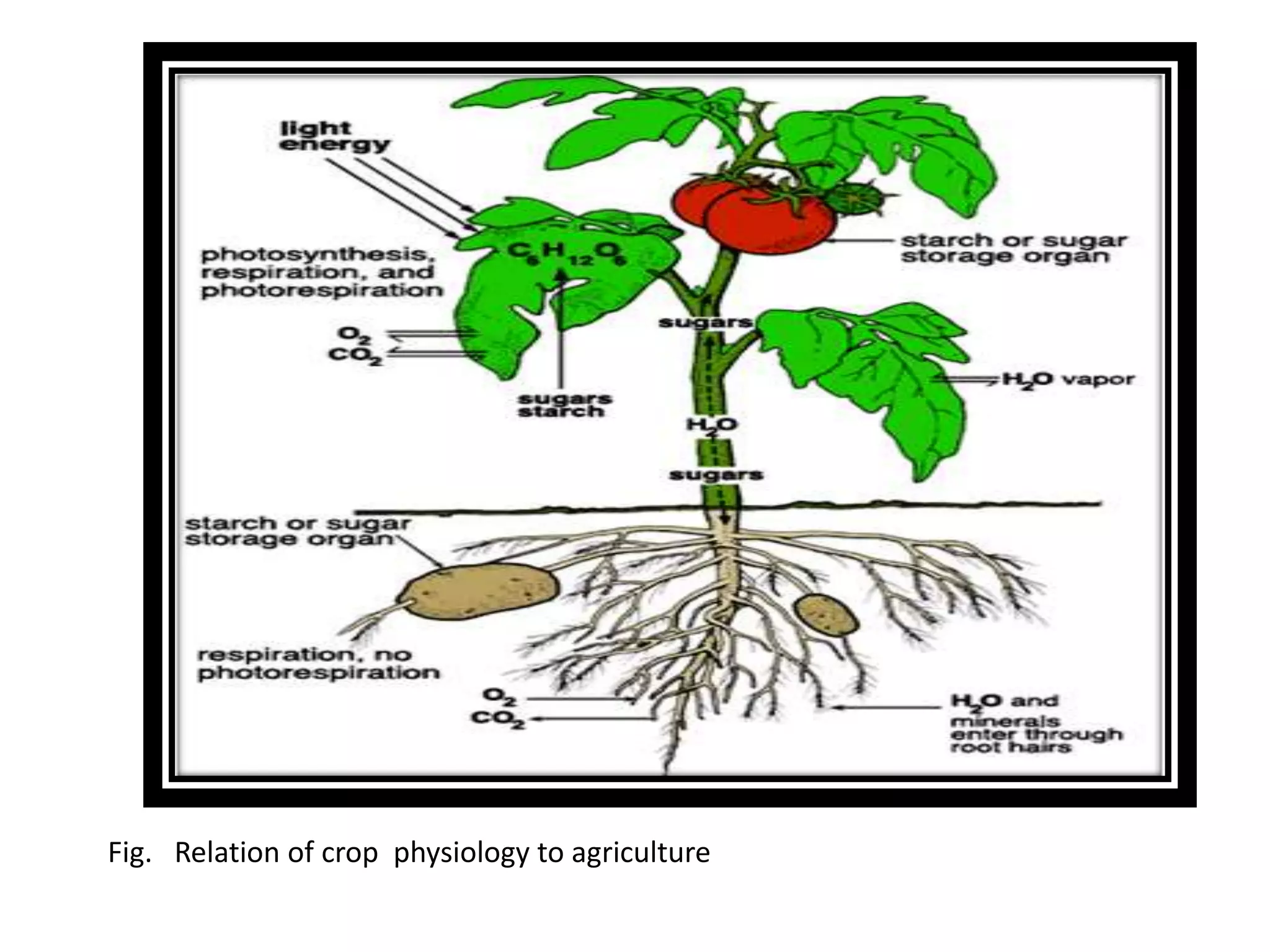
Agronomy is the science and management of crop production, including soil management and crop cultivation techniques. It draws from various disciplines like soil science, crop physiology, plant ecology, biochemistry, and economics. An agronomist studies principles of crop production and soil management in order to maximize food and fiber production while minimizing costs. They conduct research on crop varieties, cultivation methods, nutrient management, irrigation, and other techniques to improve yields. Agronomy is important for identifying suitable crops and seasons, developing efficient cultivation practices, and maintaining ecological balance on farms.