This document presents an algorithm for finding restricted shortest paths in a graph.
1. The algorithm uses breadth-first search to find paths from a source node to a target node that satisfy restrictions on path length and cost. It prunes paths that do not meet the restrictions to reduce the search space.
2. It uses adjacency lists and a shortest path tree data structure to store graph information and explored paths. A queue holds paths to explore at each level of the search.
3. The algorithm initializes data structures and the starting node, then iterates exploring neighbors of the current path until it finds a path from source to target within the restrictions or exhausts all such paths.




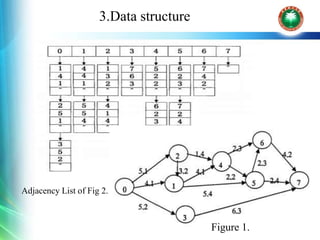
![3.Data structure
Adjacency List
typedef struct QNode{
int q; //the next node
int length; //the length from n to q
int cost; //the cost from n to q
struct Node * link; //points to another node which the node n can go to
}Node;
Node *hg [n];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmandcomplexity-191102182542/85/Algorithm-and-complexity-6-320.jpg)
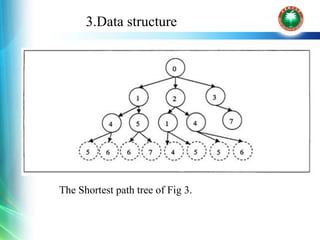
![ Shortest Tath Tree
typedef struct Anode {
int data; //the last node in current path
int length; //length of current path
int cost; //cost of current path
int distance; // nodes in current path
struct ANode * Parent; //point to the previous node
}ANode;
Anode* a[];
A Queue to store path to the current node
3.Data structure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmandcomplexity-191102182542/85/Algorithm-and-complexity-8-320.jpg)
![4.Algorithm process
Initialization
Given K as Nodes limitation, L as Cost limitation
int u = ∞ // u is a positive value that is much larger than the possible path length
int flag = 0 //flag notes whether we find a path satisfied the Restriction
Anode *a[]
The Source node s(s->data = 0, s->distance = 1)
Queue.push(s);
Target node n;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmandcomplexity-191102182542/85/Algorithm-and-complexity-10-320.jpg)
![1. While:
2. if Queue.head->distance < K(4): // judge the nodes of current path
3. p = Queue.pop()
4. if p->cost < L(8): // judge the sum of cost of current path
5. if p->data == n: //judge is a path from source to target
6. if p->length < u: u = p->length, flag = 1
7. add p into the Array A
8. else: i = p->data
9. for q in hg[i]:
10. add value from q to p as new path
11. add new path in to Queue
12. else:
13. continue
14. else:
15. break
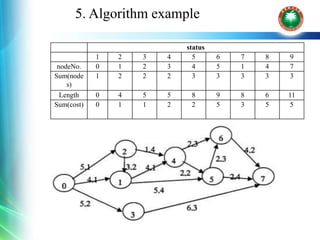
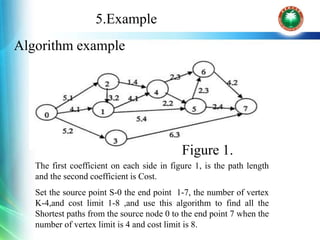
4.Algorithm process
Adjacency List “q(hg)” Fig 2.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmandcomplexity-191102182542/85/Algorithm-and-complexity-11-320.jpg)