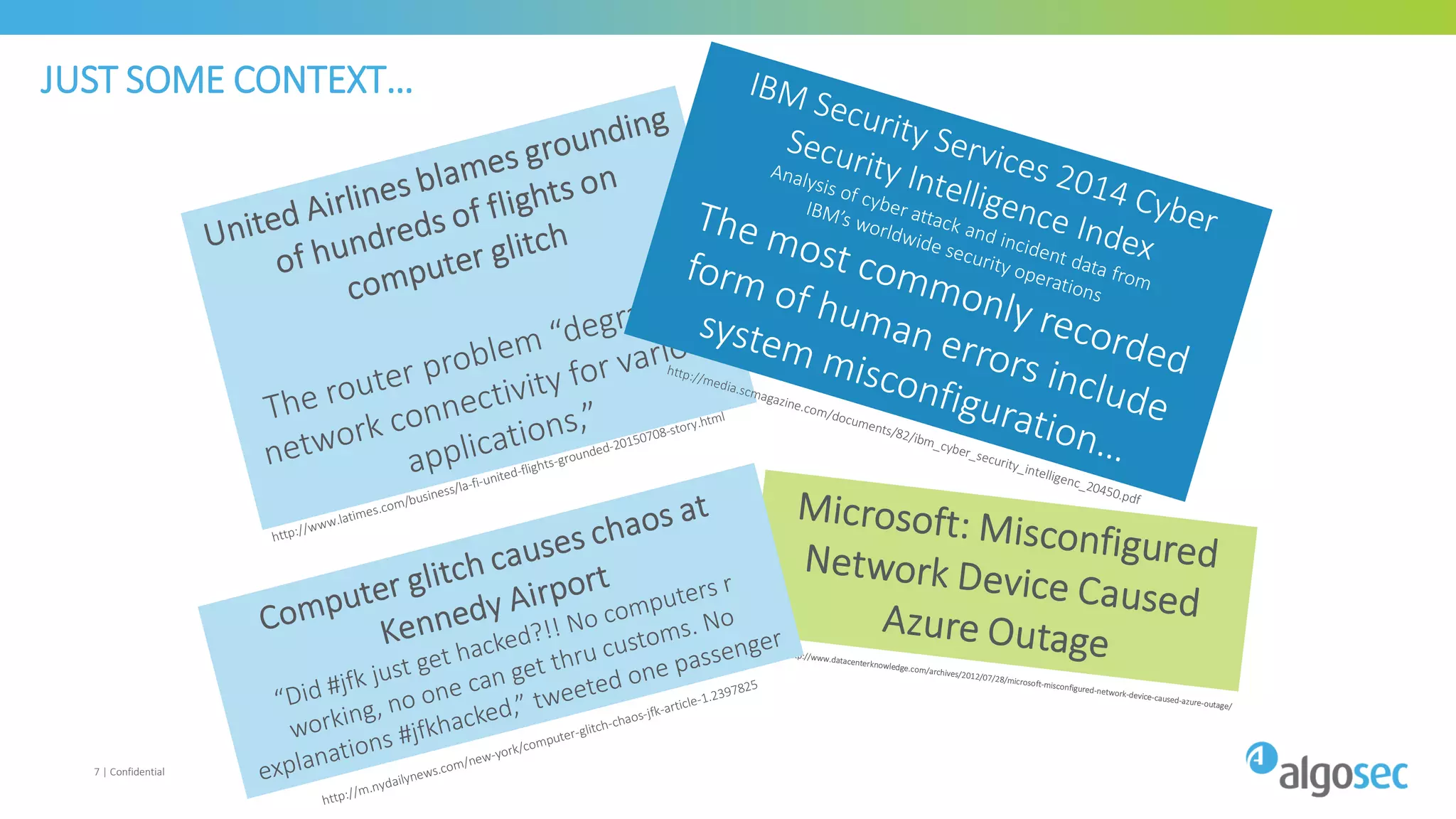
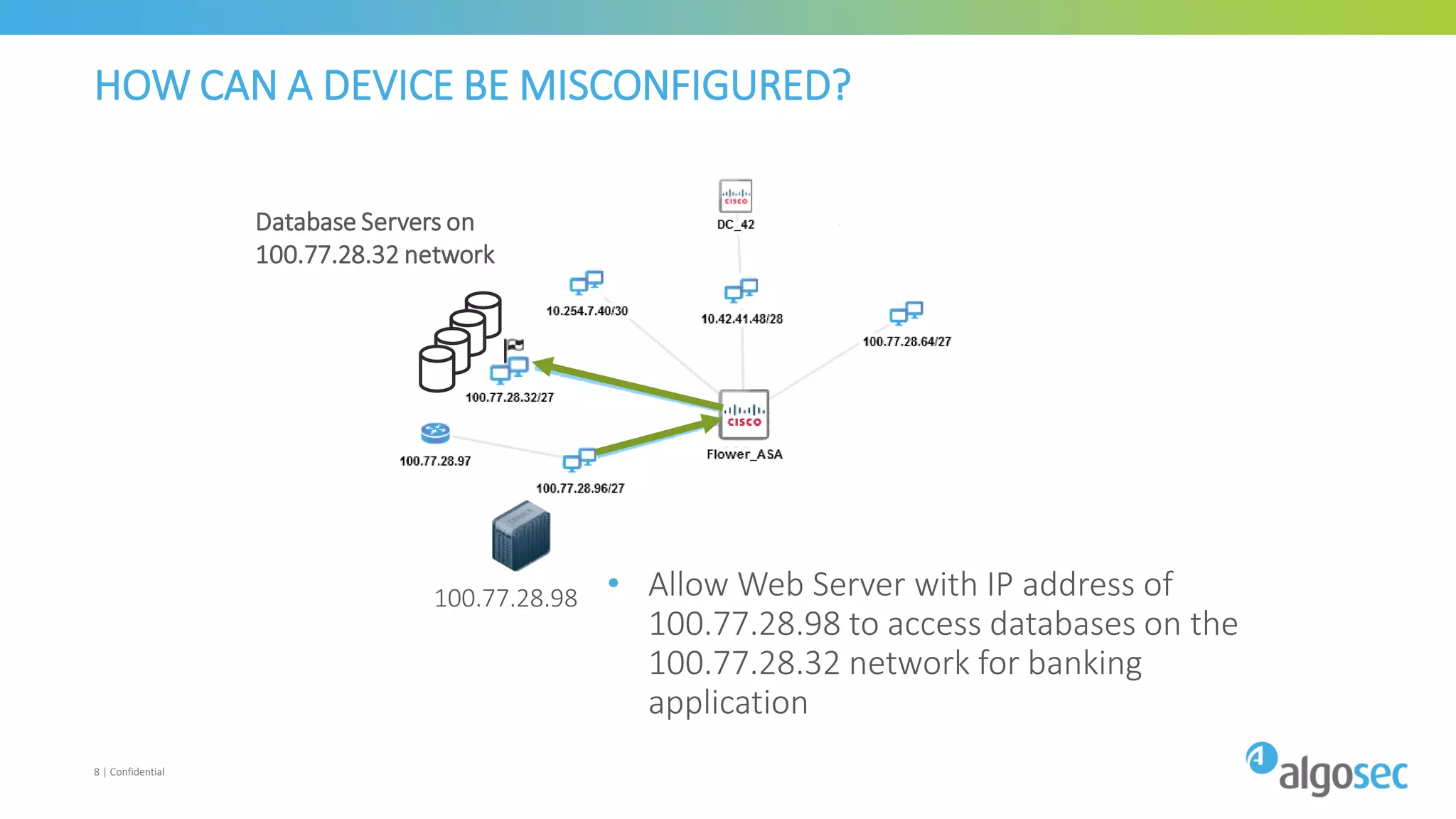
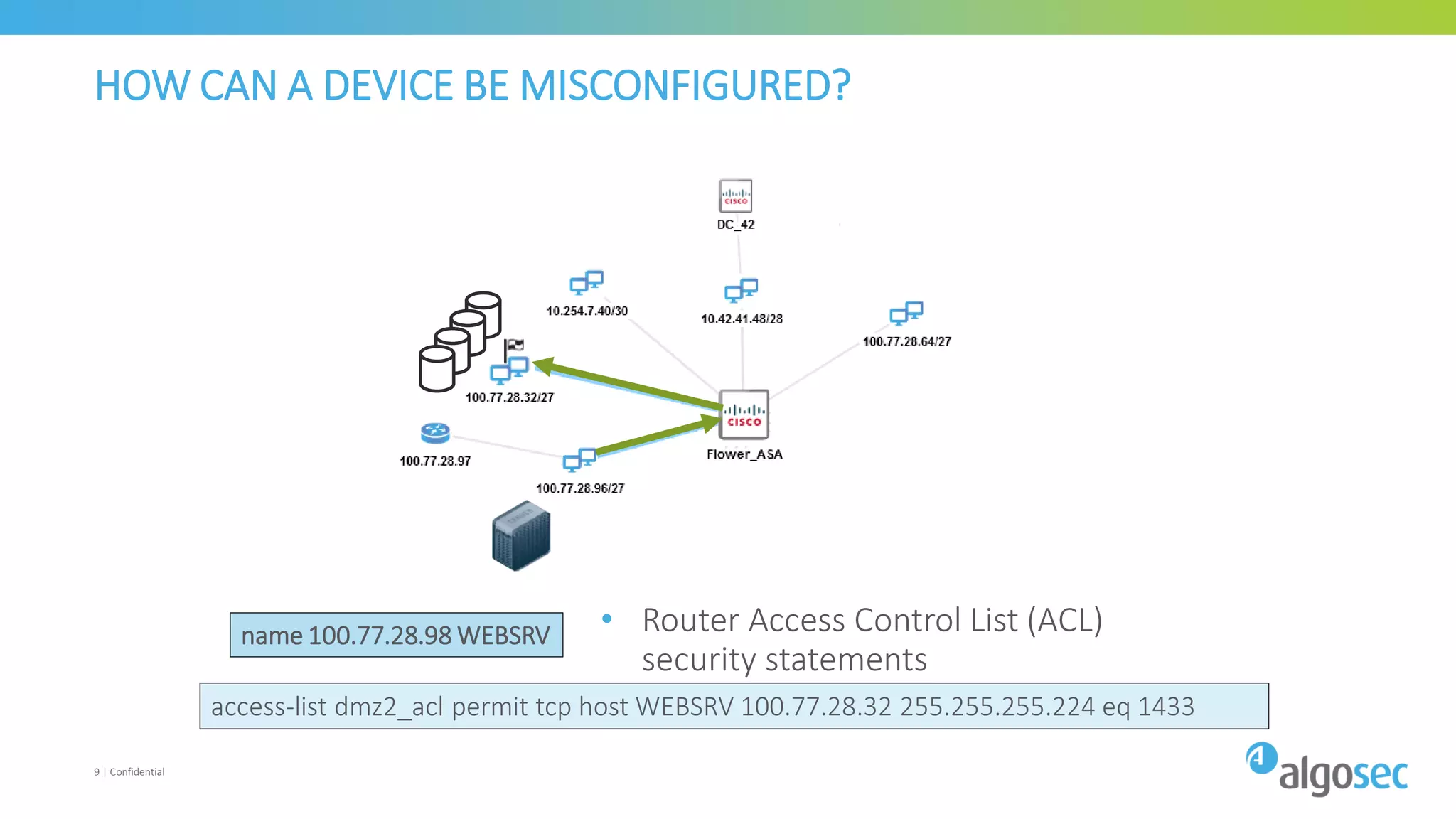
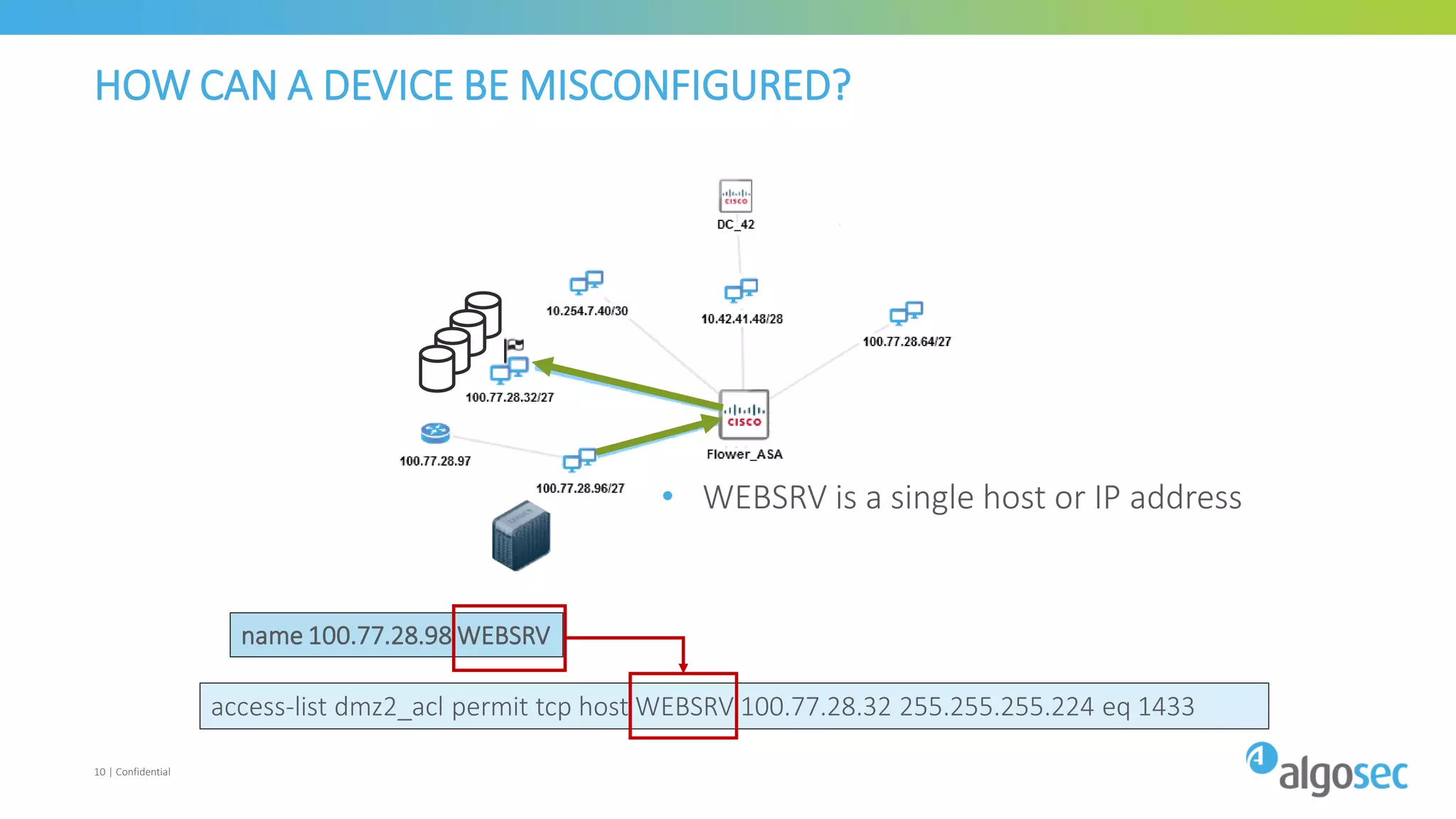
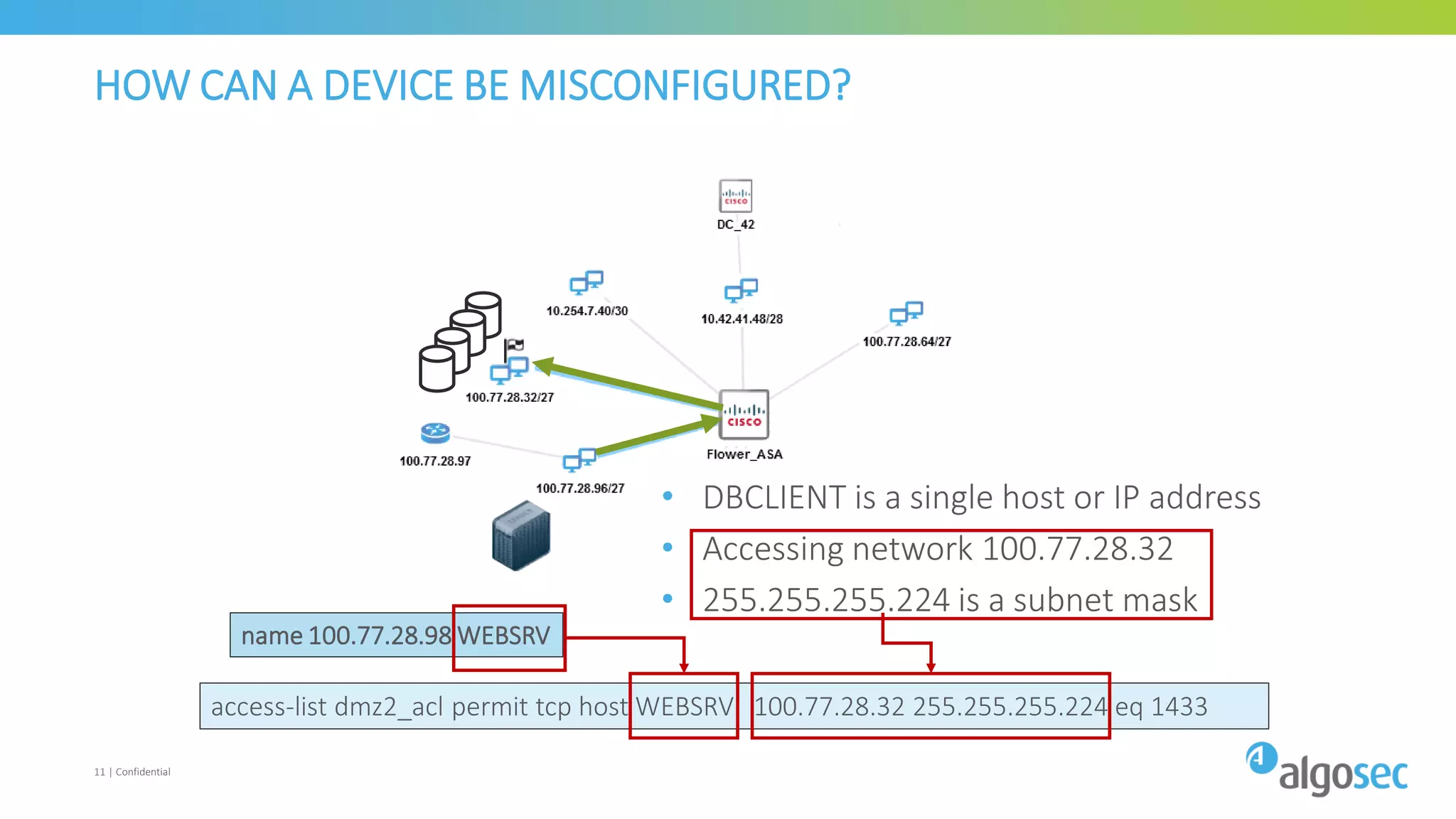
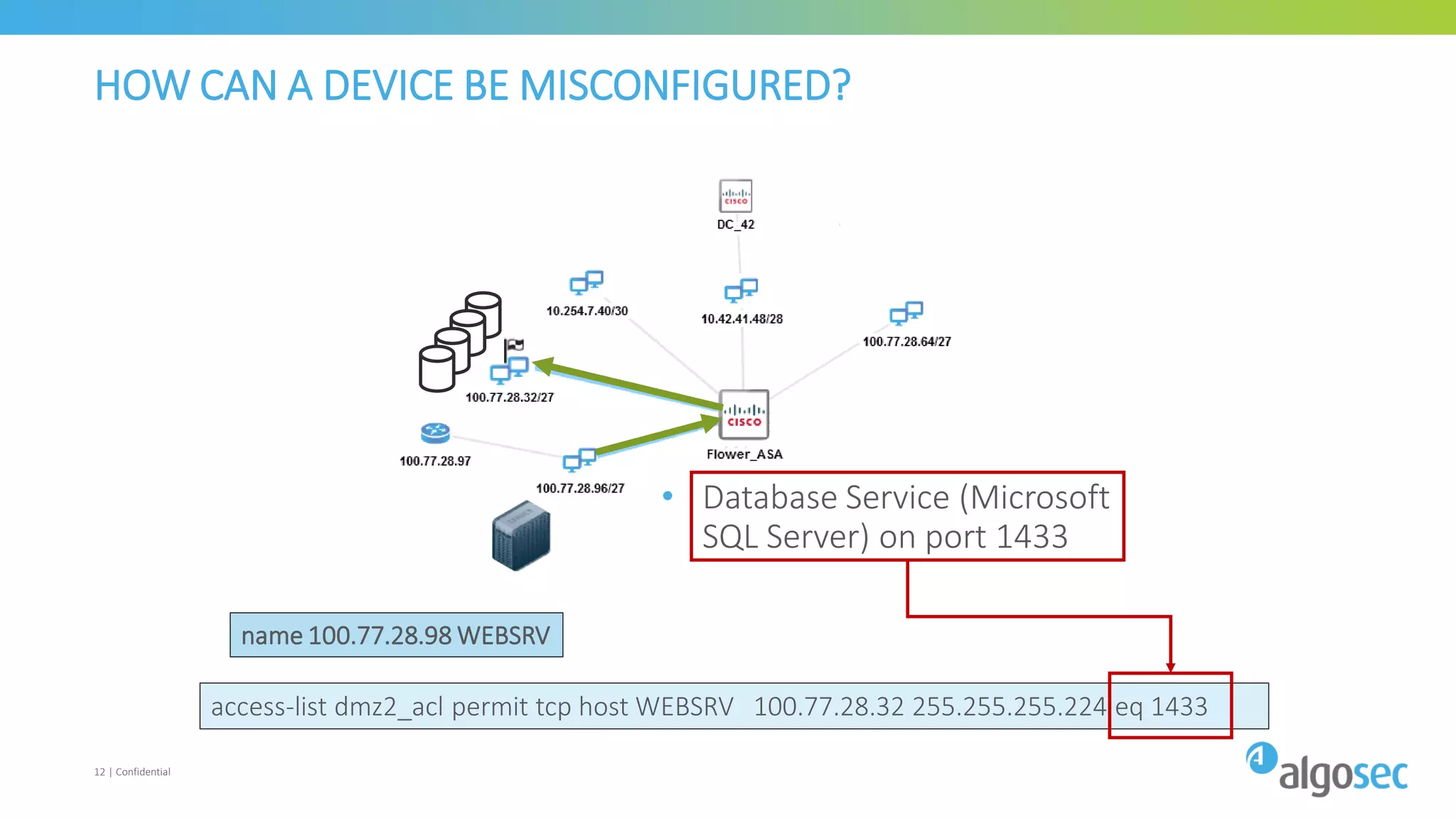
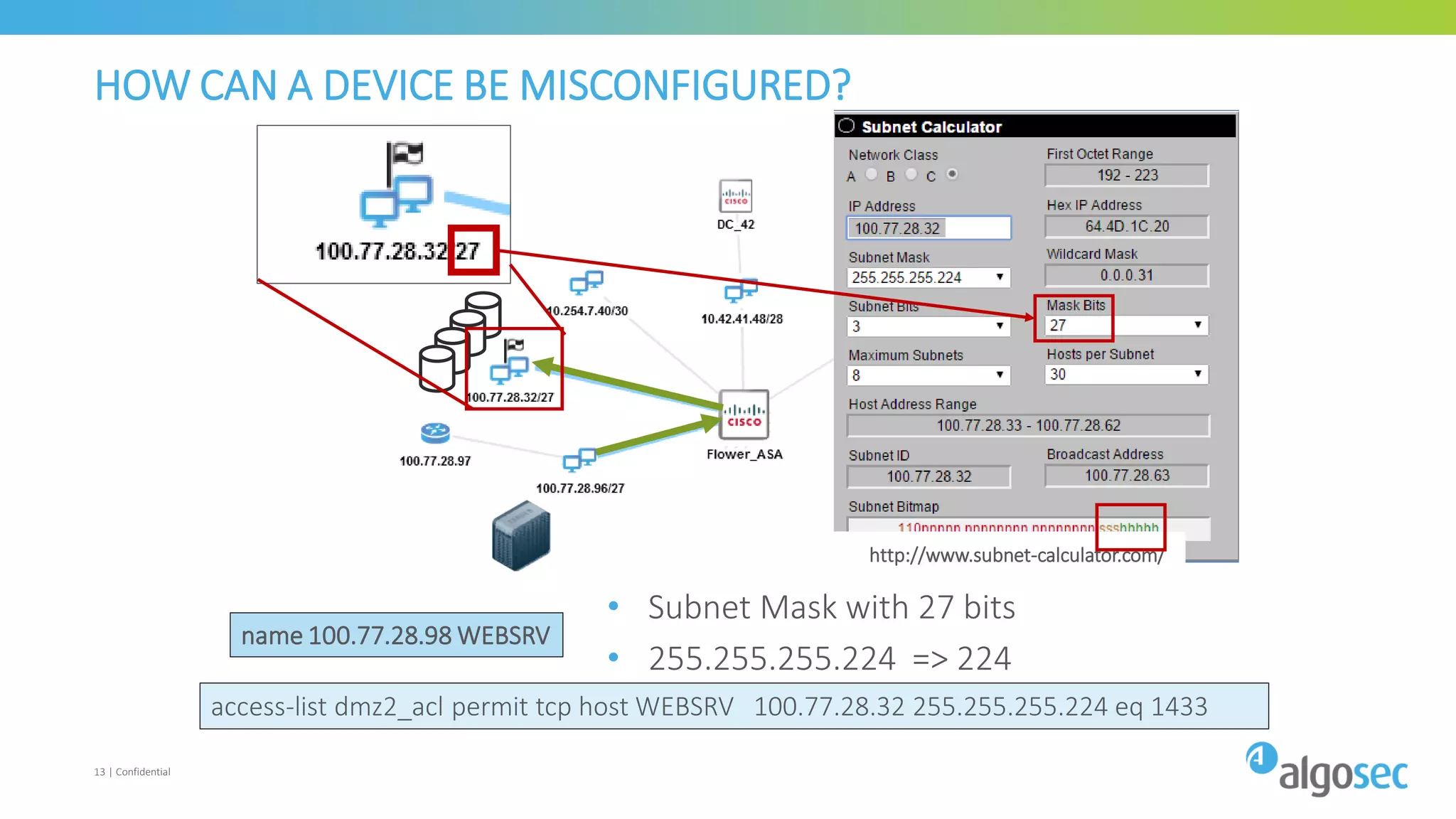
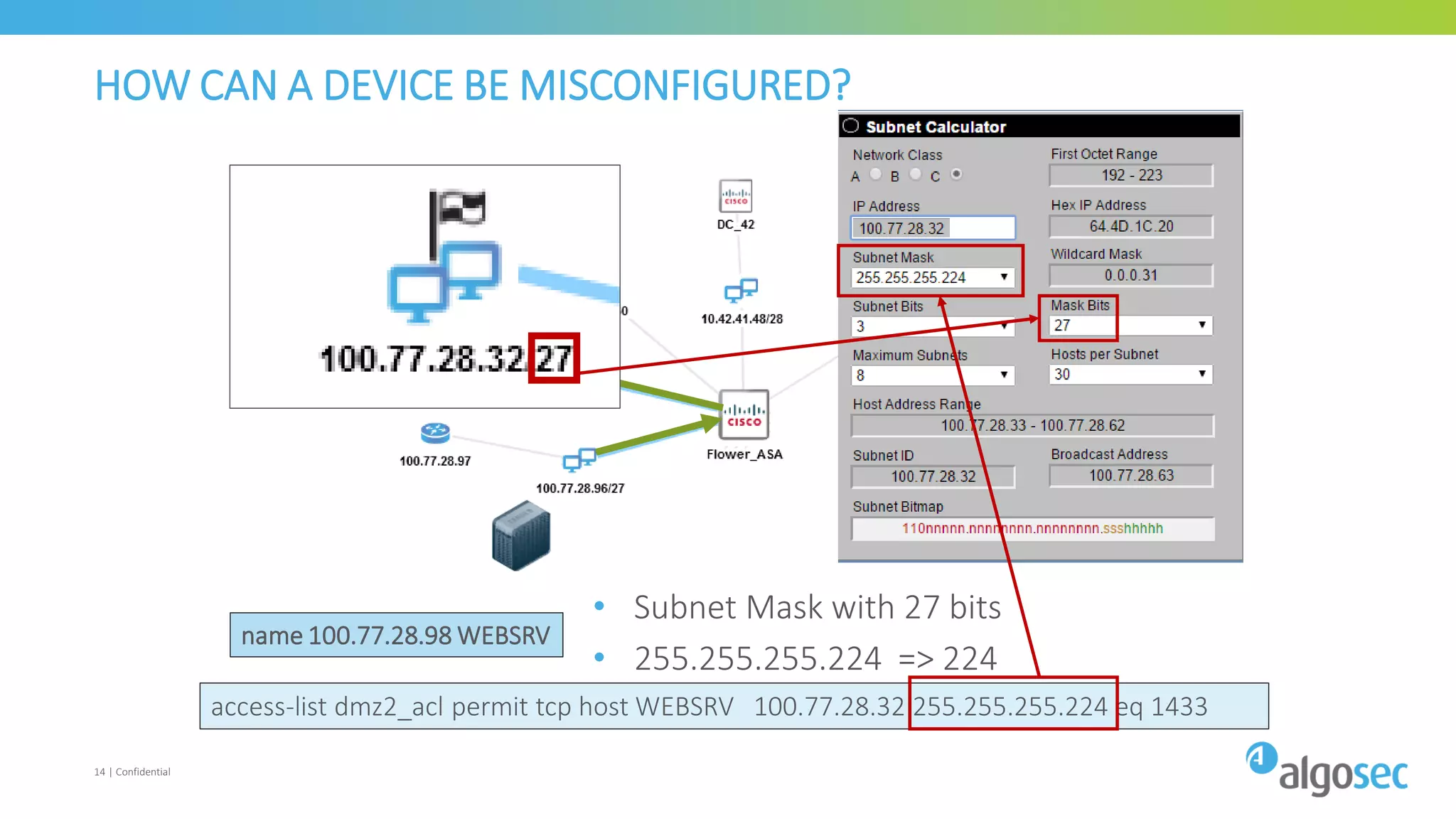
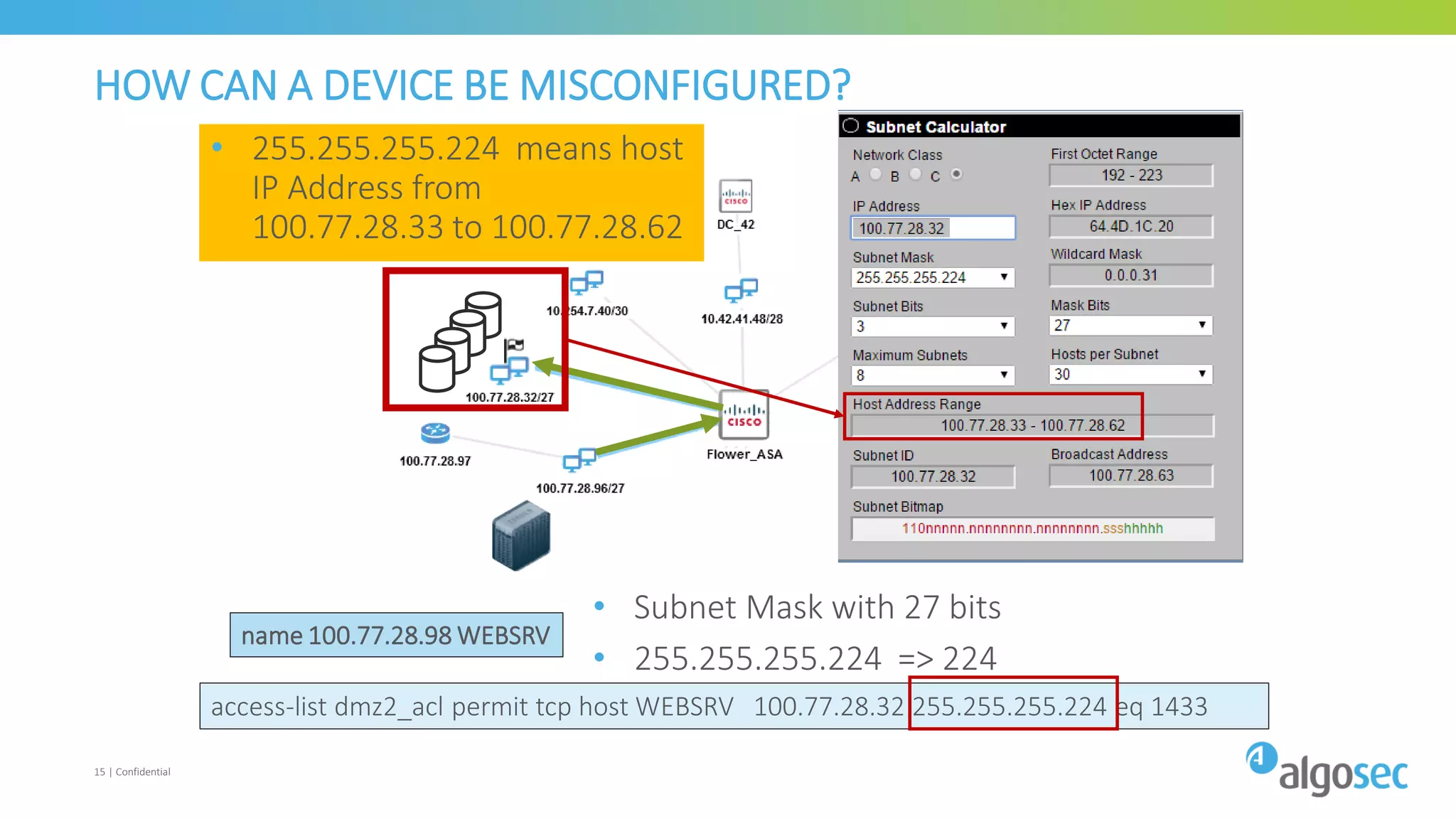
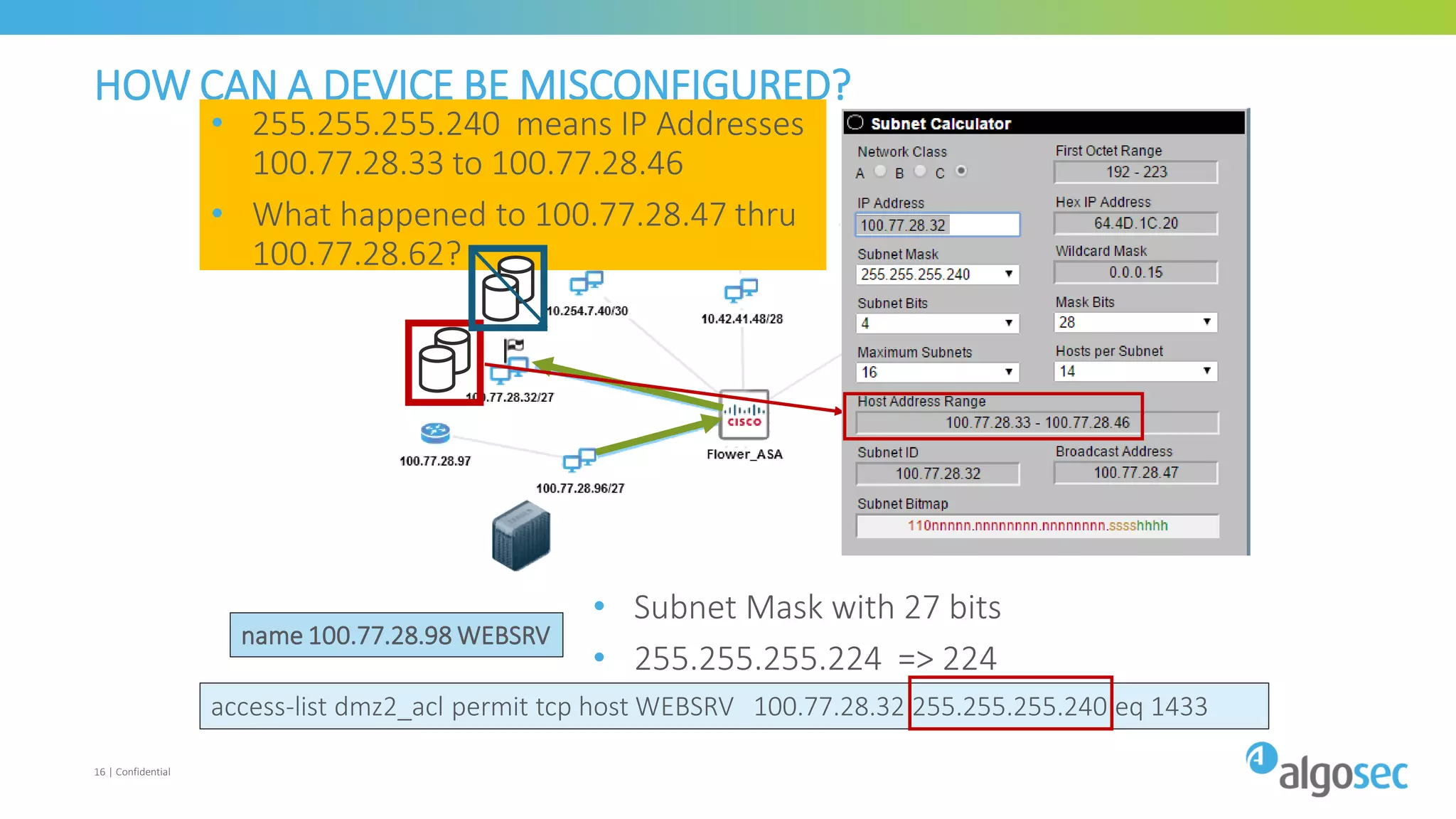
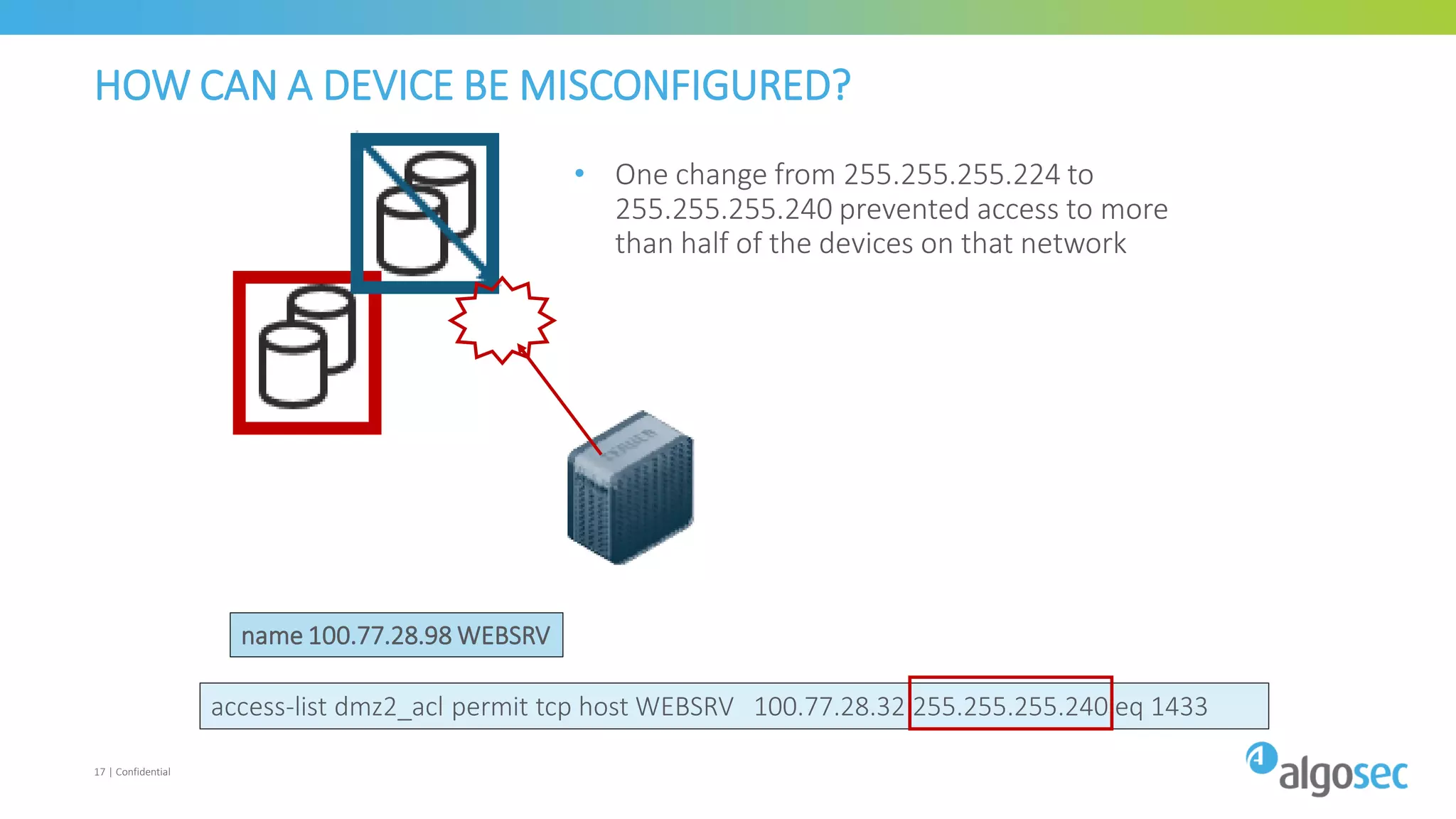
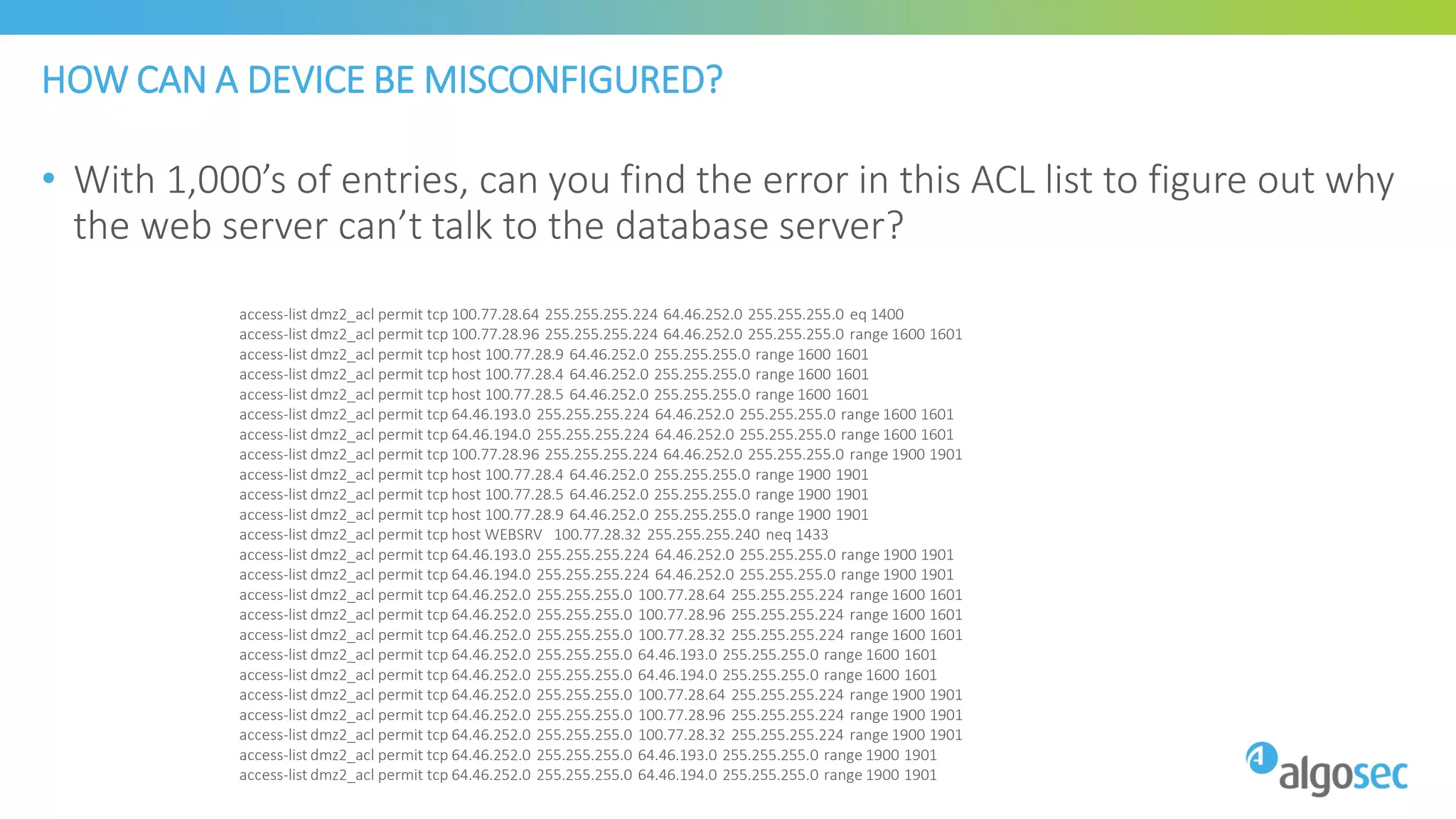
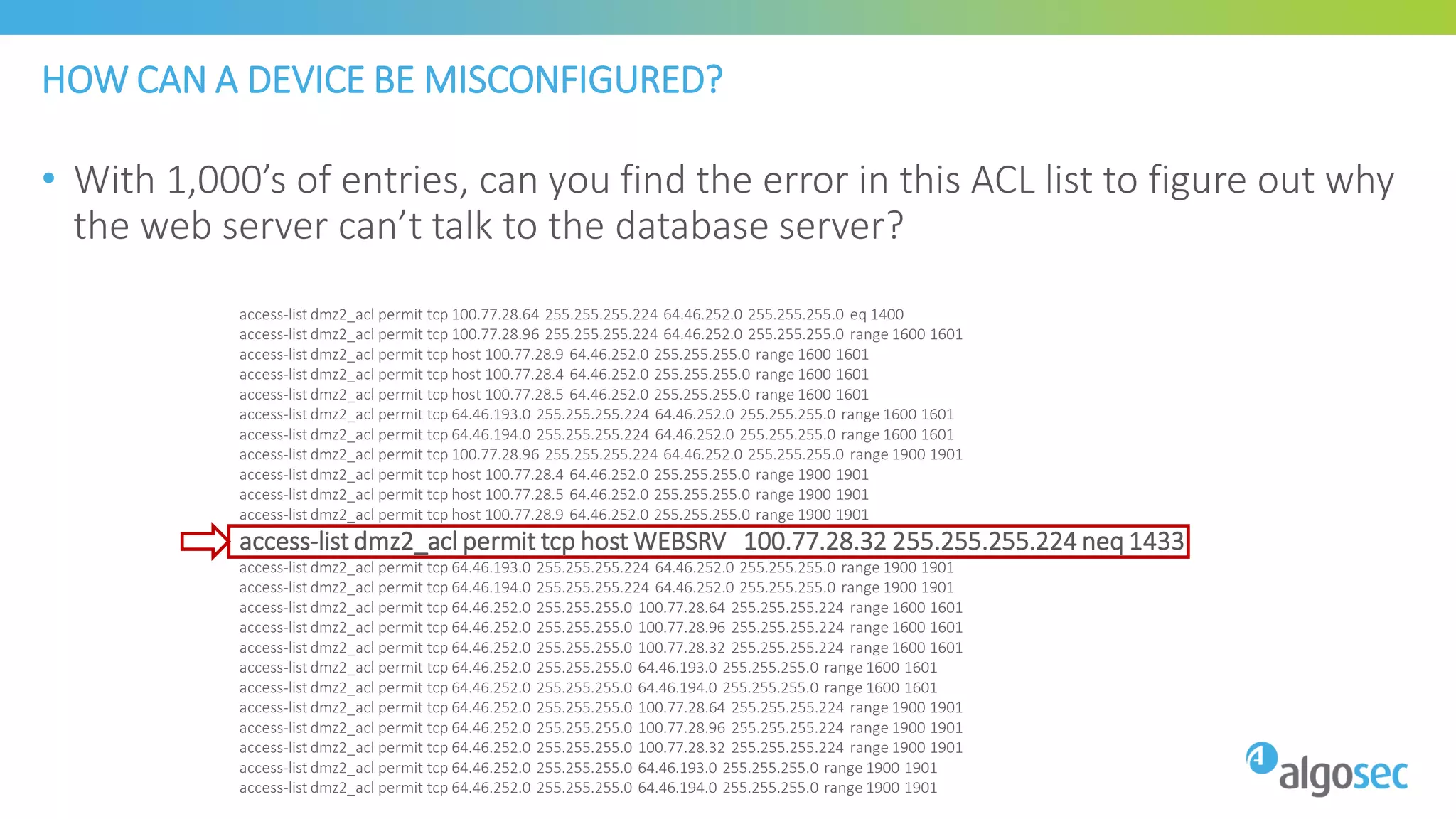
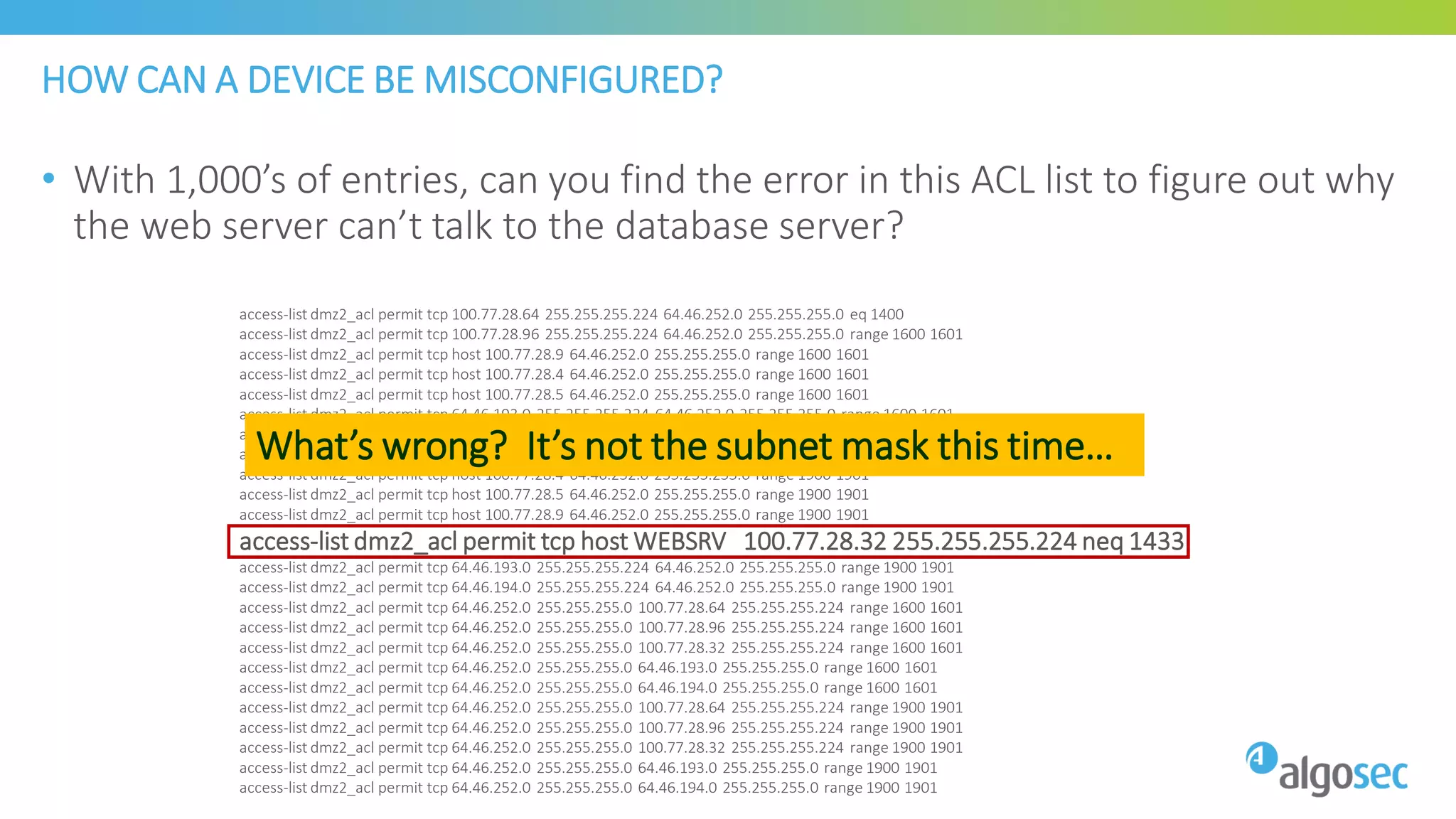
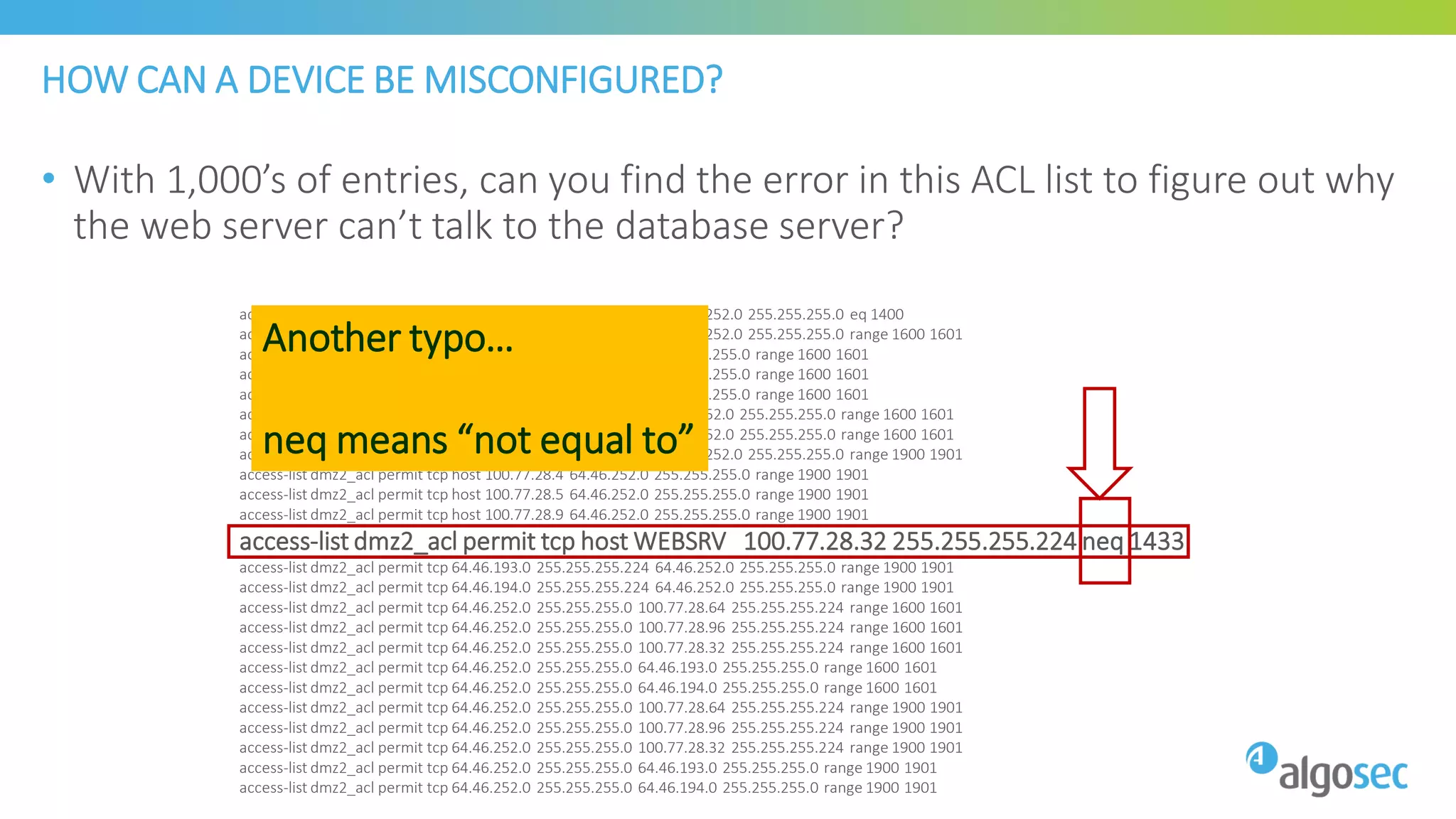
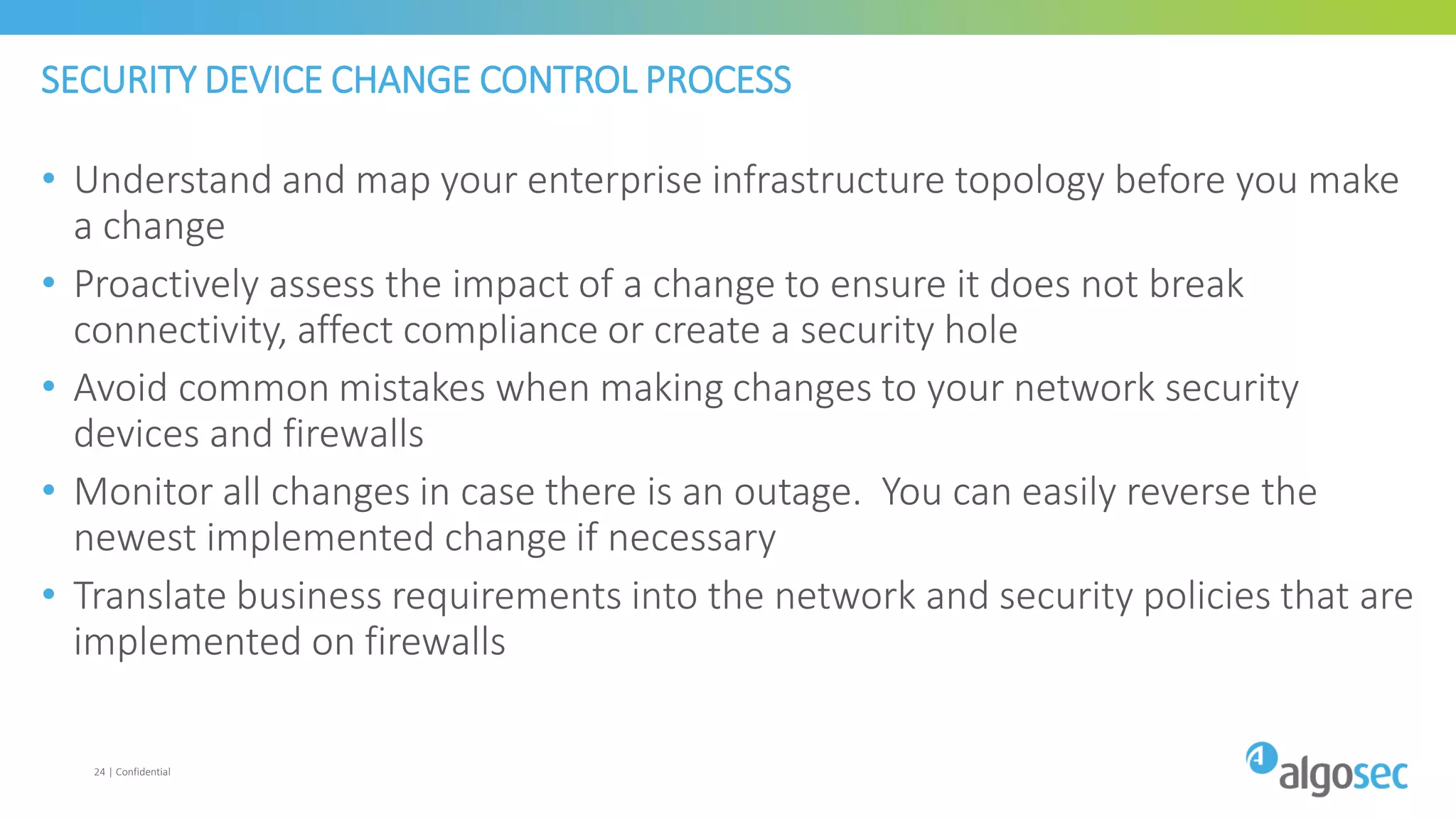
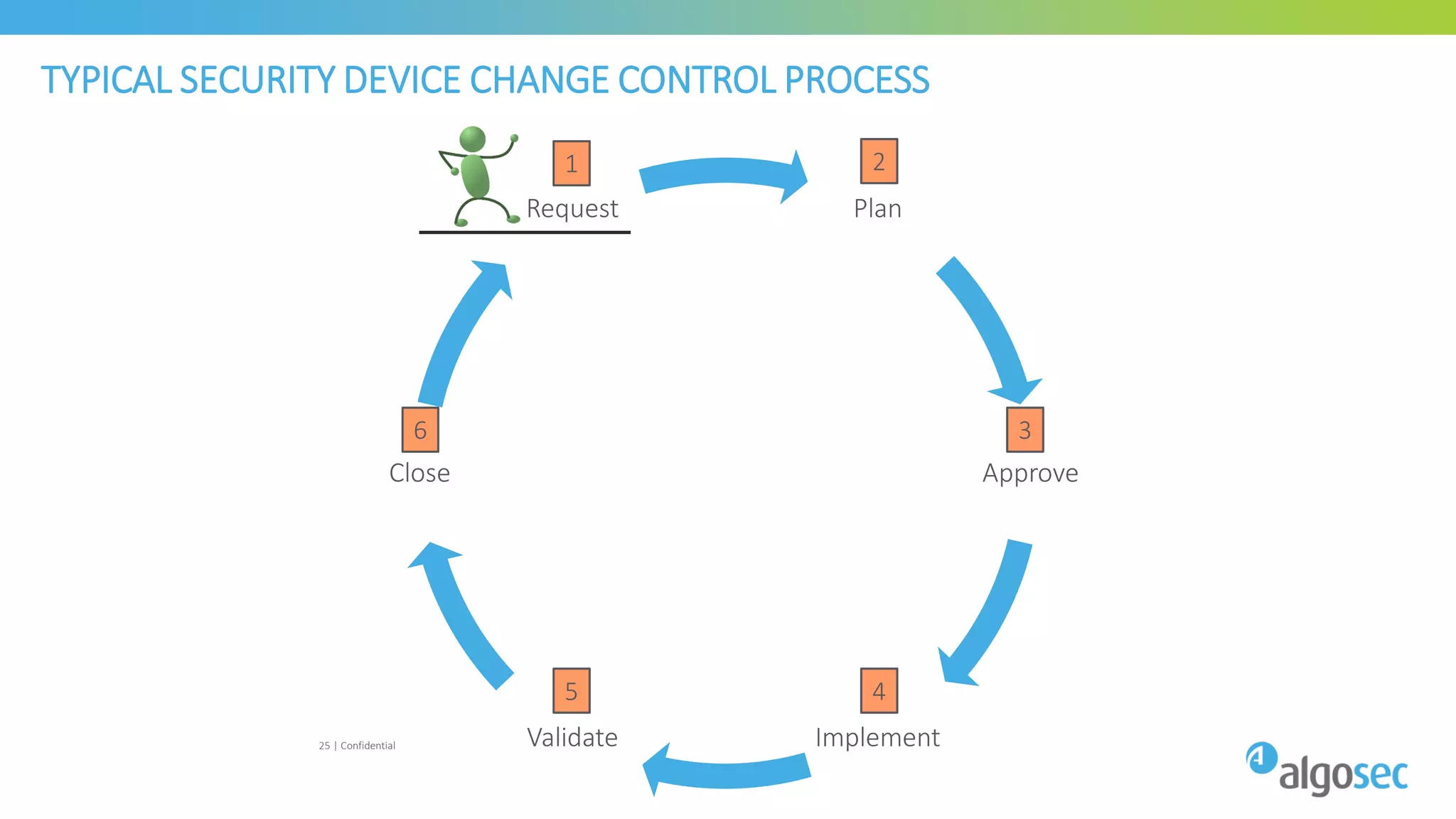
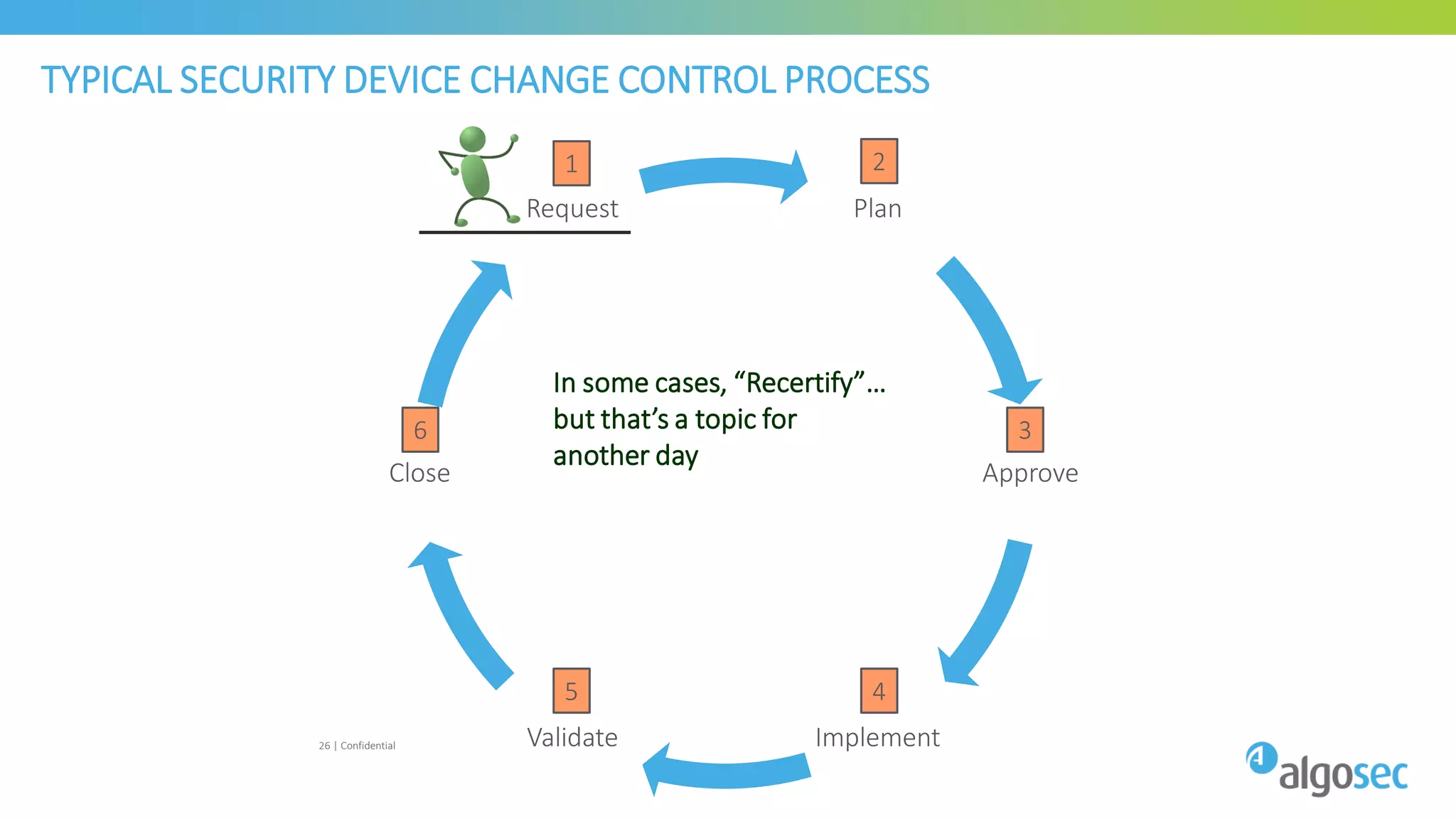
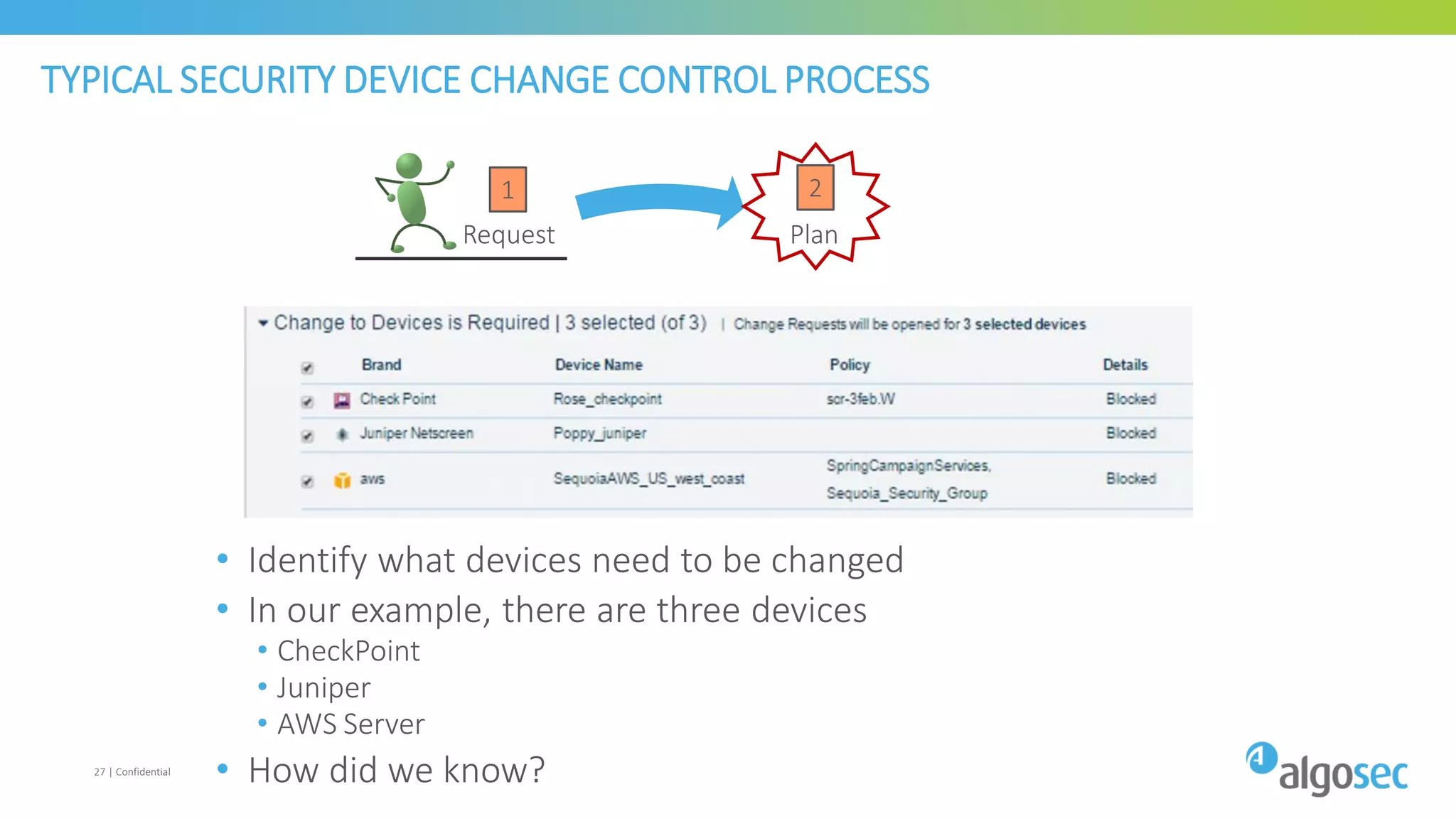
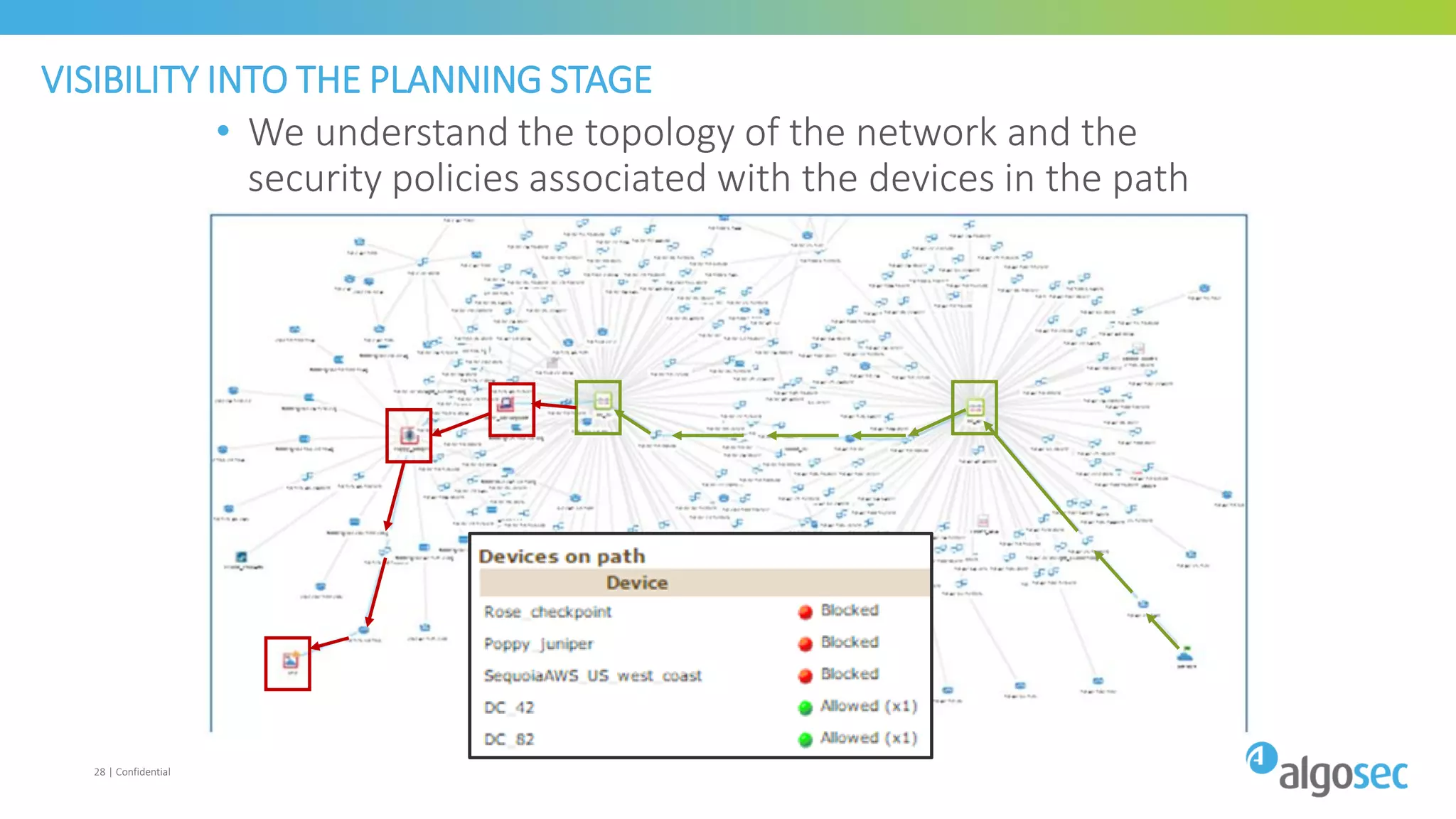
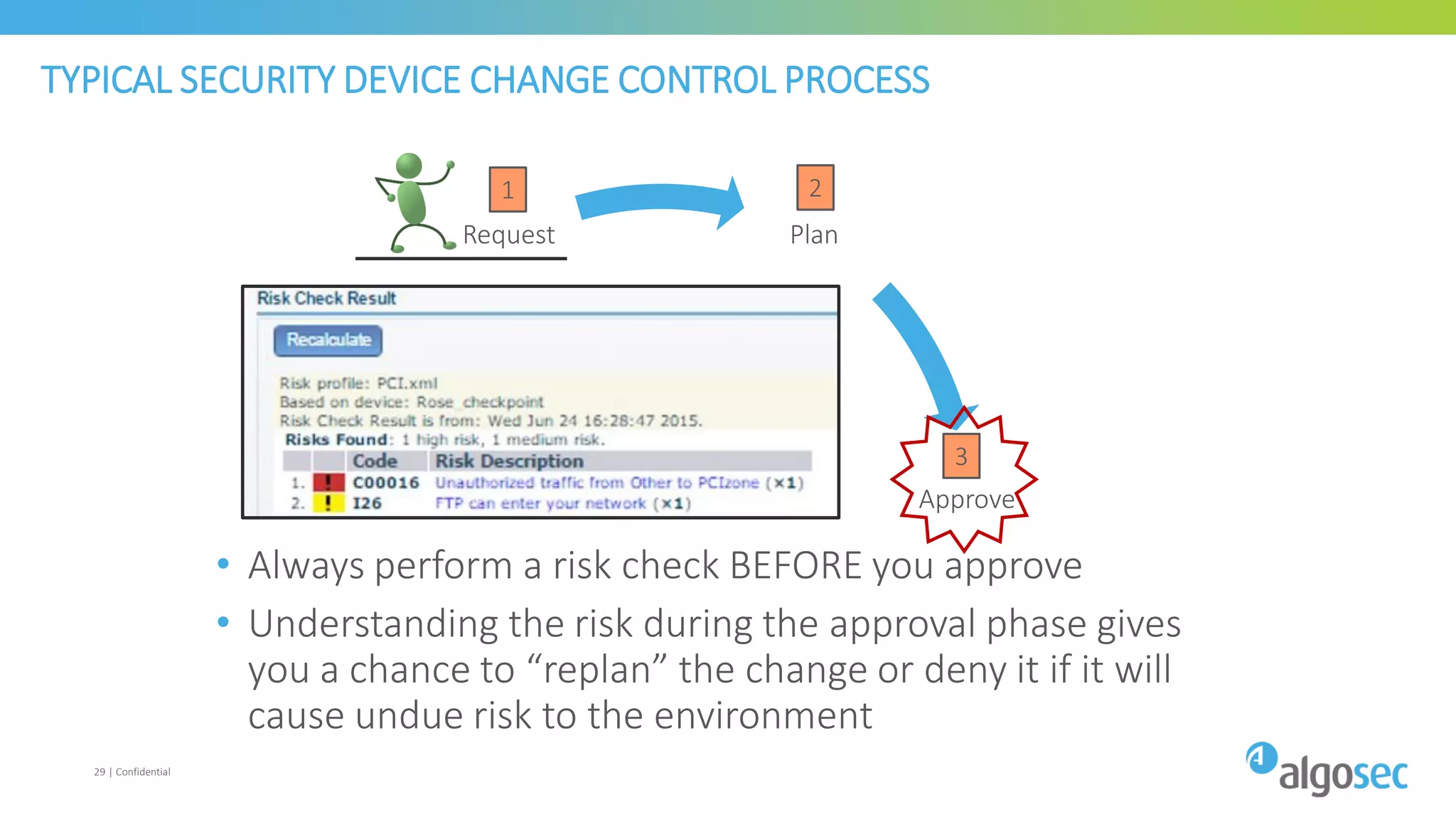
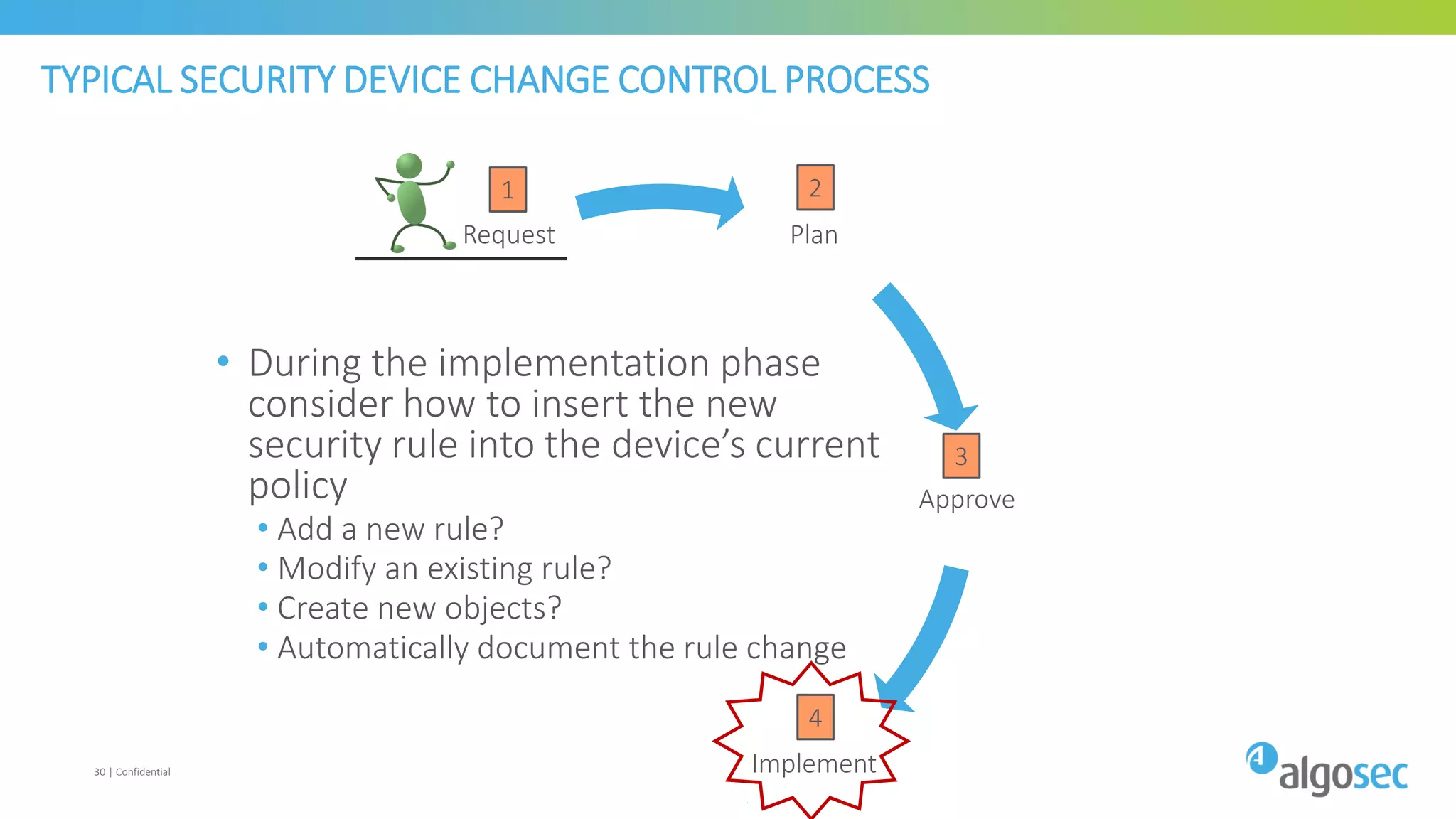
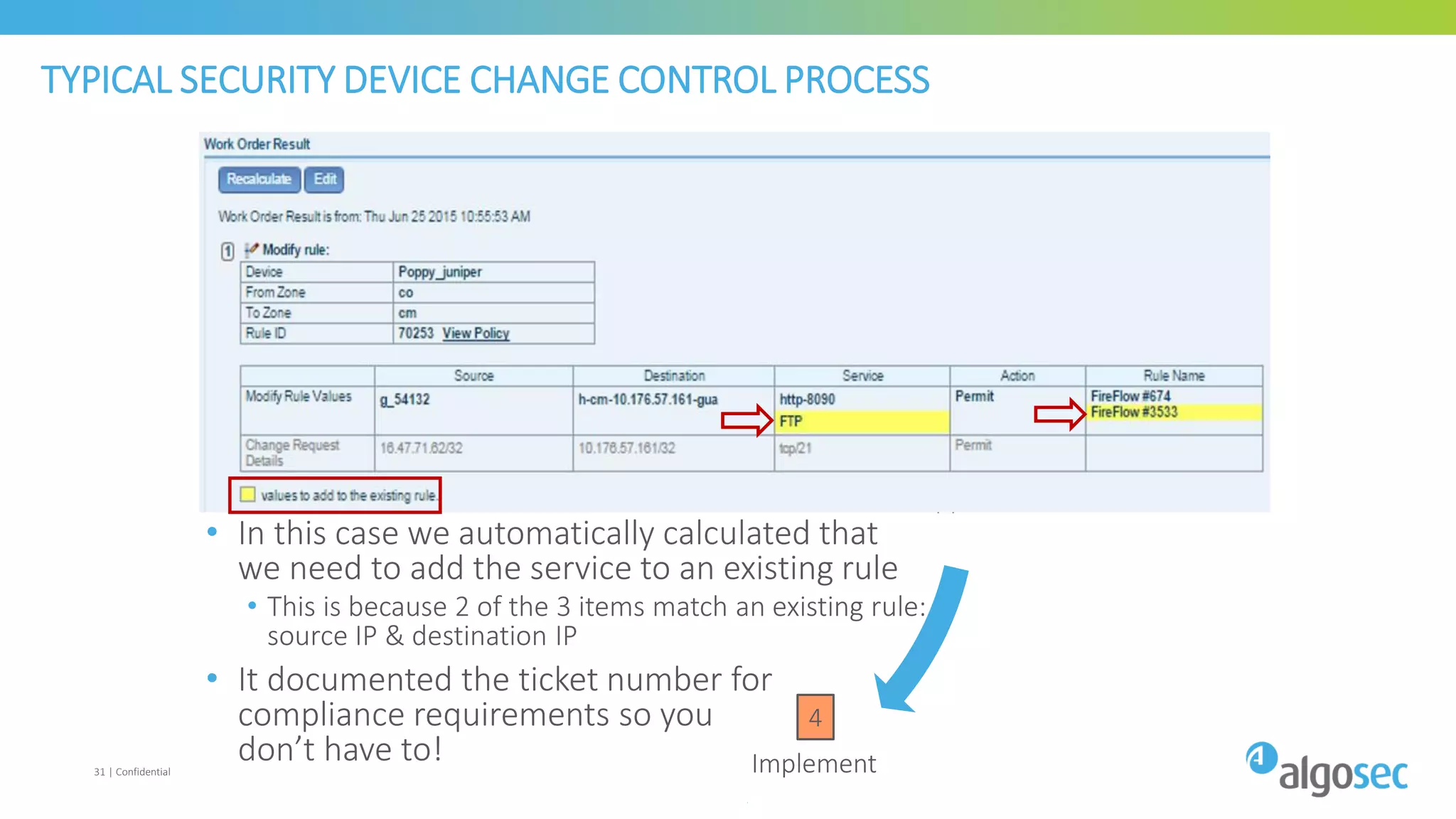
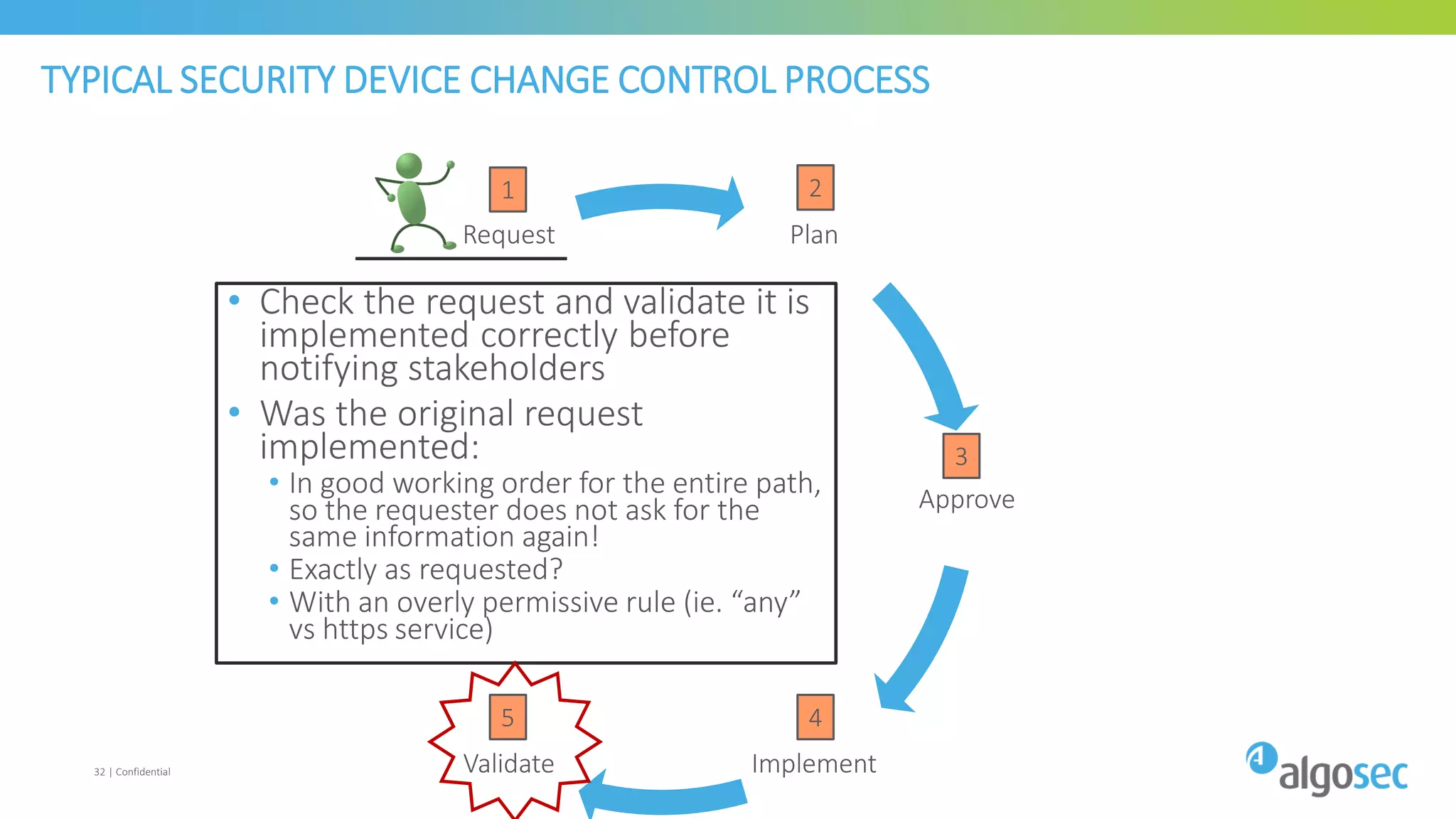
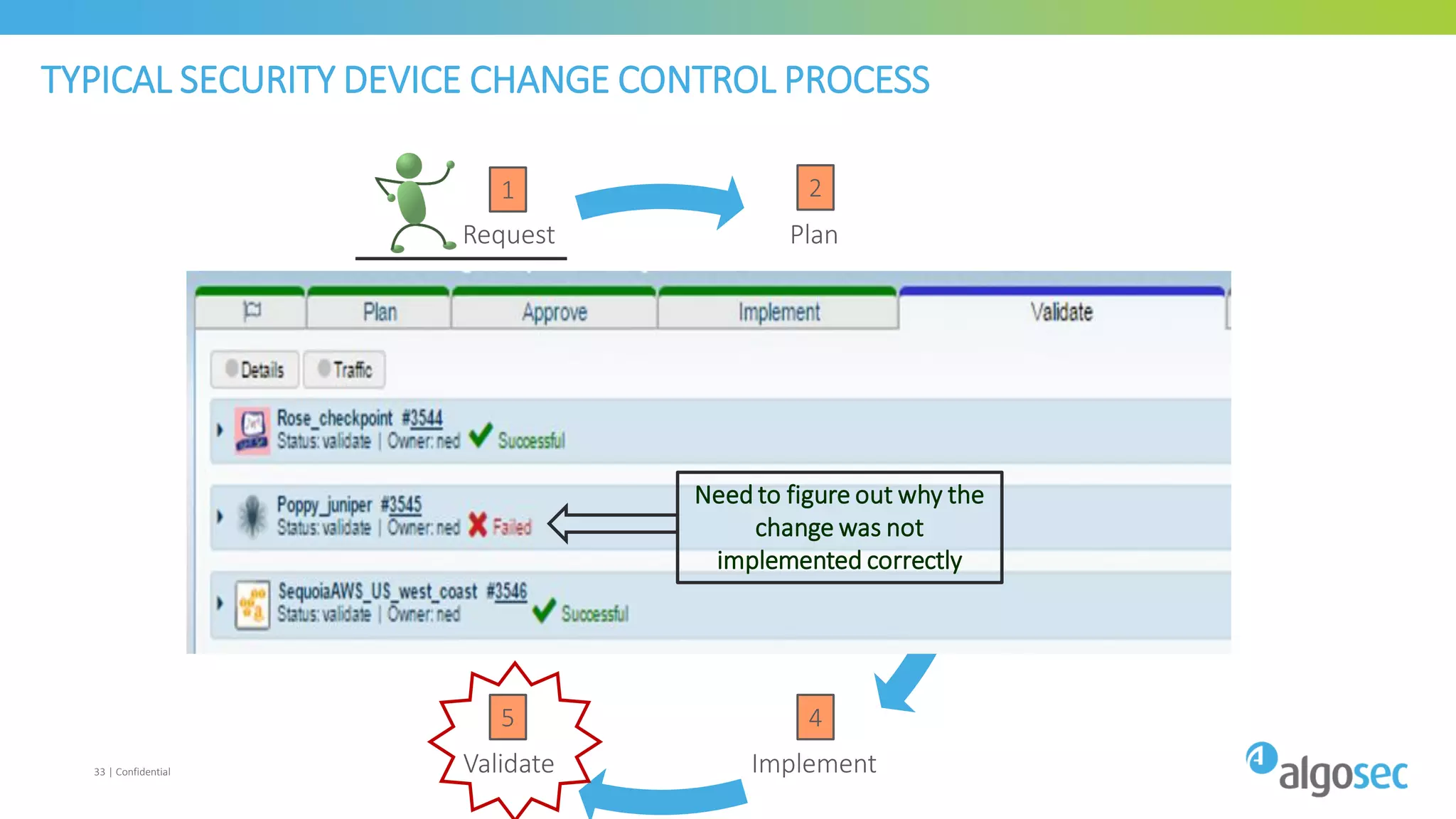
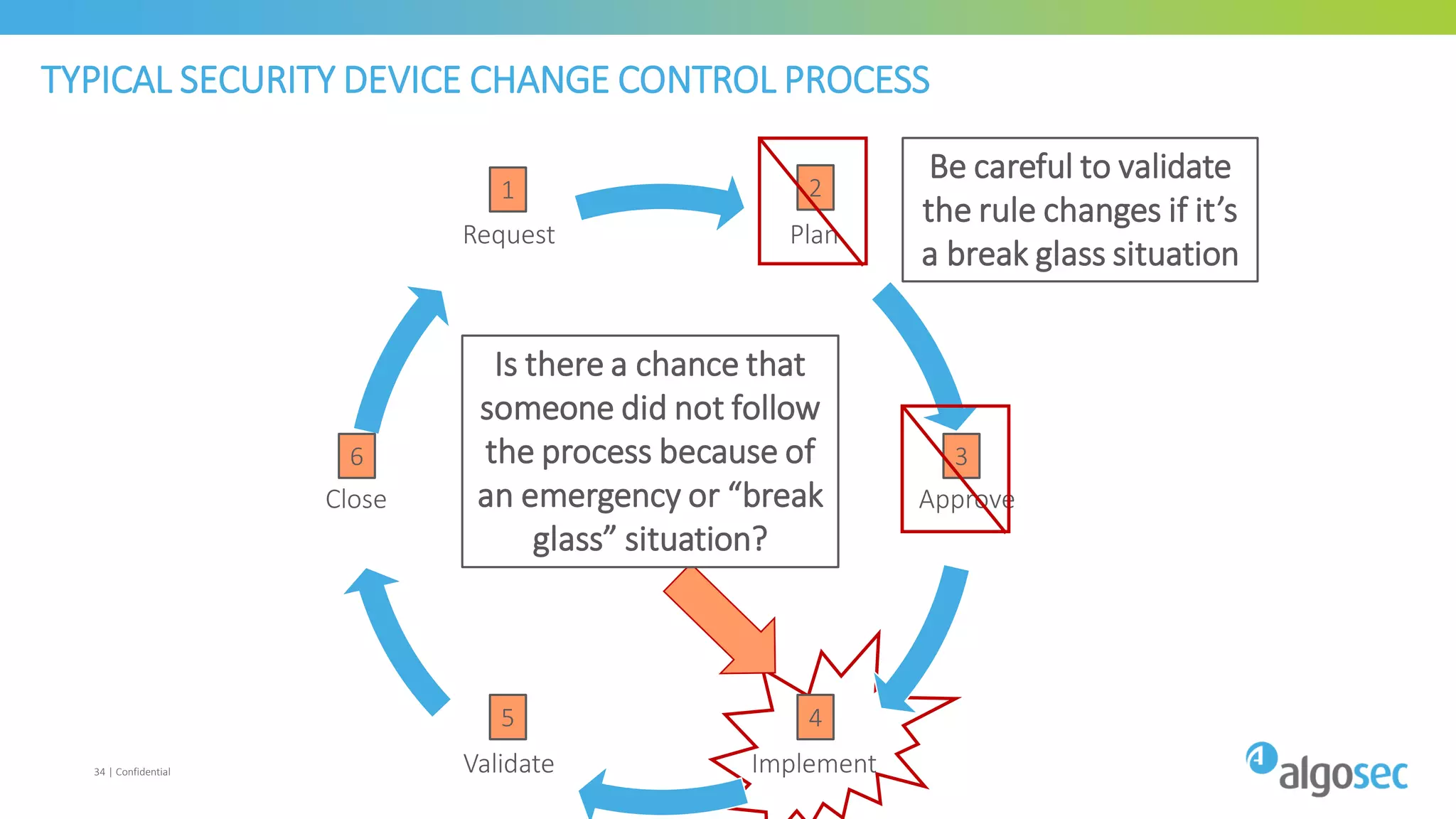
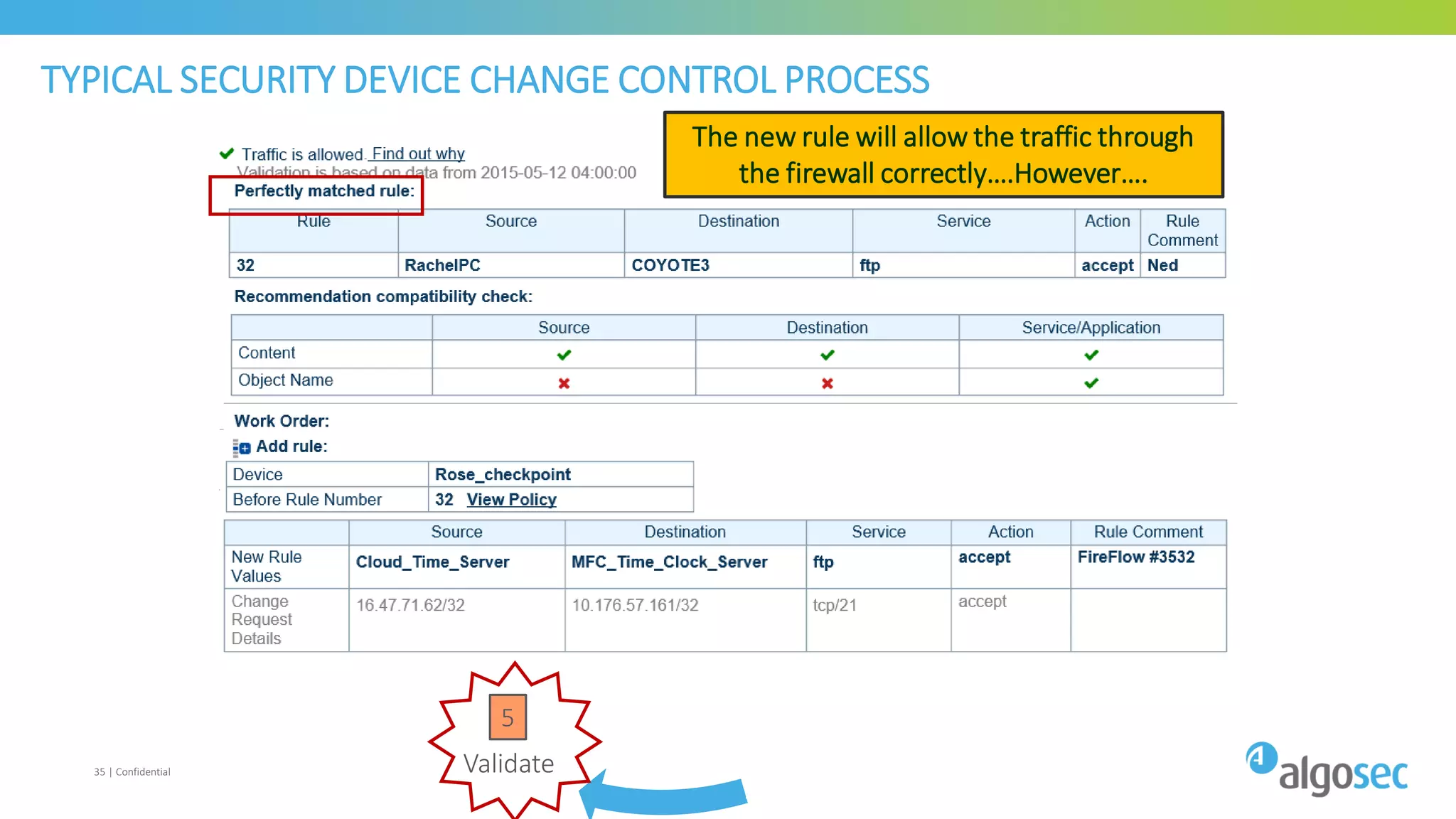
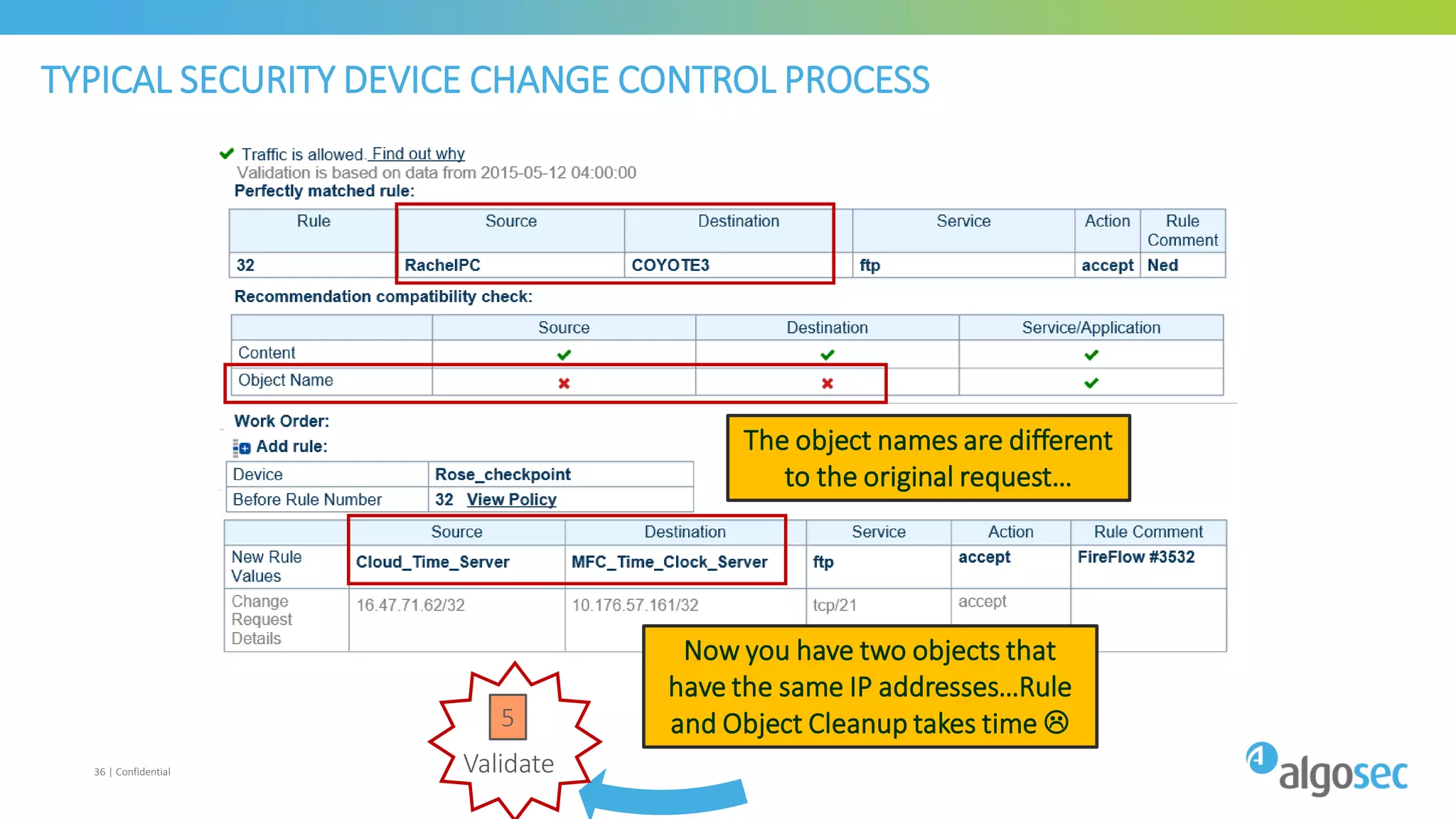
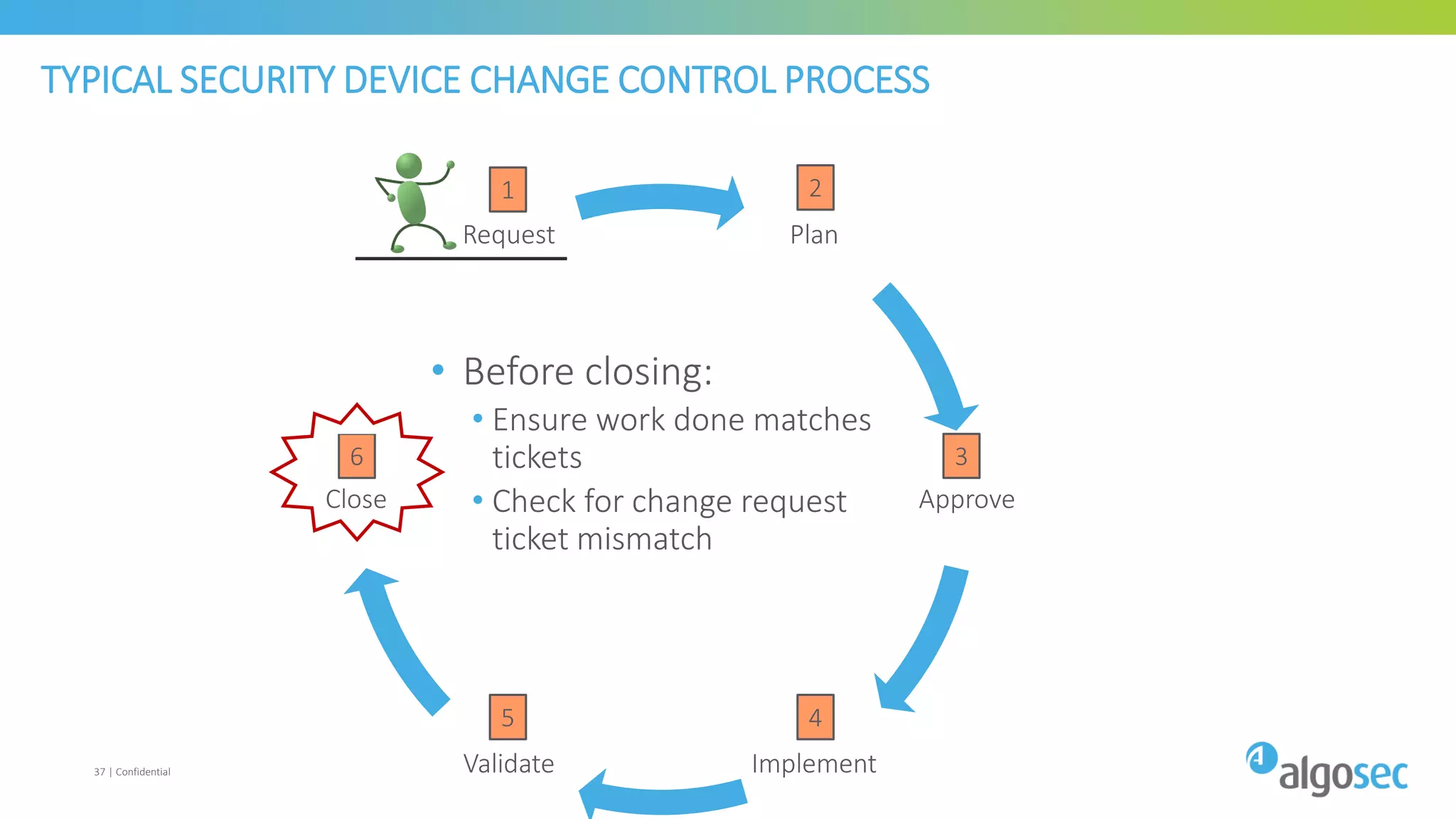
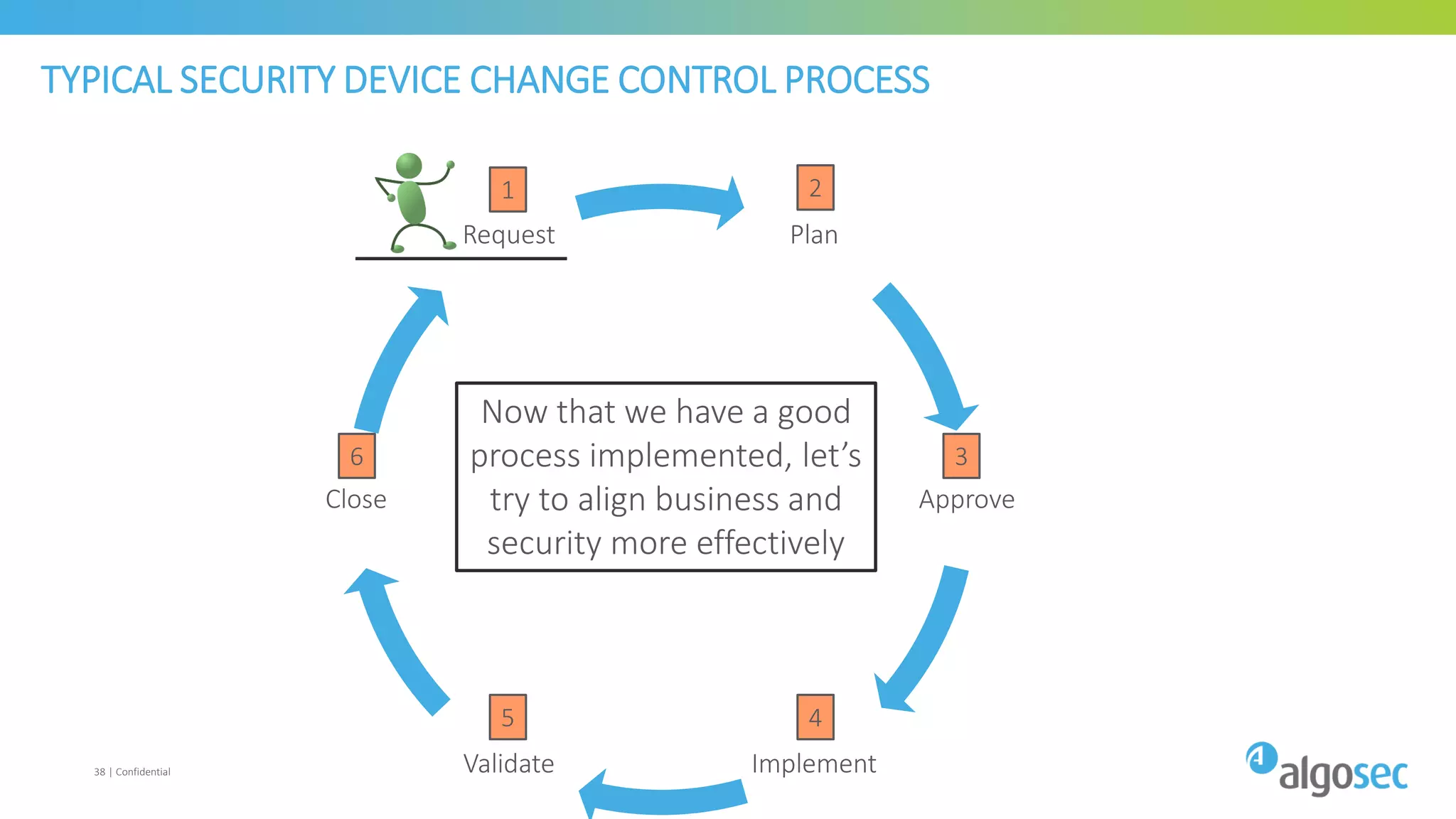
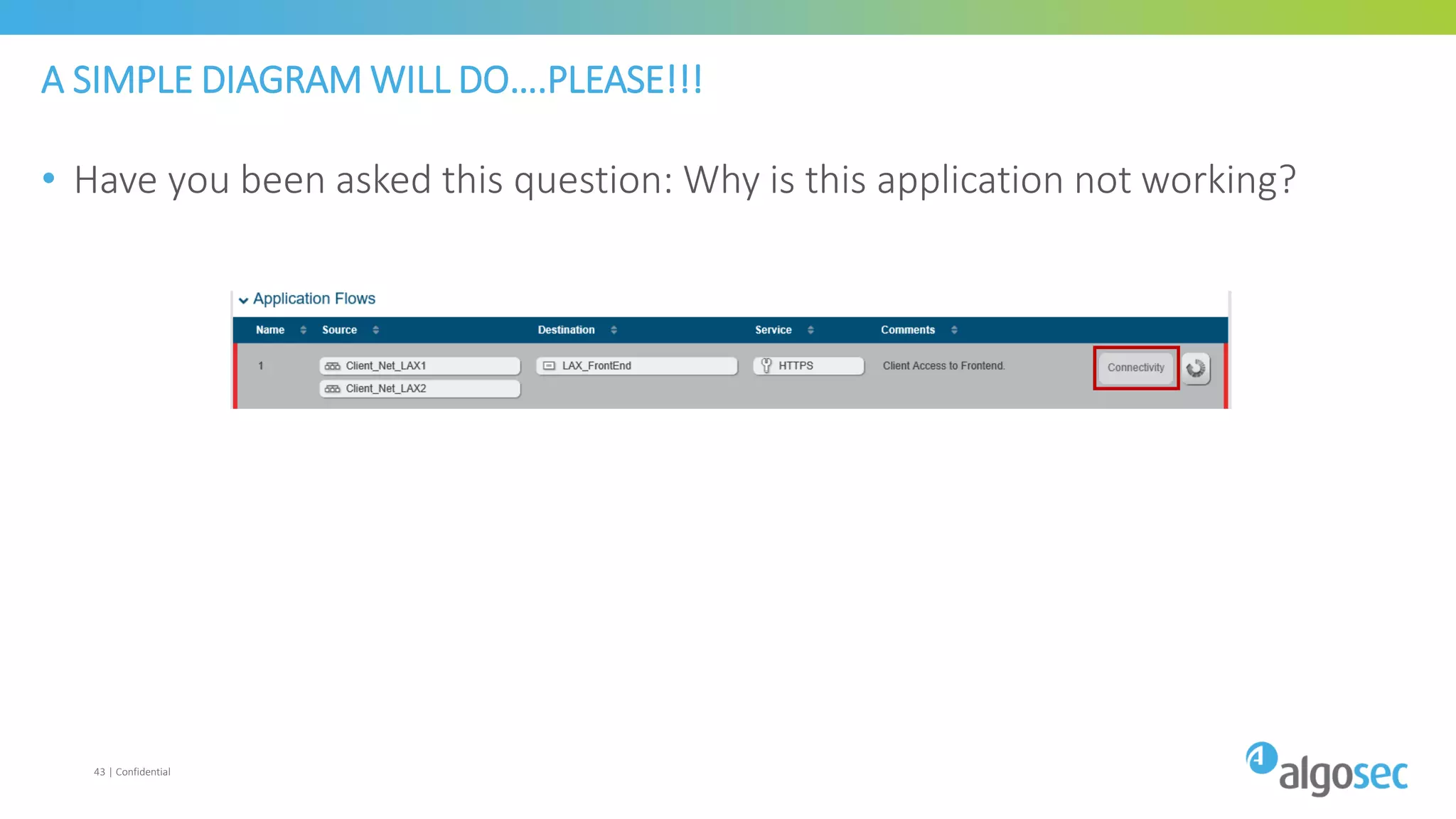
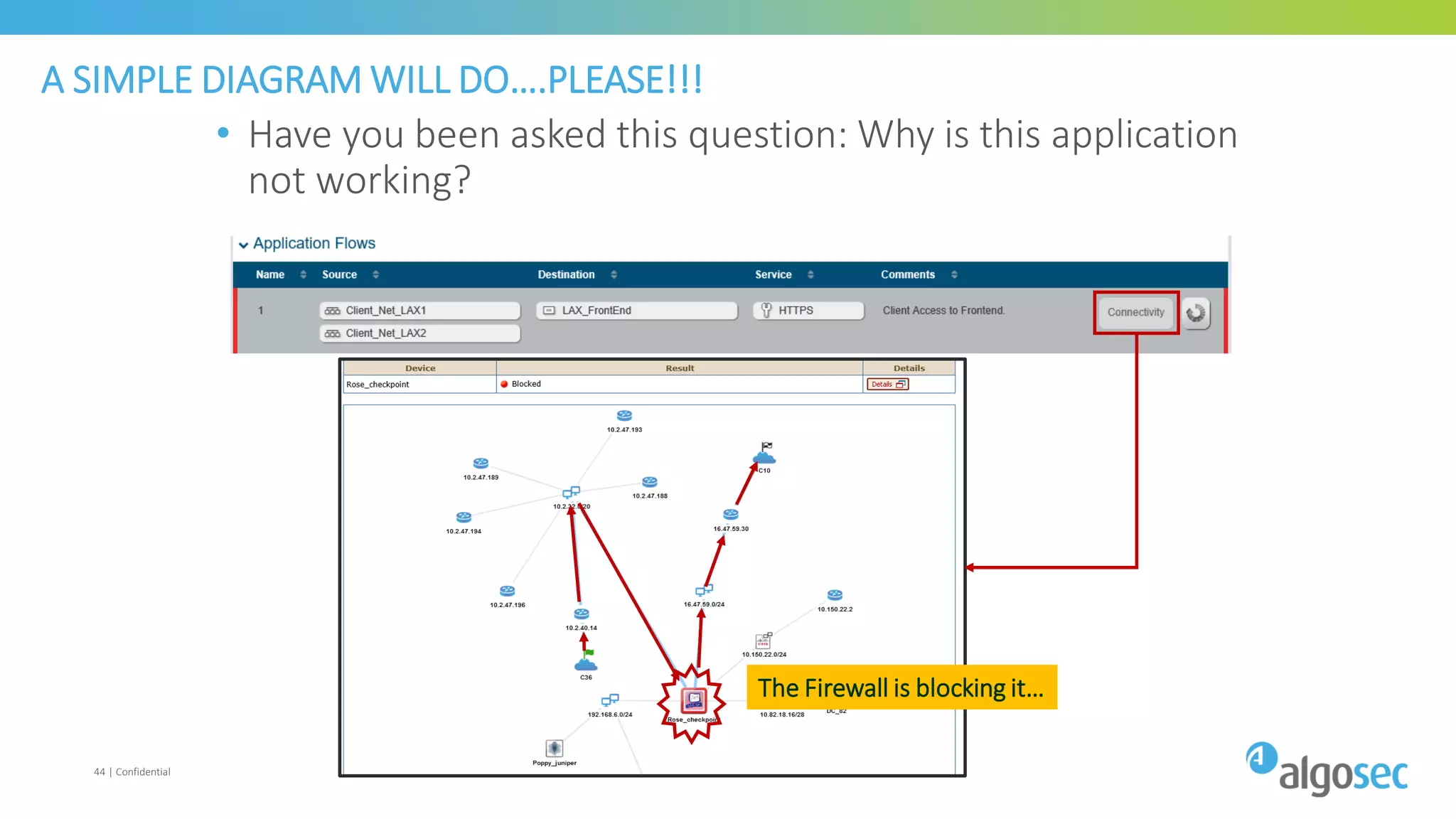
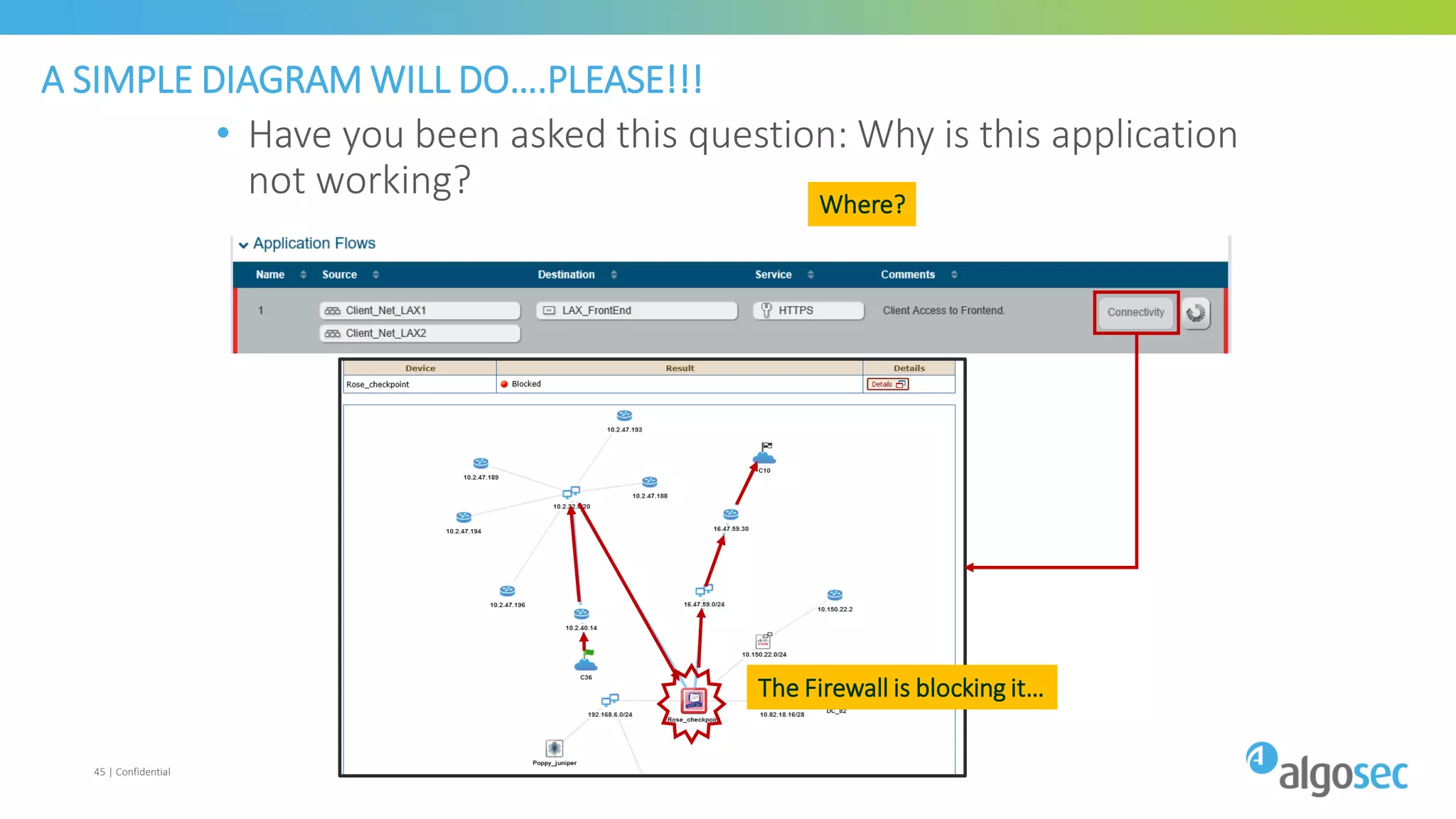
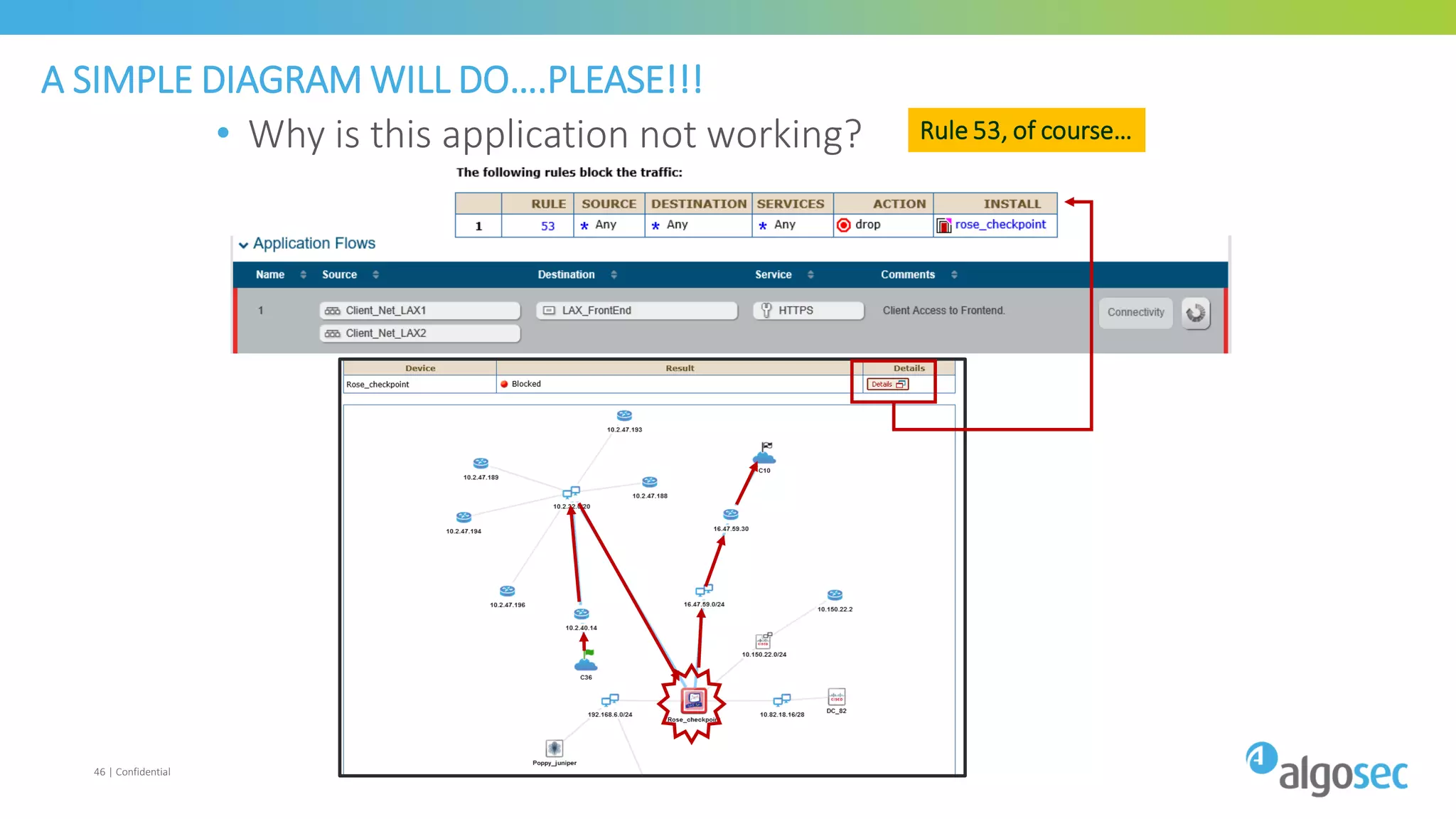
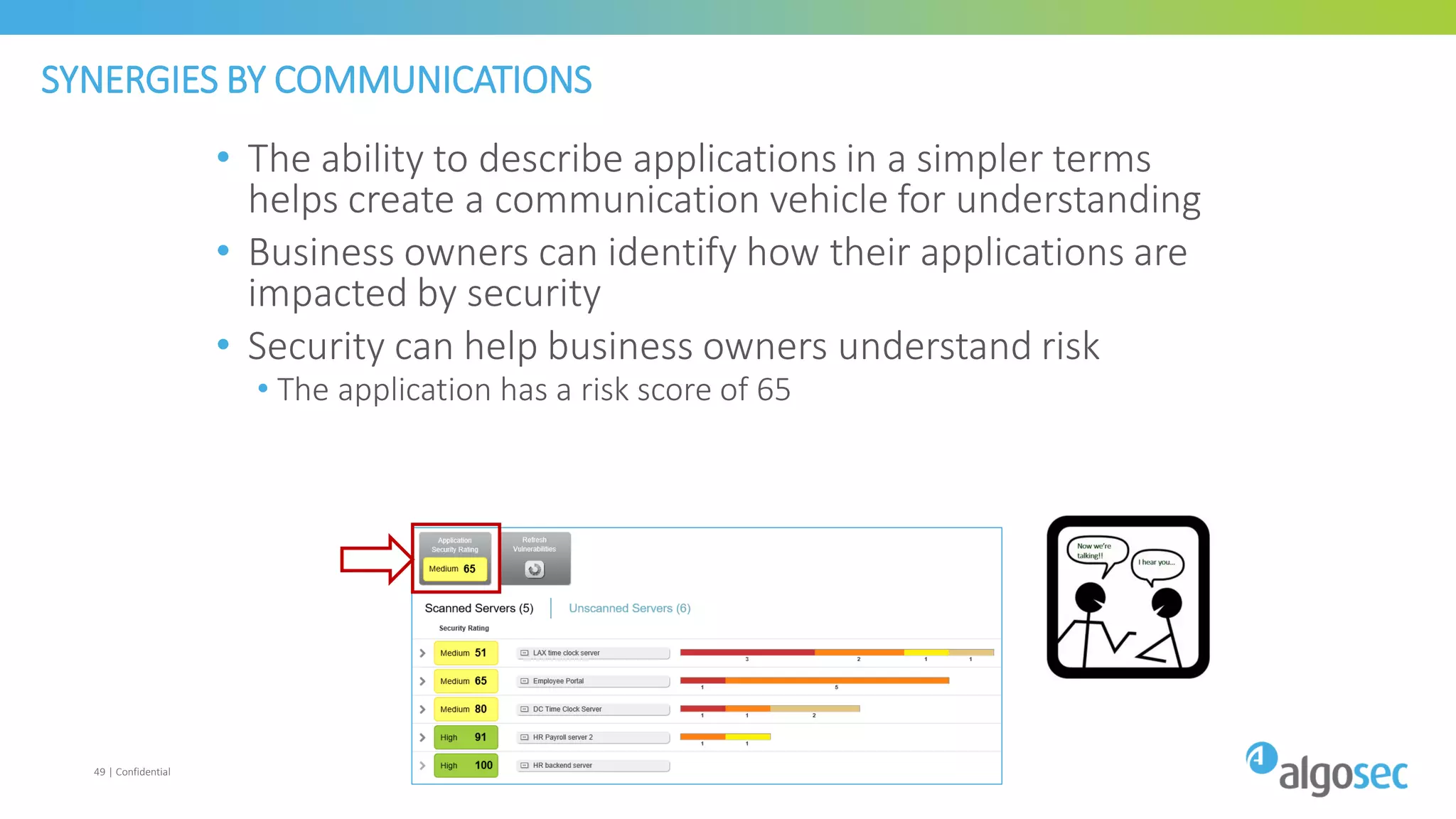
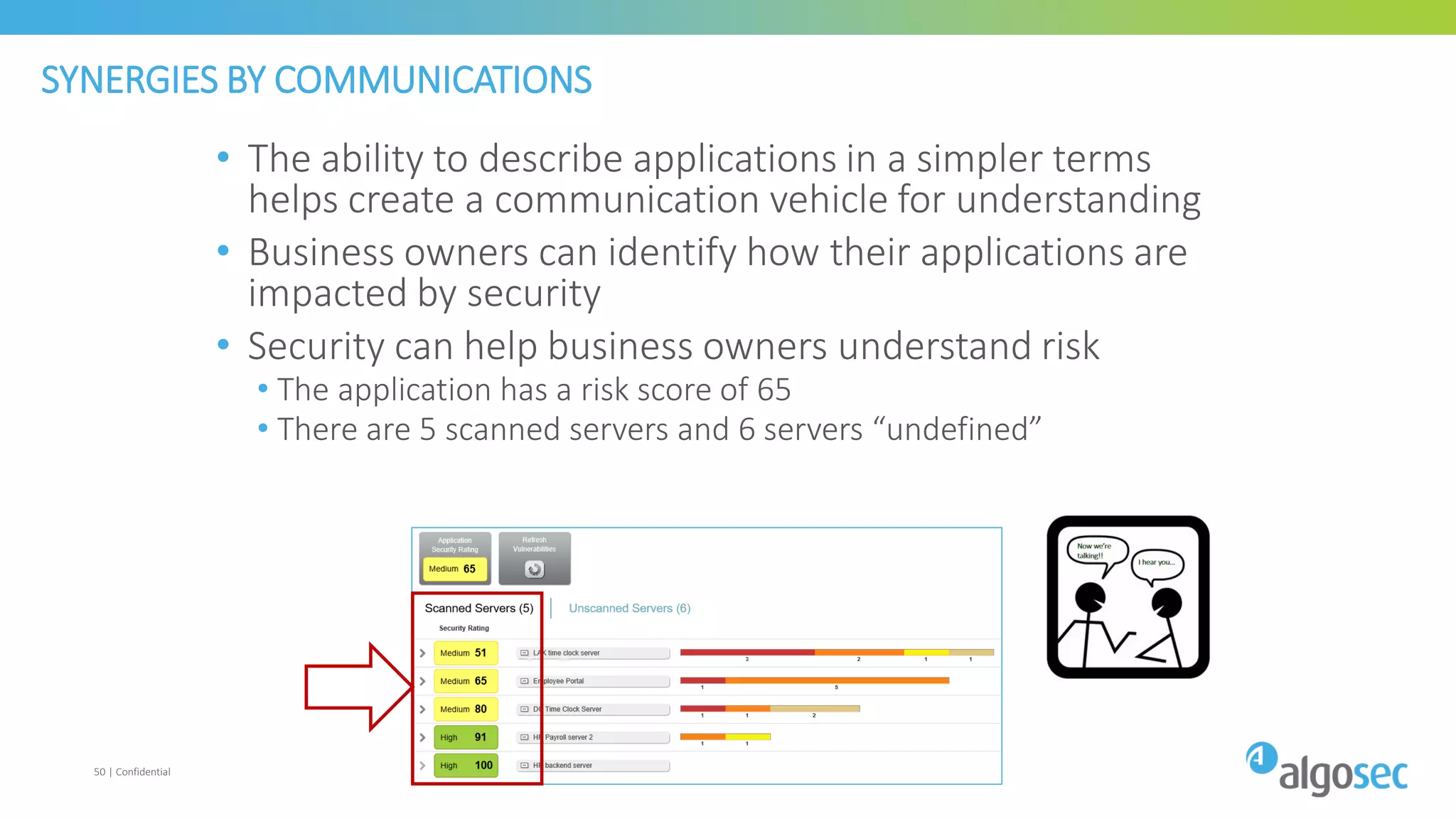
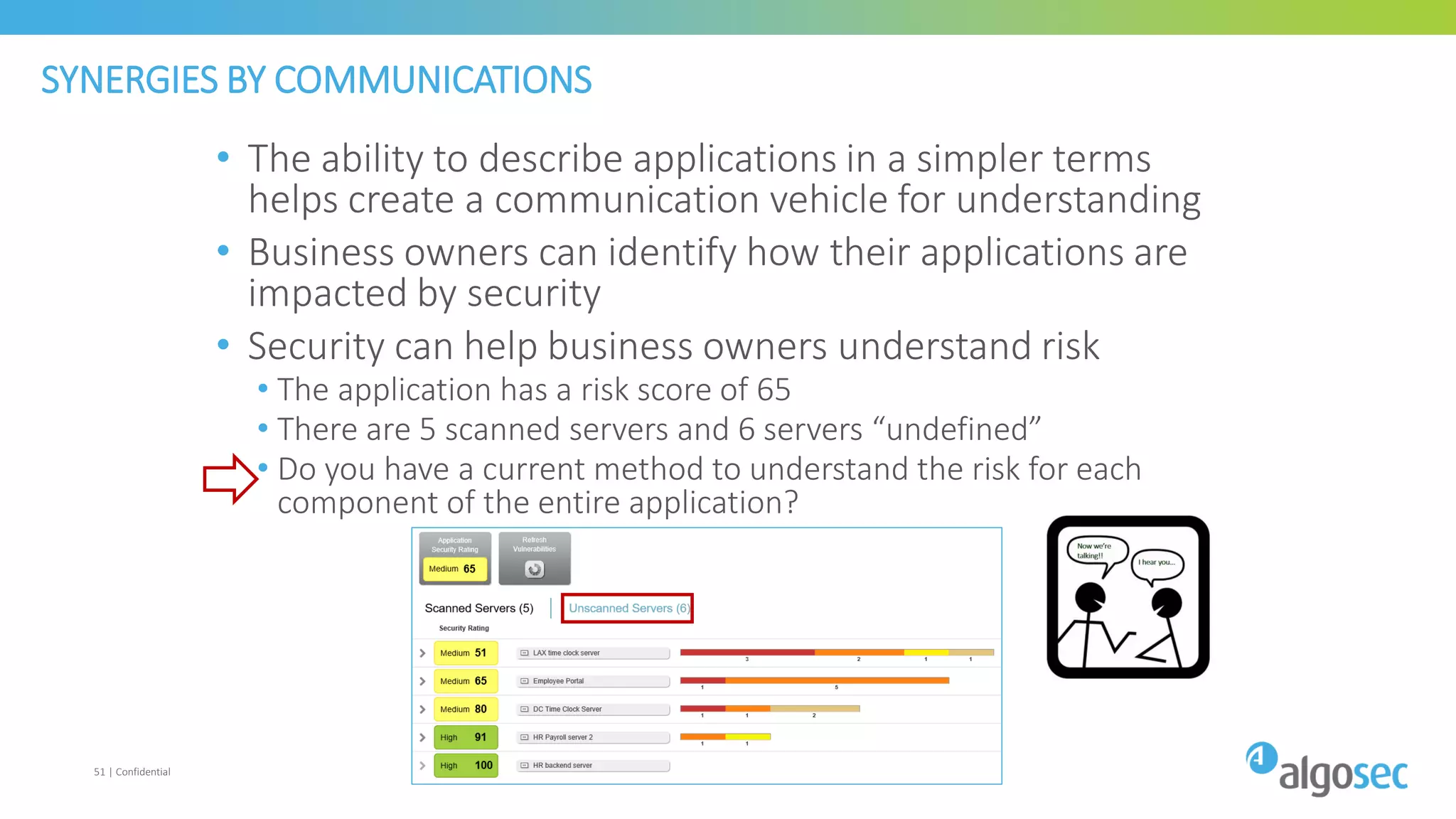
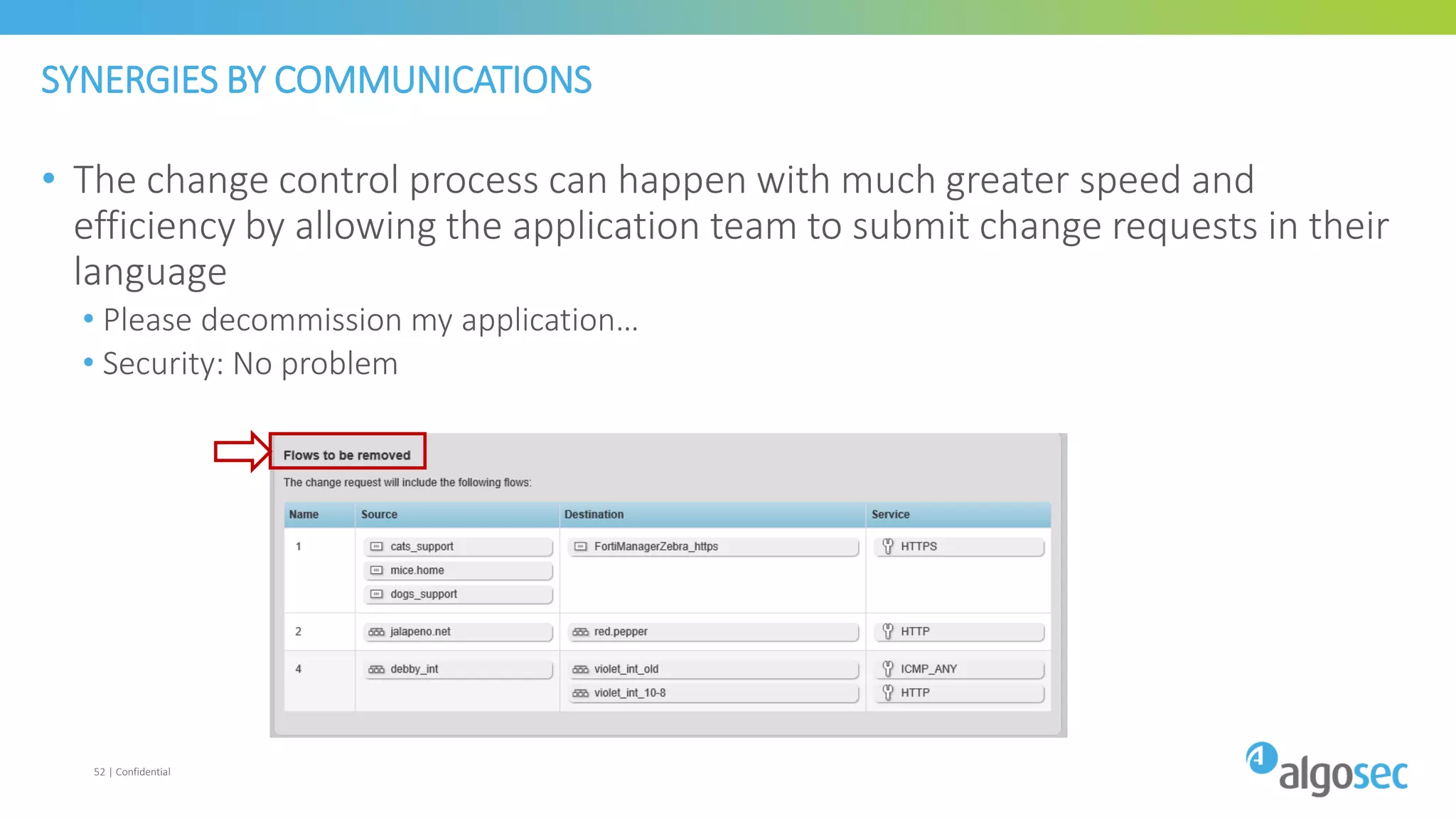
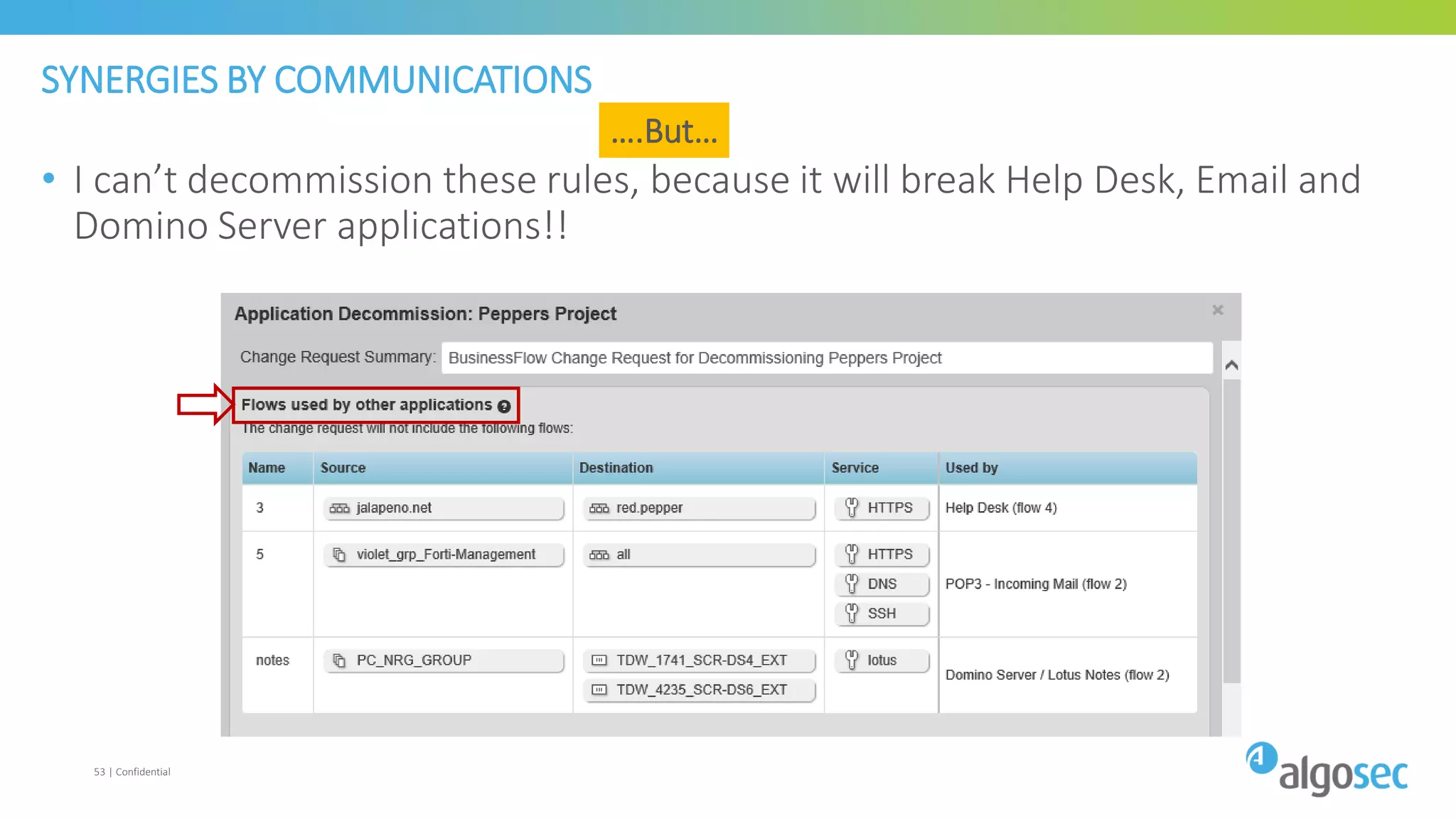
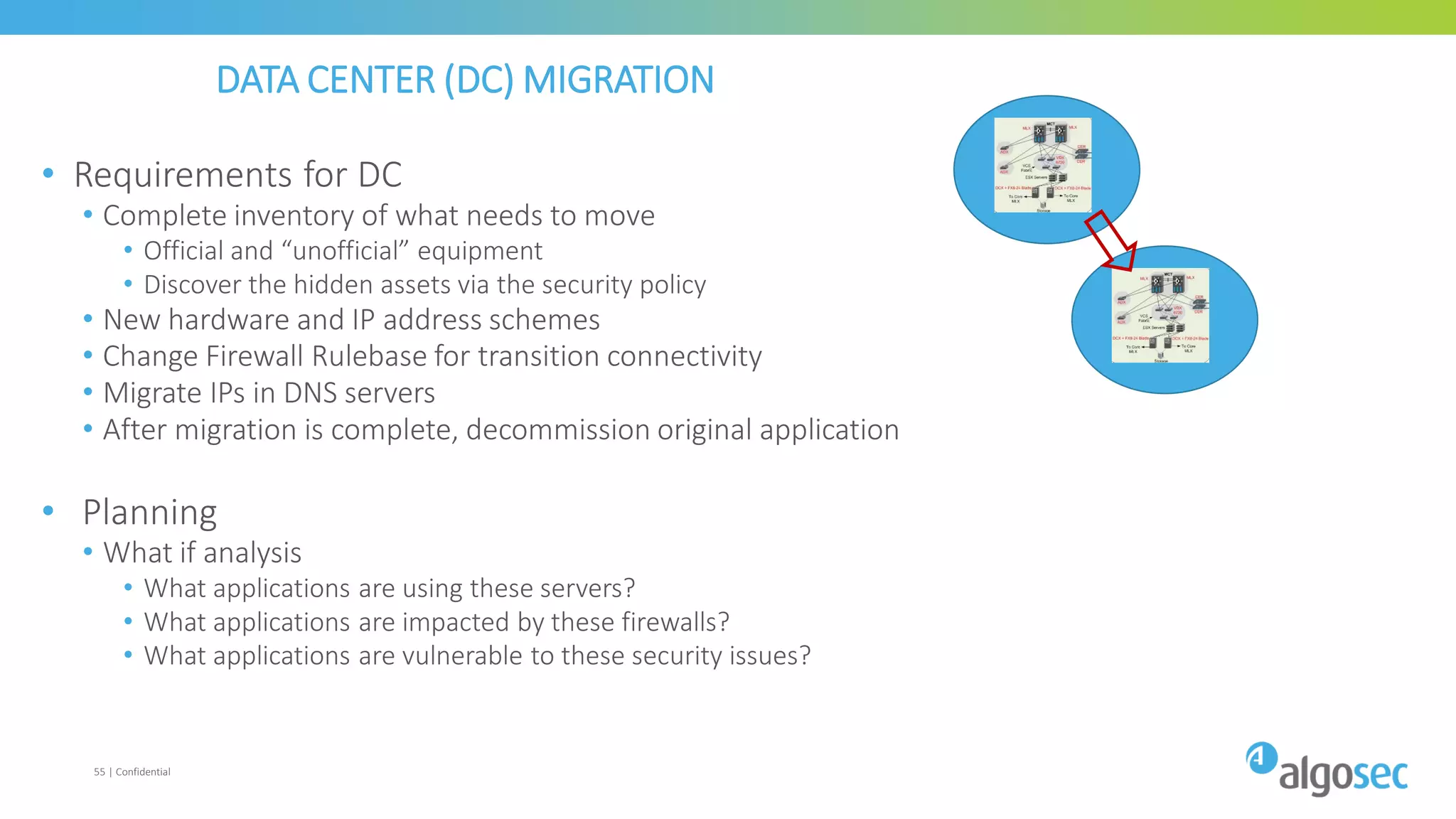
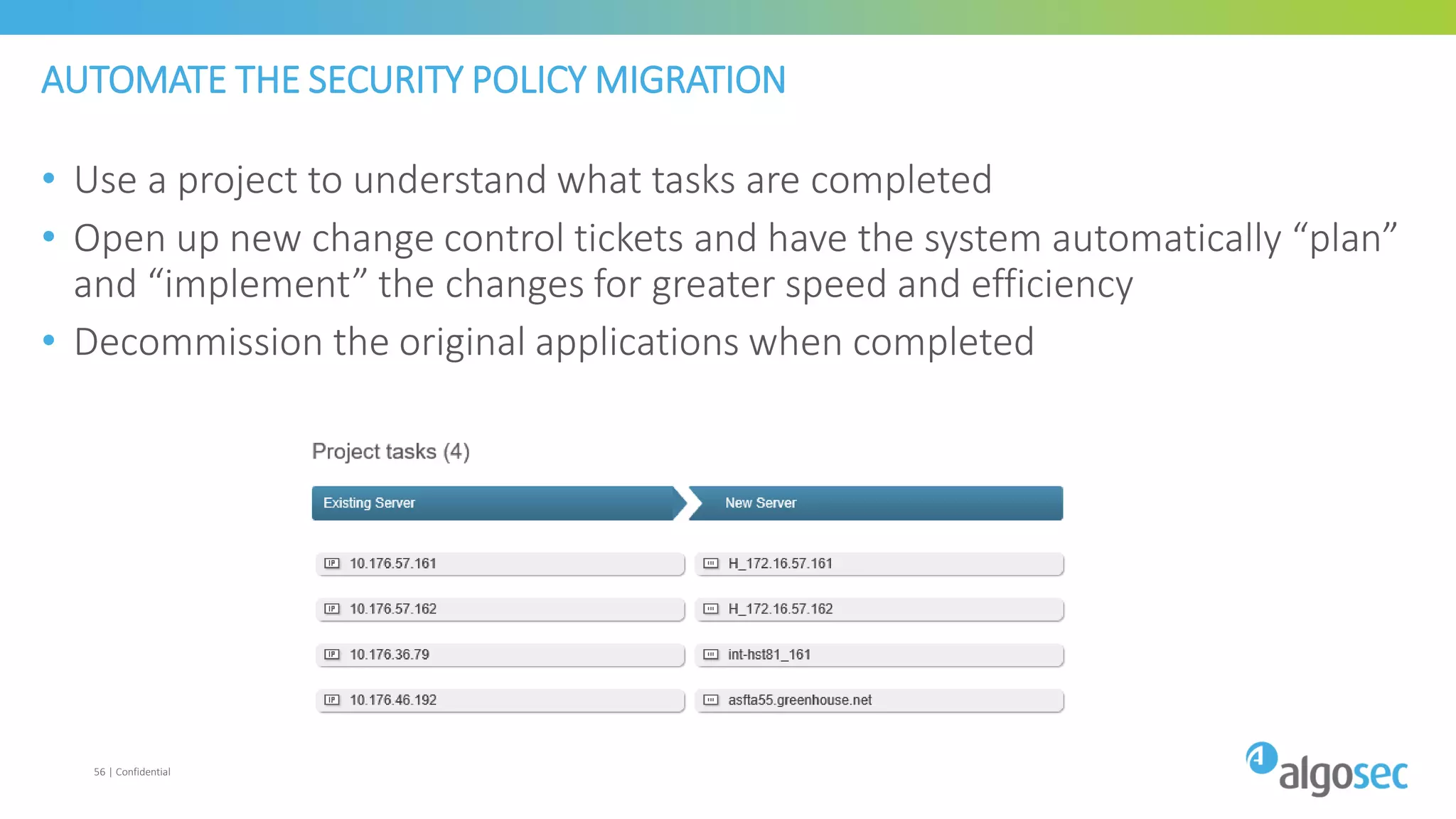
The document discusses how network devices can be misconfigured, leading to security issues and business outages. It provides examples of misconfigured firewall rules that incorrectly allow access between servers. Proper change management processes are needed to prevent misconfigurations during network changes. The document emphasizes that even small errors in configurations, like using the wrong subnet mask, can expose many devices. Close review of access control lists is required to find misconfigurations when issues occur, as even long lists may contain small errors allowing unintended access.