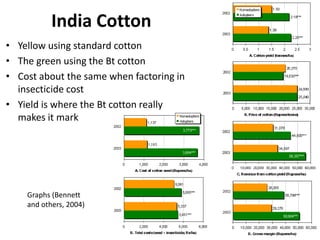
This document discusses genetically modified (GM) crops and some of the key issues surrounding their use. It begins by defining GM crops as organisms that have been genetically altered using biotechnology. It then examines several social, political, environmental, economic, and ethical issues related to GM crops. Socially, some studies have found health issues in people exposed to certain GM crops. Politically, the US does not require GM food labeling while Europe does. Environmentally, there are concerns GM crops could become weeds or invade natural habitats. Economically, a case study found Bt cotton in India increased yields while maintaining similar costs to traditional cotton. Ethically, there are debates around consumer and environmental risks versus benefits.