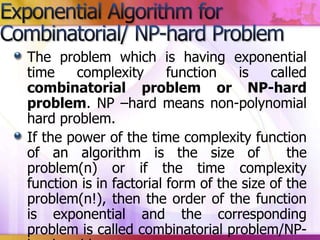
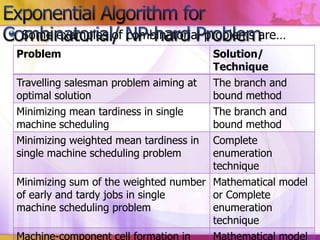
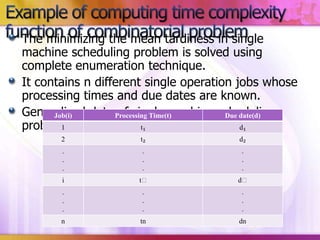
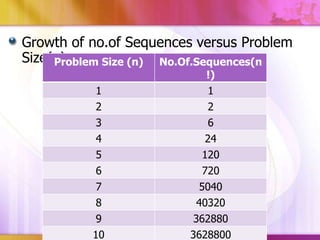
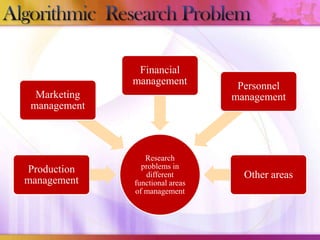
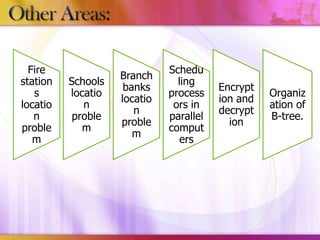
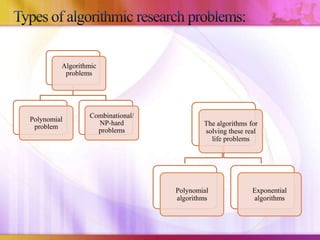
This document discusses algorithmic research problems and different types of algorithms used to solve them. It begins by defining an algorithm and providing examples of common algorithm types like search, sorting, shortest path, and more. It then covers different types of algorithmic problems like polynomial problems, which can be solved in polynomial time by polynomial algorithms, and NP-hard or combinatorial problems, which typically require exponential algorithms. Several examples are given of problems that fall into each category. The document also discusses how problem complexity is analyzed and how it relates to the algorithm types.















![Step 1: Set k=0
Step 2: From the initial distance matrix [D⁰]
and the initial precedence matrix[P⁰] from
the distance network
Step 3: Set k = k+1
Step 4: Obtain the values of the distance
matrix, [ ] for all the cells, where i is not
equal to j using the following formula:
Step 5: Obtain the values of the precedence](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmresearch-131118184139-phpapp02/85/Algorithmic-research-19-320.jpg)

![Critical analysis of execution of steps are
presented
The step-1 is executed only once.
The step-2 will be executed n² times to read
the distance matrix, [Dº]as well as the
precedence matrix[Pº]
Step-3 is repeated for one more time
In each of the step-4 and the step-5,
calculations for n² cells in the distance matrix,
as well as in the precedence matrix,
are
done for n times.
The step-6 is repeated for n times.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmresearch-131118184139-phpapp02/85/Algorithmic-research-21-320.jpg)

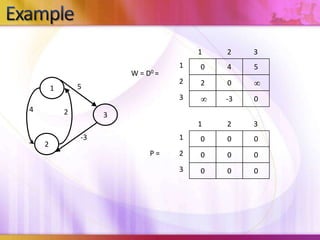
![1
4
2
1
D1 =
D0 =
5
2
-3
2
3
5
1
0
4
2
3
2
0
3
2
3
1
0
4
5
2
2
0
7
-3
-3
0
D1[2,3] = min( D0[2,3], D0[2,1]+D0[1,3] )
= min ( , 7)
=7
0
3
1
2
3
1
P=
1
0
0
0
2
0
0
1
3
0
0
0
D1[3,2] = min( D0[3,2], D0[3,1]+D0[1,2] )
= min (-3, )
= -3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmresearch-131118184139-phpapp02/85/Algorithmic-research-24-320.jpg)
![1
1
4
2
D1 =
5
2
-3
0
4
5
2
2
0
7
-3
0
3
2
3
1
0
4
5
2
2
0
7
3
-1
-3
2
D2[1,3] = min( D1[1,3], D1[1,2]+D1[2,3] )
= min (5, 4+7)
=5
0
1
3
1
P=
3
1
3
1
D2 =
2
0
0
0
2
0
0
1
3
2
0
0
D2[3,1] = min( D1[3,1], D1[3,2]+D1[2,1] )
= min ( , -3+2)
= -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmresearch-131118184139-phpapp02/85/Algorithmic-research-25-320.jpg)