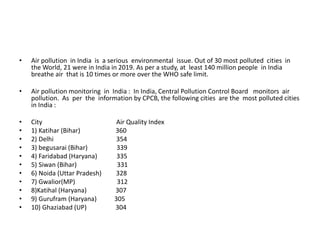
Human activities release naturally occurring hydrogen sulphide into the air, forming it during processes like coke production and waste water treatment. It has unpleasant odors and can cause neurological symptoms in workers exposed to over 30 micrograms per cubic meter. Combustion of fuels releases polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, which cause cancers. Particulate matter in air comes from various natural and industrial sources, with 100 micrograms considered the safe daily limit. Air pollution is a major issue in India, with many of the most polluted cities globally located there. Sources of pollution include dust, waste burning, vehicles, and domestic cooking. Air pollution negatively impacts health, increasing risks of respiratory and cardiac diseases. Various efforts are being made