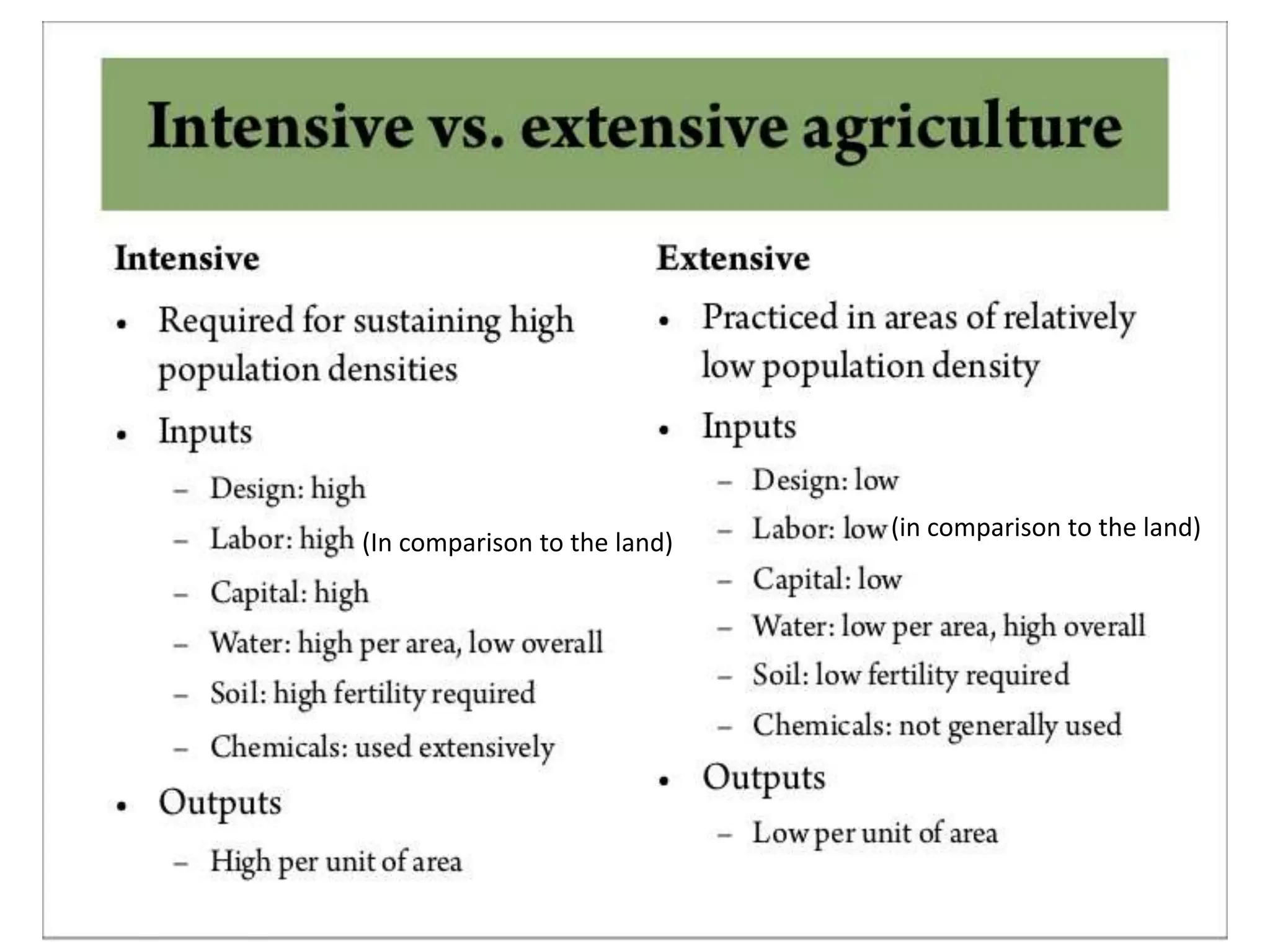
Agriculture involves cultivating crops and rearing livestock. There are two main types: subsistence agriculture, which is for personal use, and commercial agriculture, where products are sold for profit. Extensive agriculture uses large areas of land with low levels of capital, labor, machinery, and fertilizer. It relies on natural conditions and is suitable for grazing animals or crops that don't require fertile soil. Extensive agriculture is common in regions with abundant land but sparse populations, such as the grasslands of North America, Argentina, Europe, and Australia.