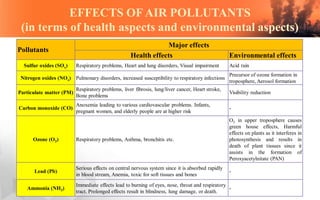
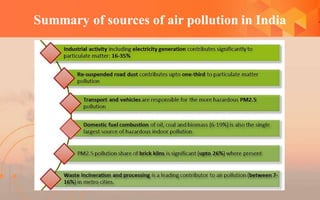
This document discusses air pollution sources and effects. It identifies four main types of air pollution sources: natural sources, stationary point sources, mobile sources, and waste disposal. Air pollutants are categorized based on their source, method of origin, chemical compound, and state of matter. Major air pollutants and their health and environmental effects are described. Methods for controlling air pollution are outlined, including using cleaner fuels and promoting public transportation. Summaries of the main sources of air pollution in India and its action plan for combating air pollution are also provided.