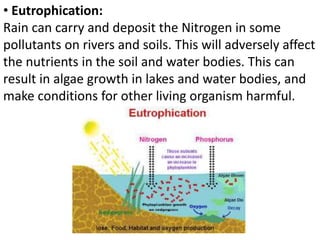
Air pollution occurs when harmful substances like gases, dust, fumes or smoke are introduced into the atmosphere. There are two types of pollutants: primary, which are directly emitted, and secondary, which form from chemical reactions between primary pollutants. Major causes of air pollution include emissions from industries, burning fossil fuels for transportation, and household/farming chemicals. Effects of air pollution include acidification, eutrophication, ground-level ozone formation, and particulate matter in the air. Control measures involve reducing emissions through planting trees, using cleaner fuels, mass transportation, and separating industrial and residential areas.