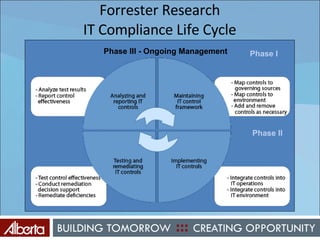
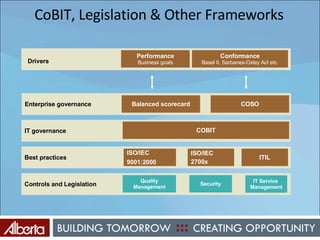
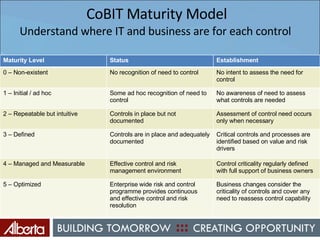
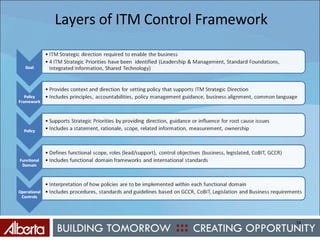
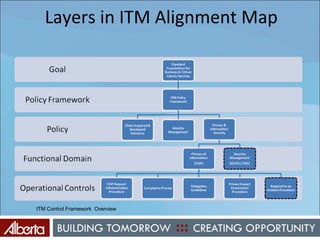
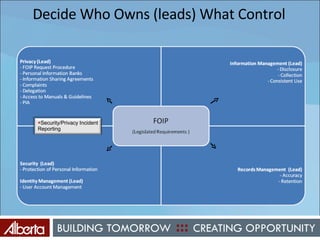
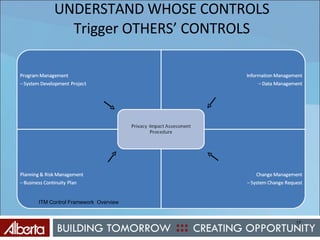
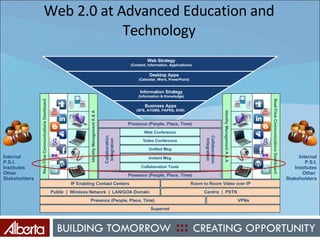
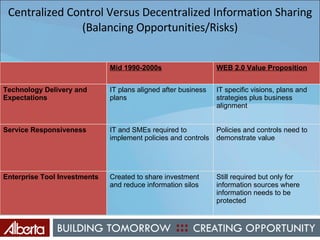
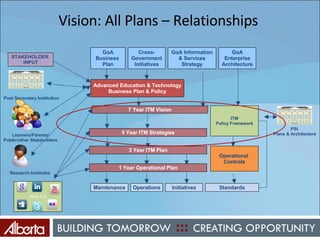
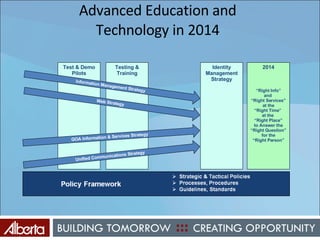
The document discusses Alberta's approach to developing an information technology management (ITM) control framework. It notes challenges with the previous policy approach and outlines plans to implement a new strategic framework aligned across government. This will include centralizing security oversight, defining policies, controls and standards, and addressing issues raised by new technologies like web 2.0 such as decentralized information sharing and changing user expectations.