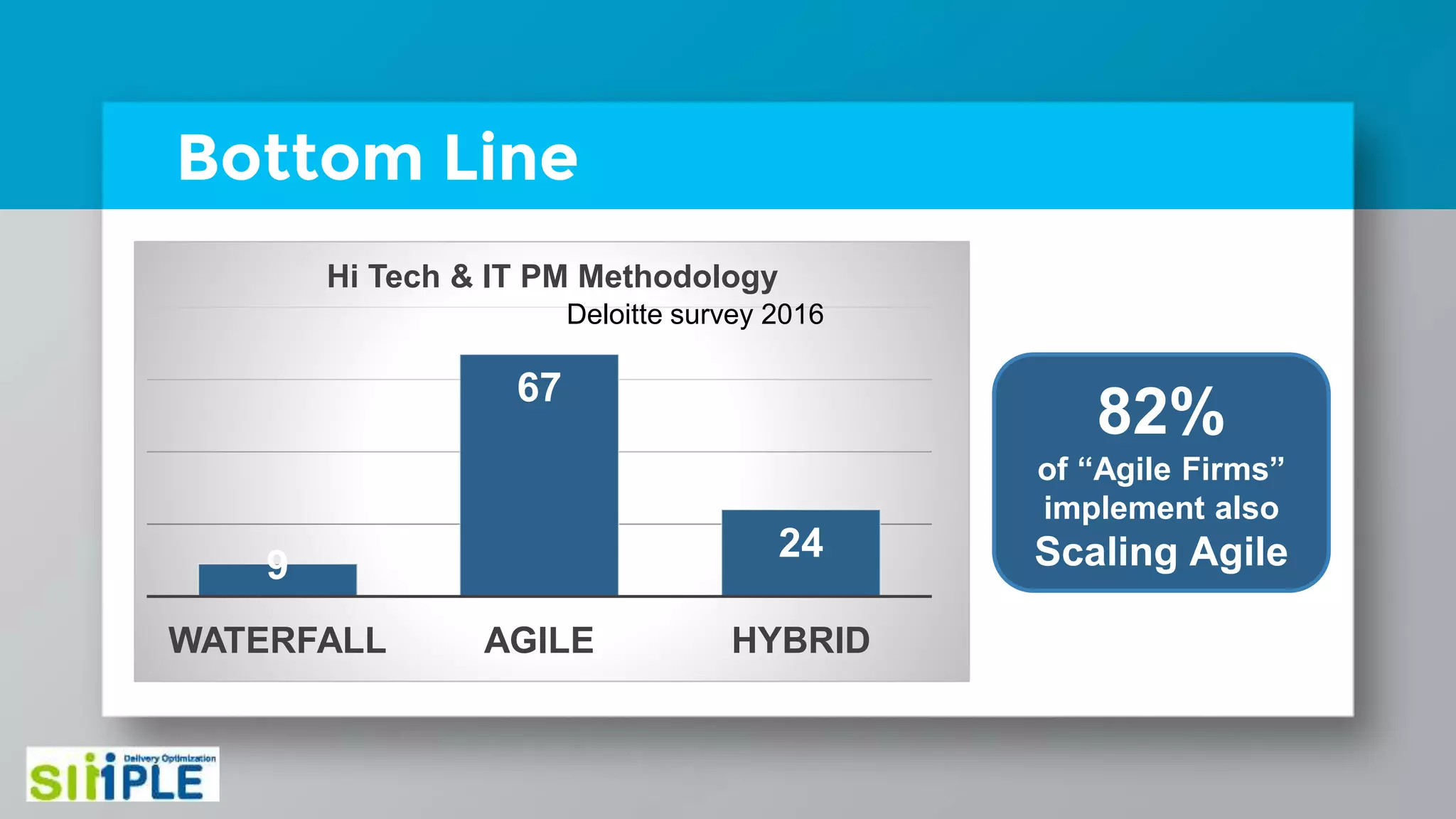
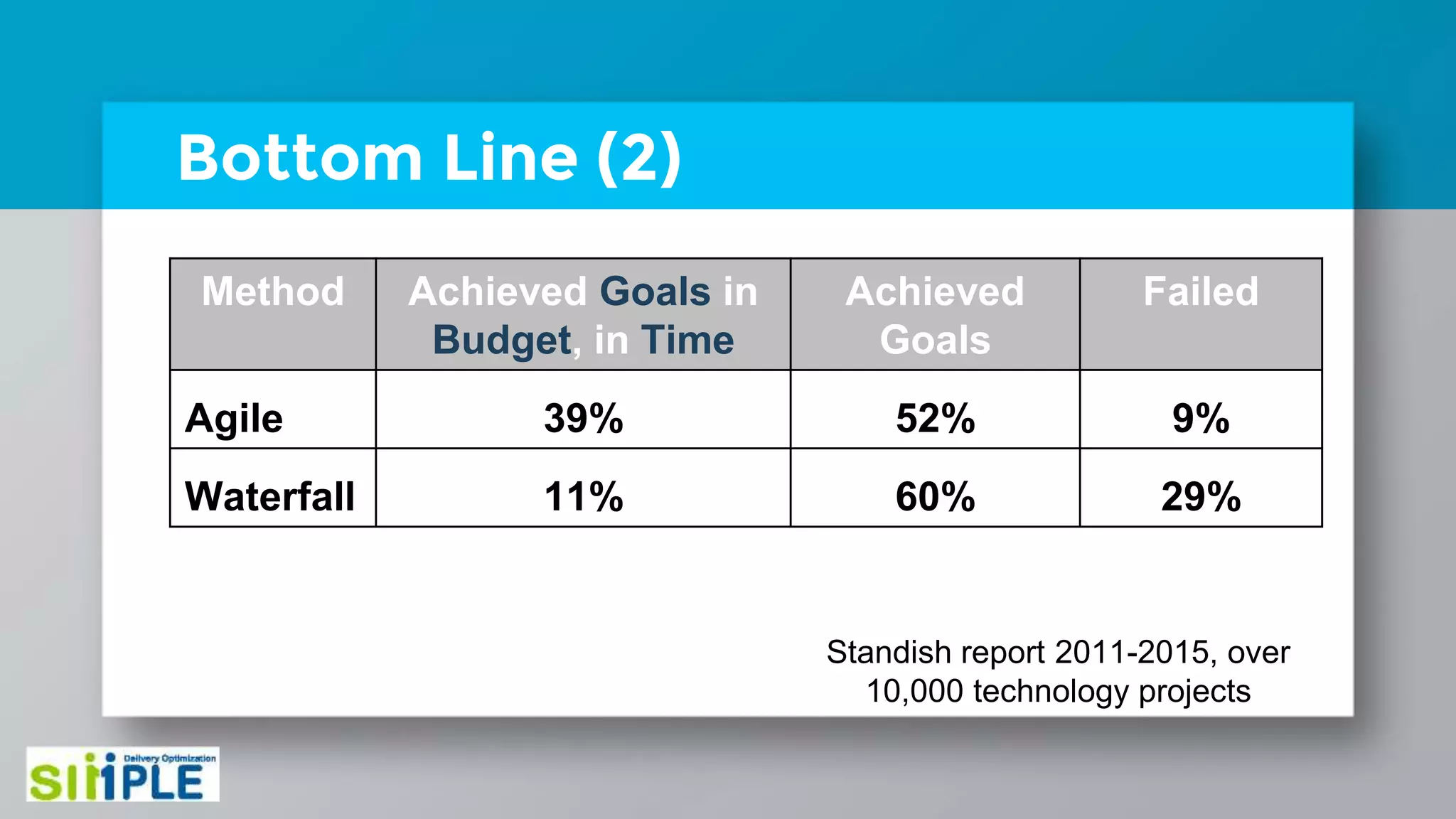
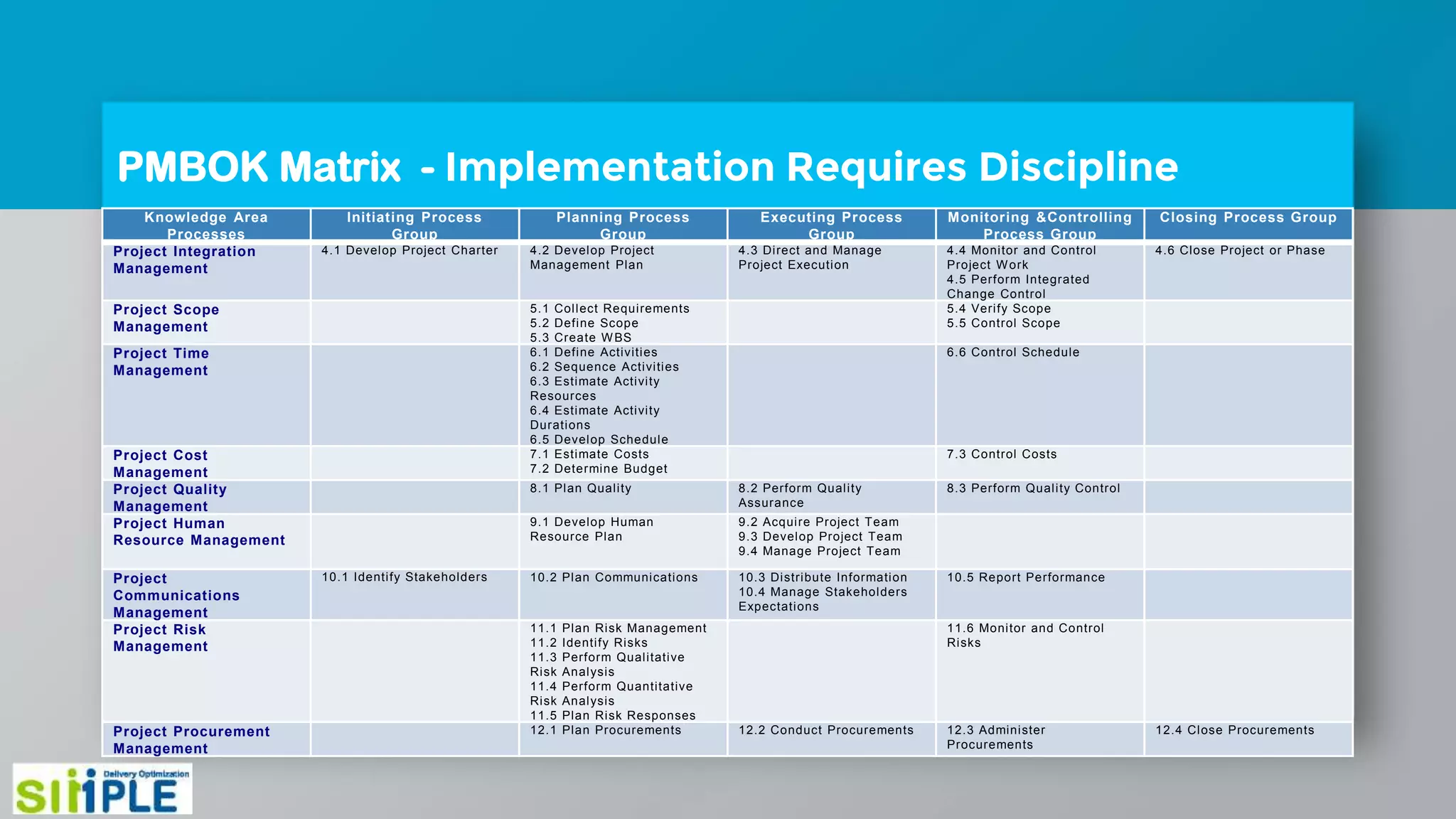
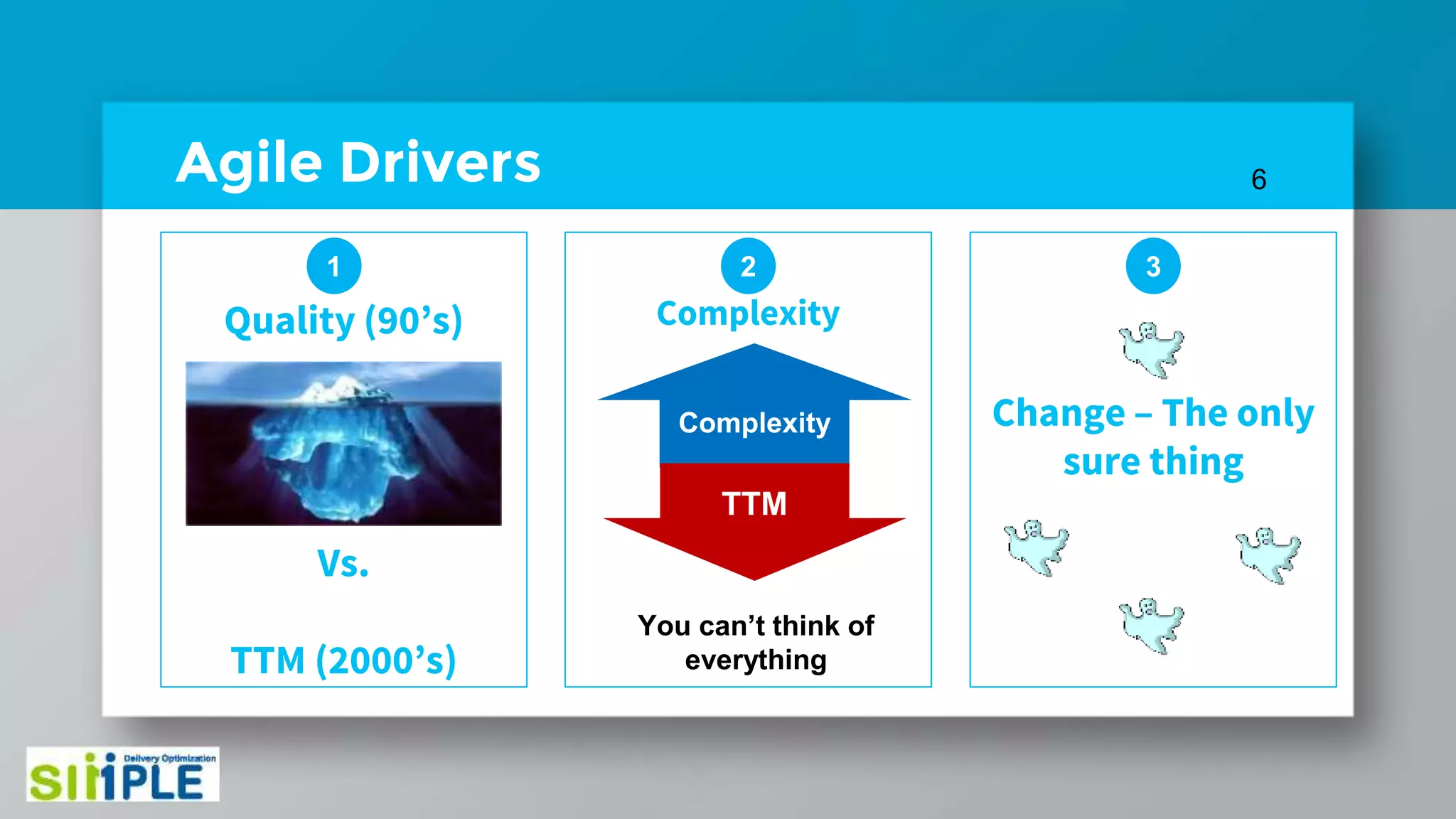
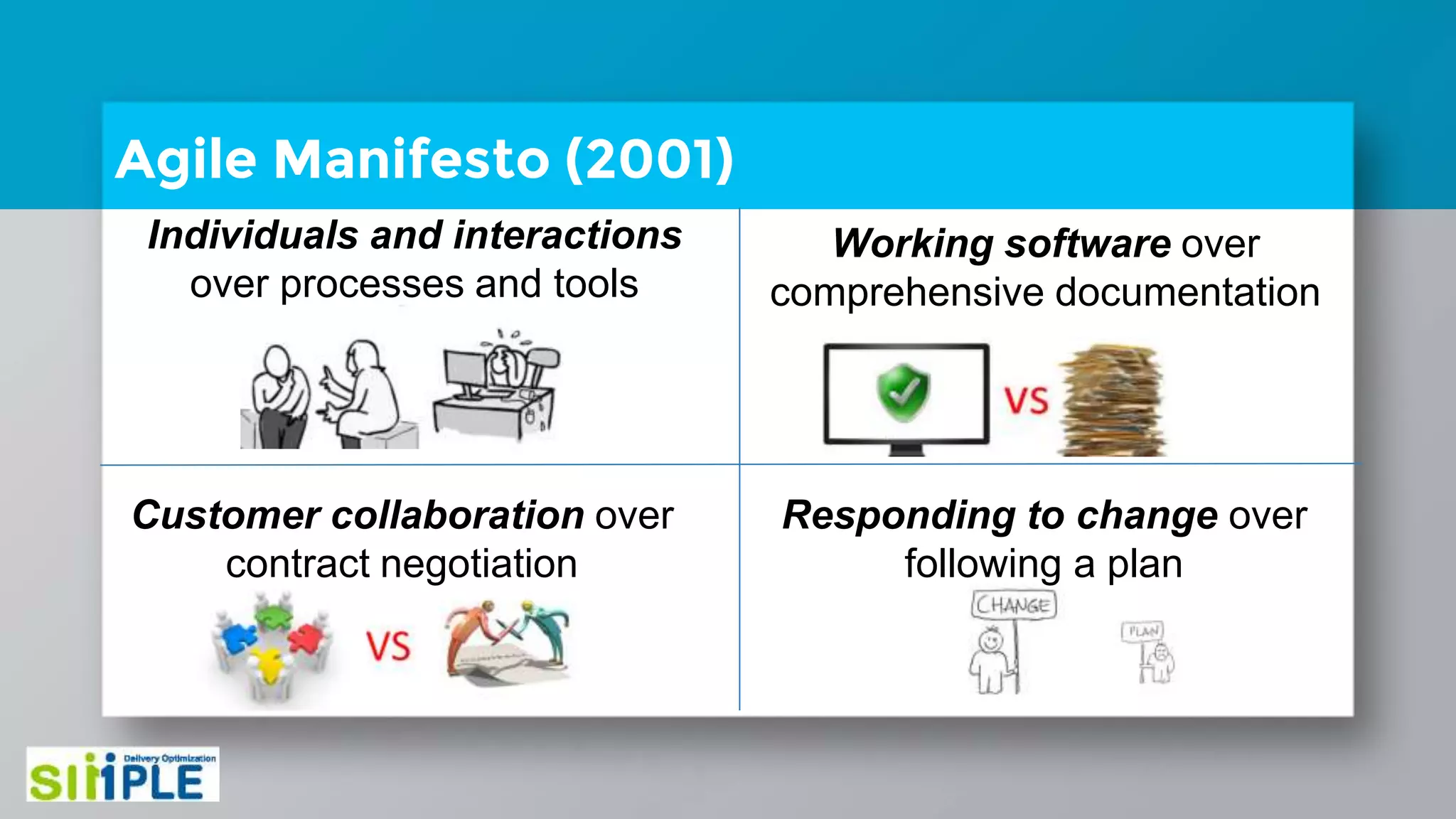
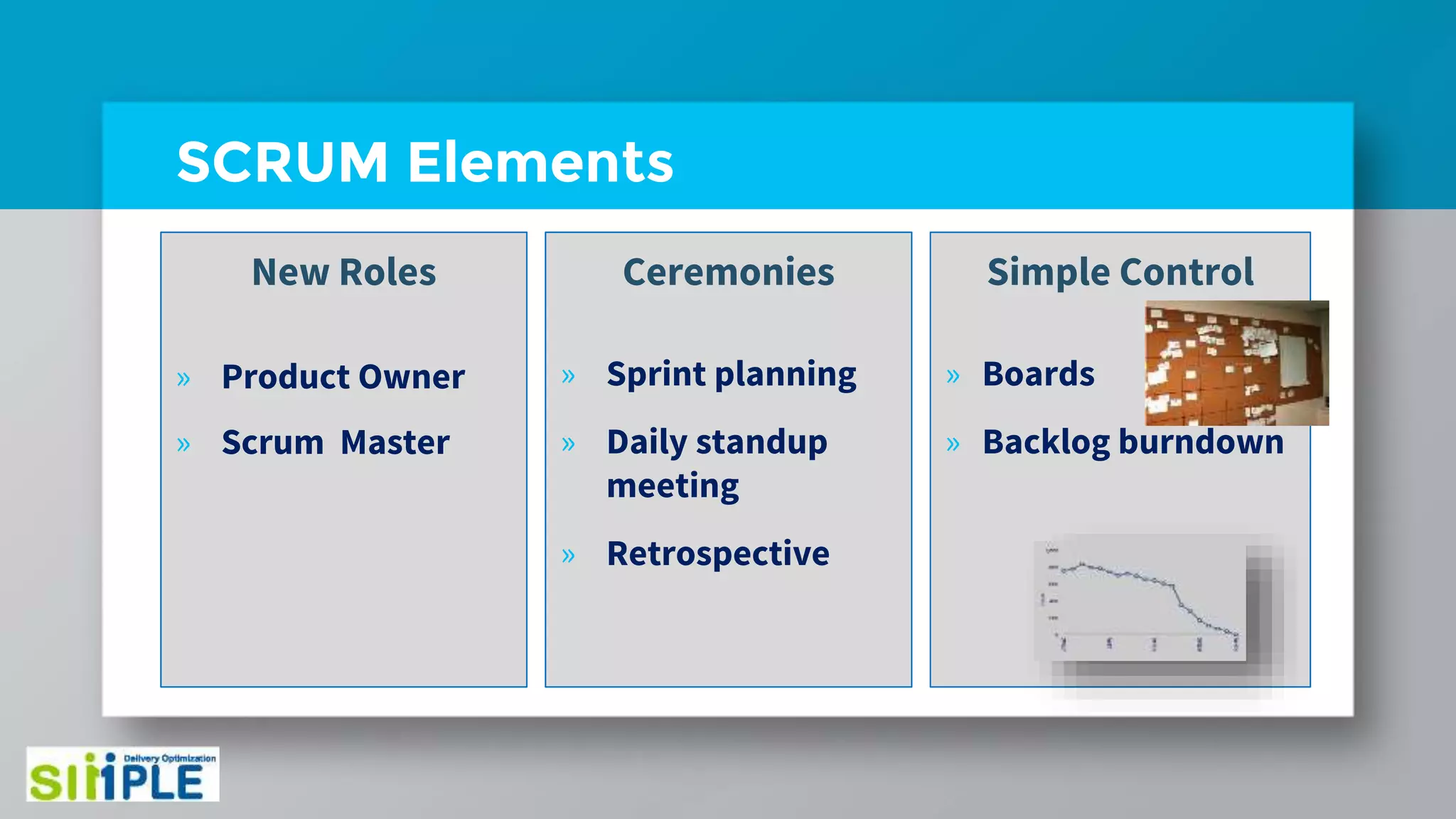
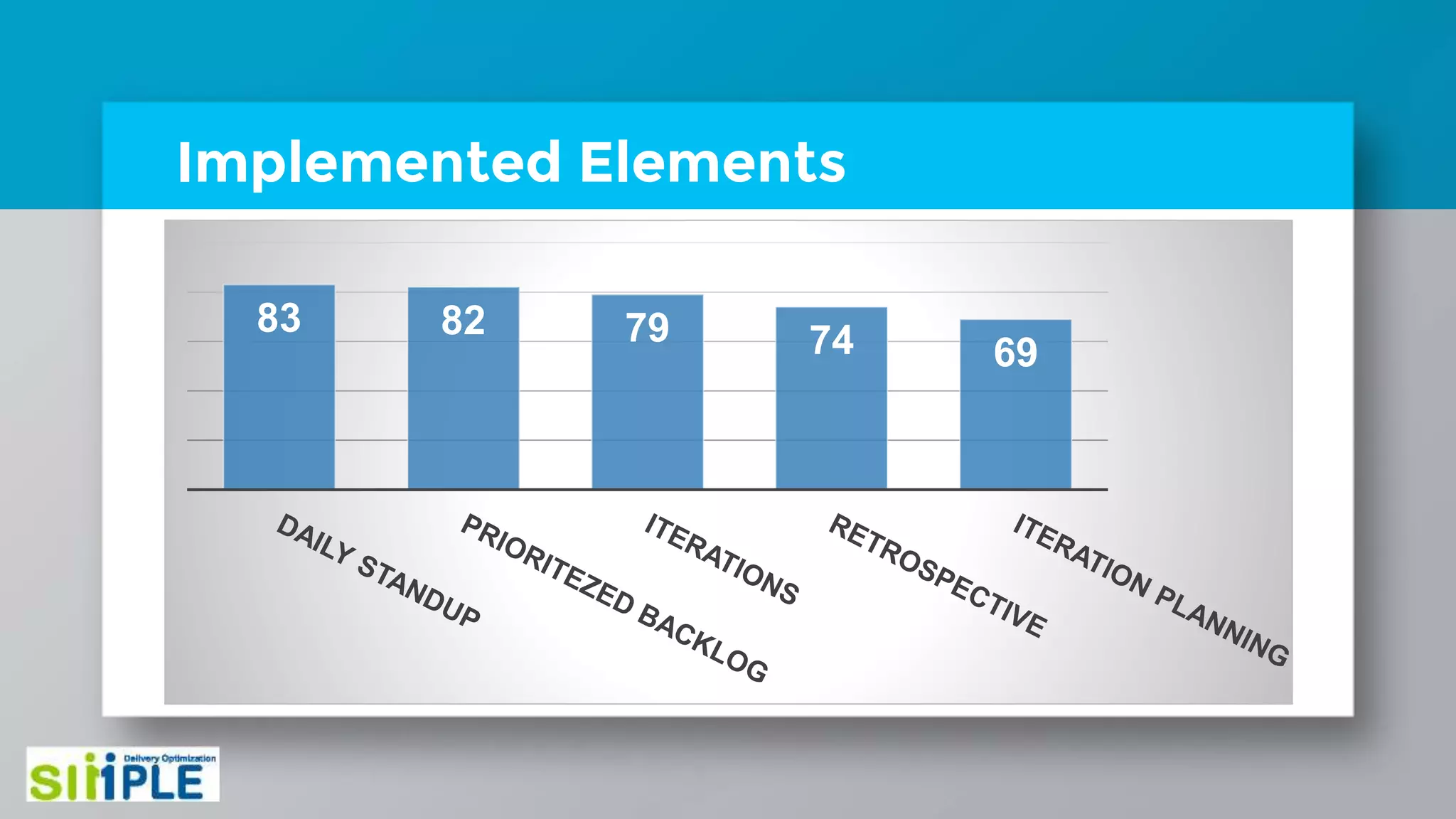
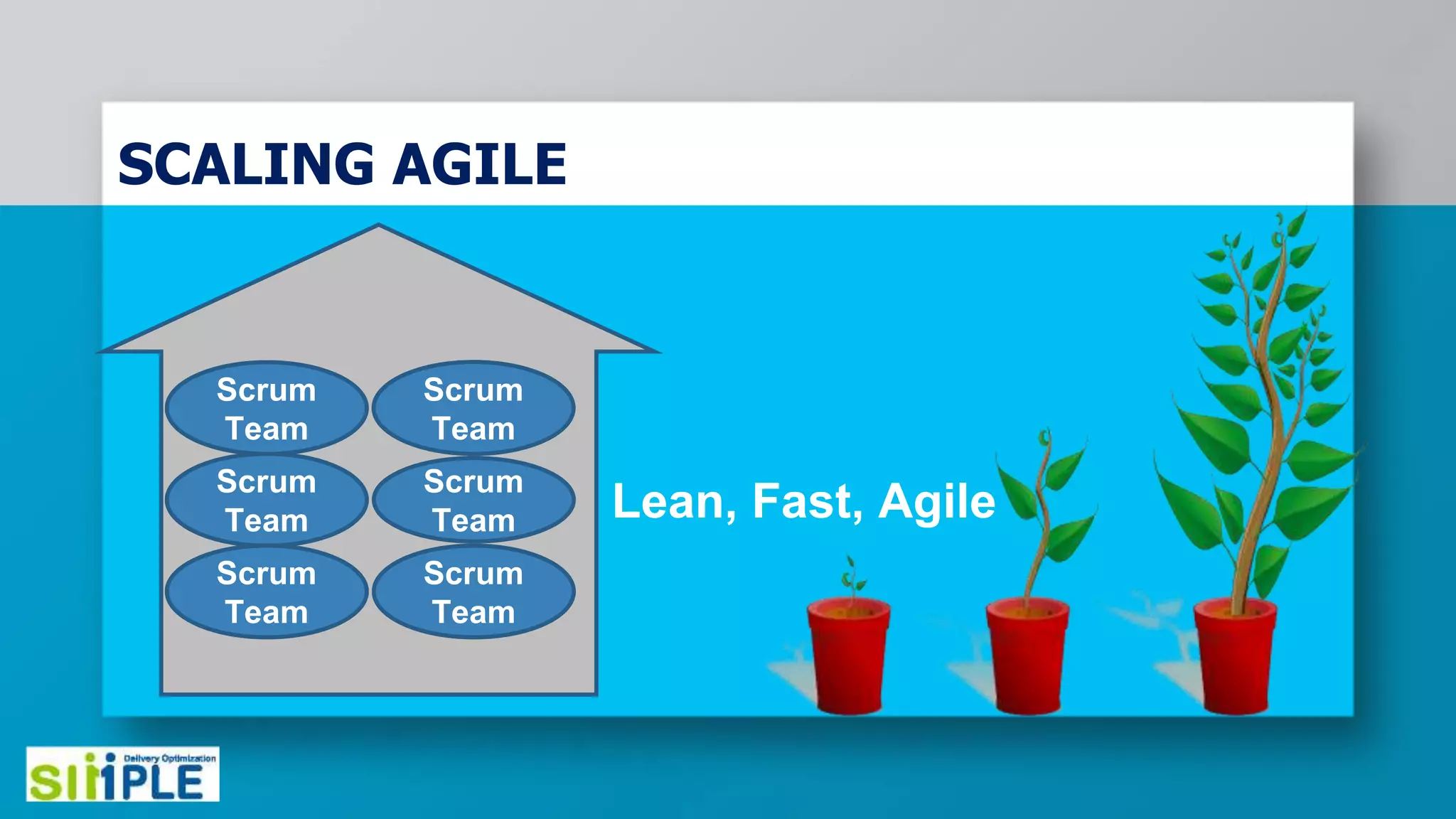
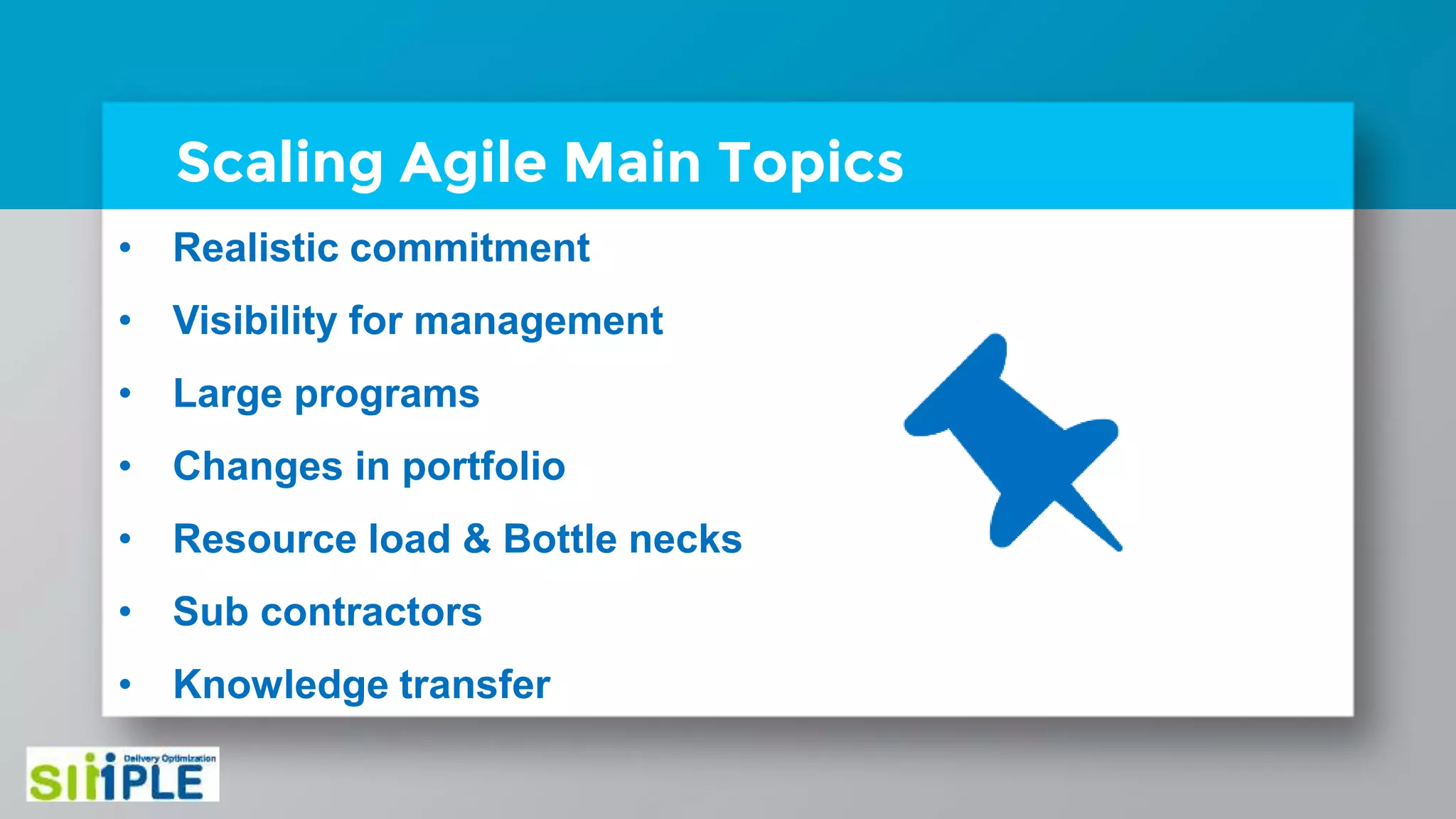
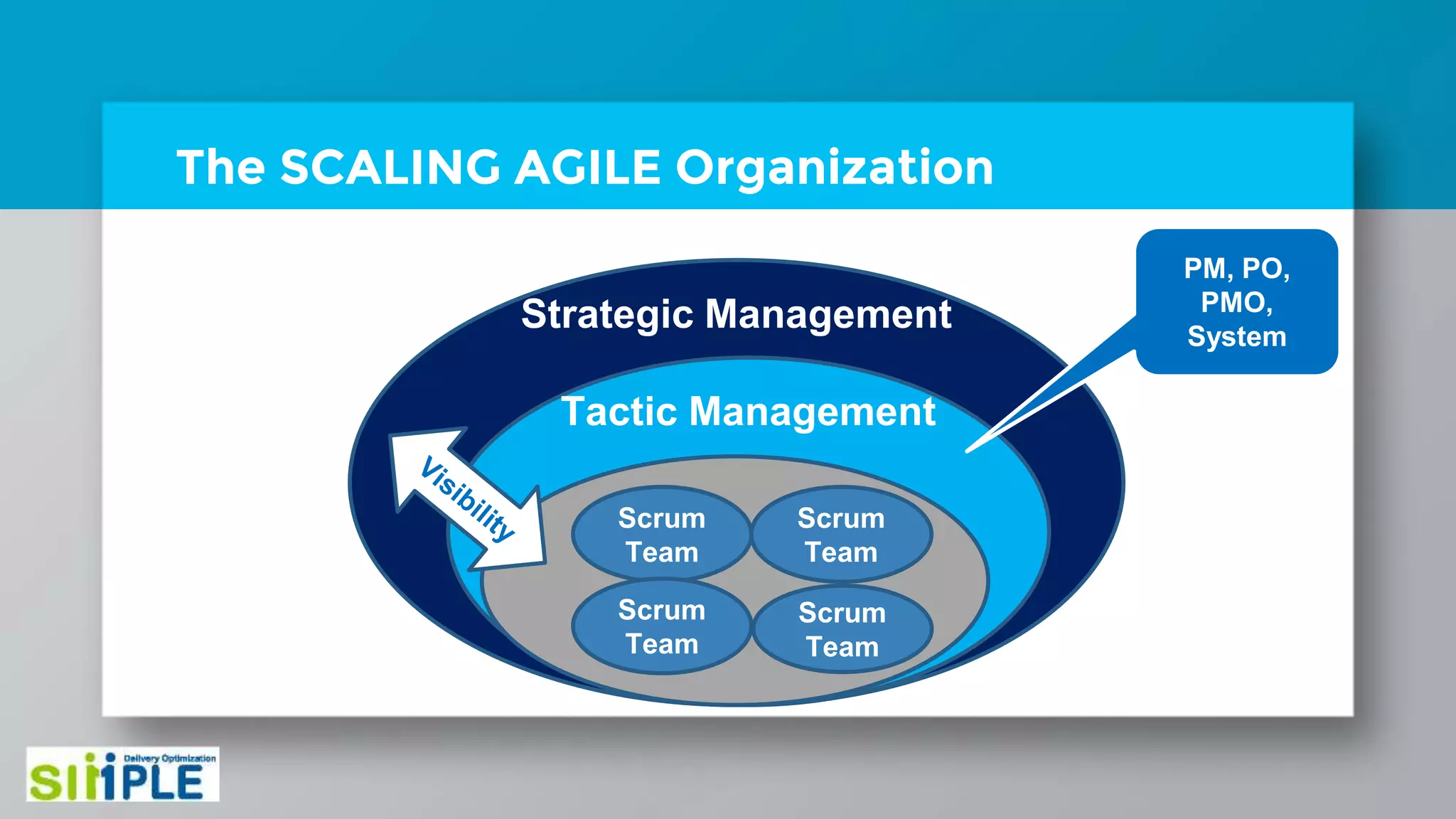
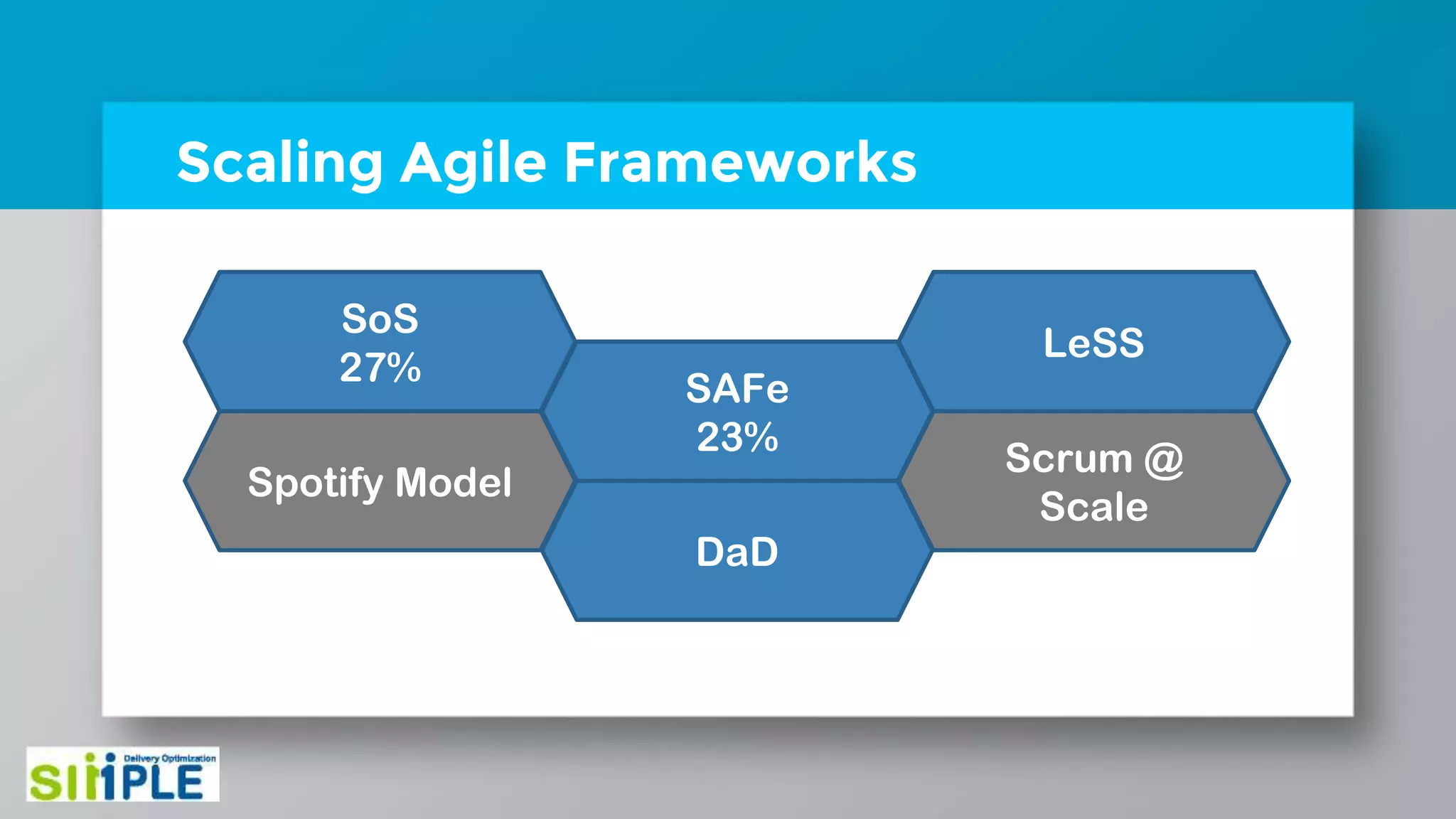
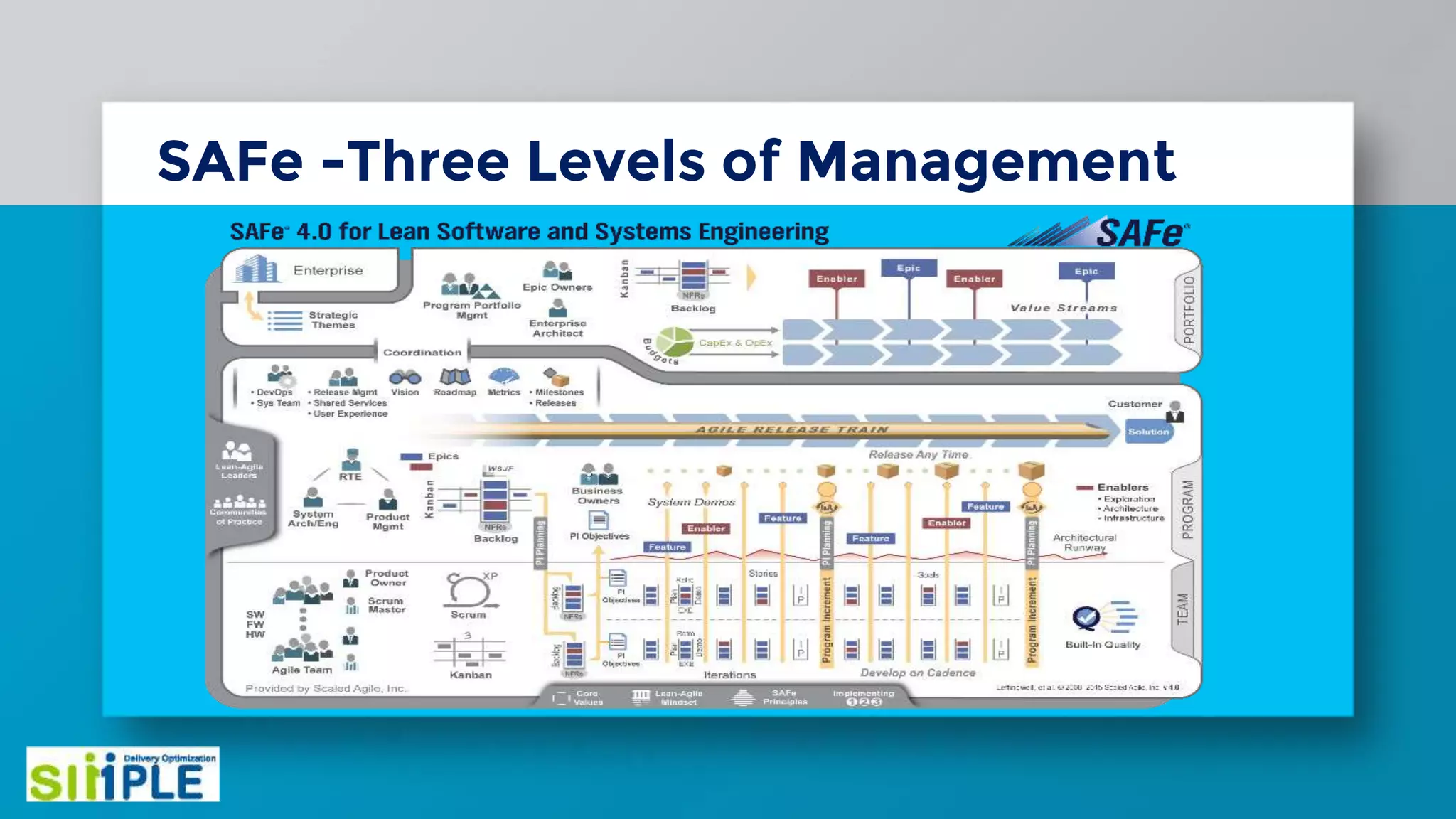
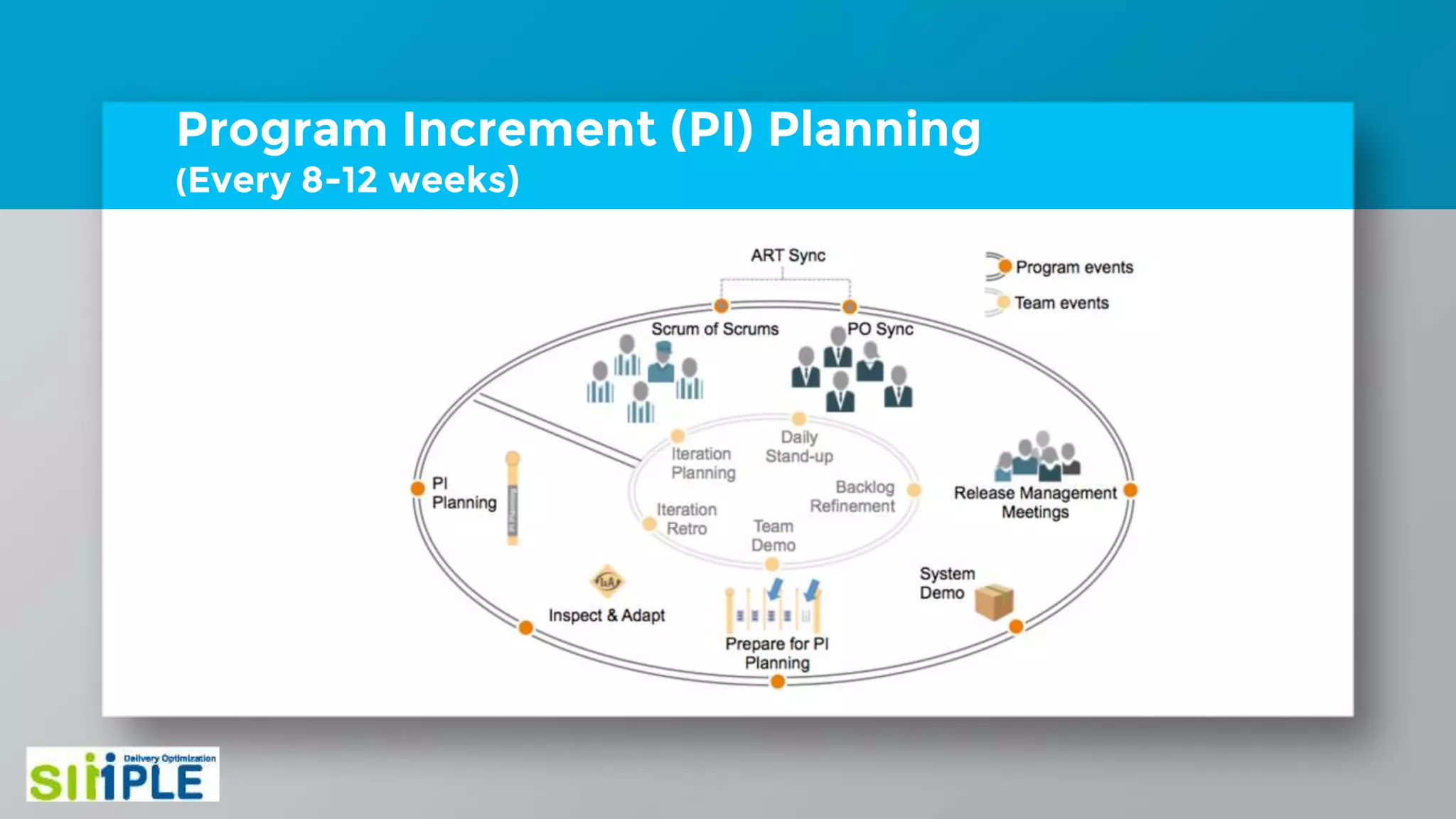
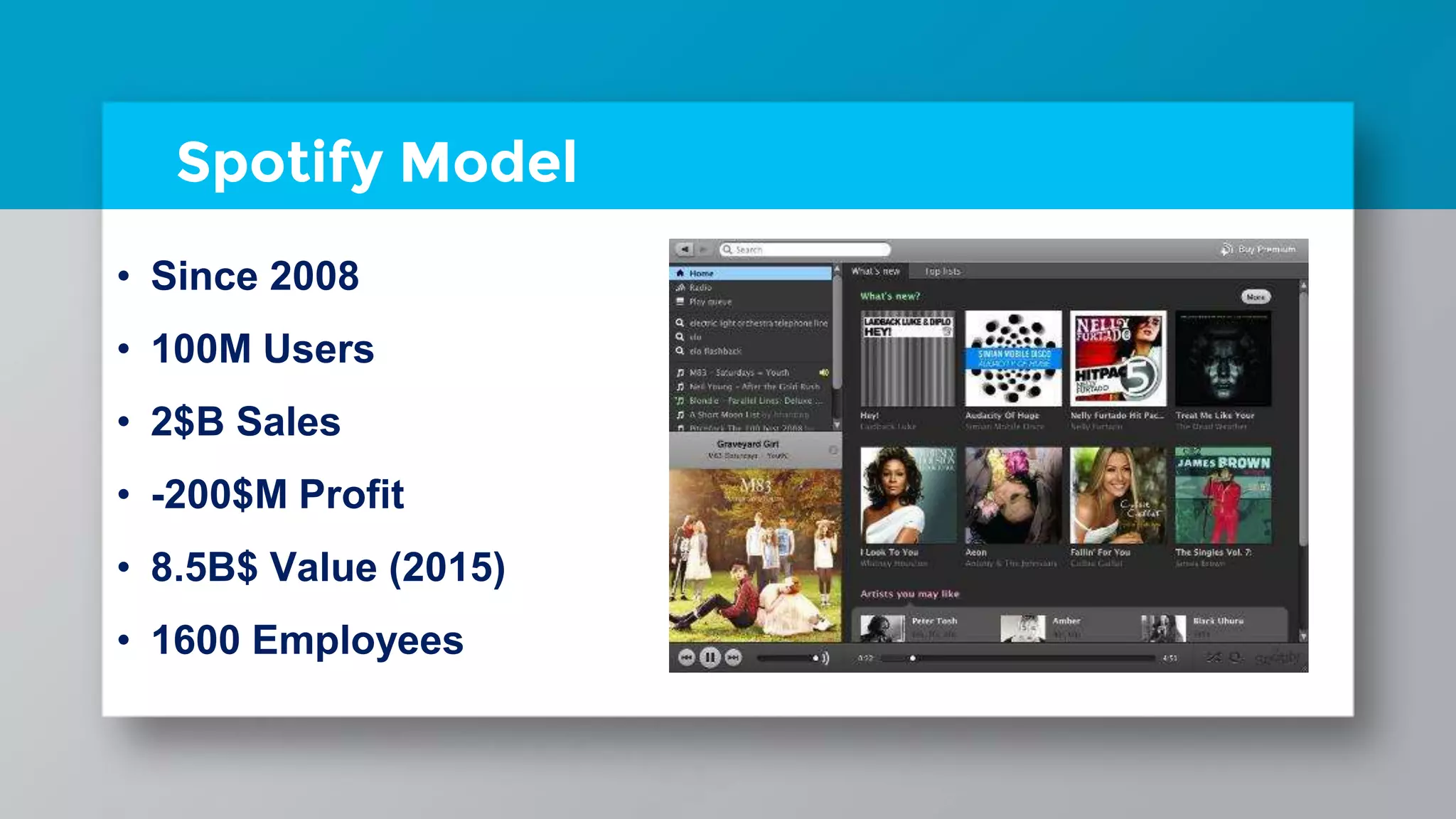
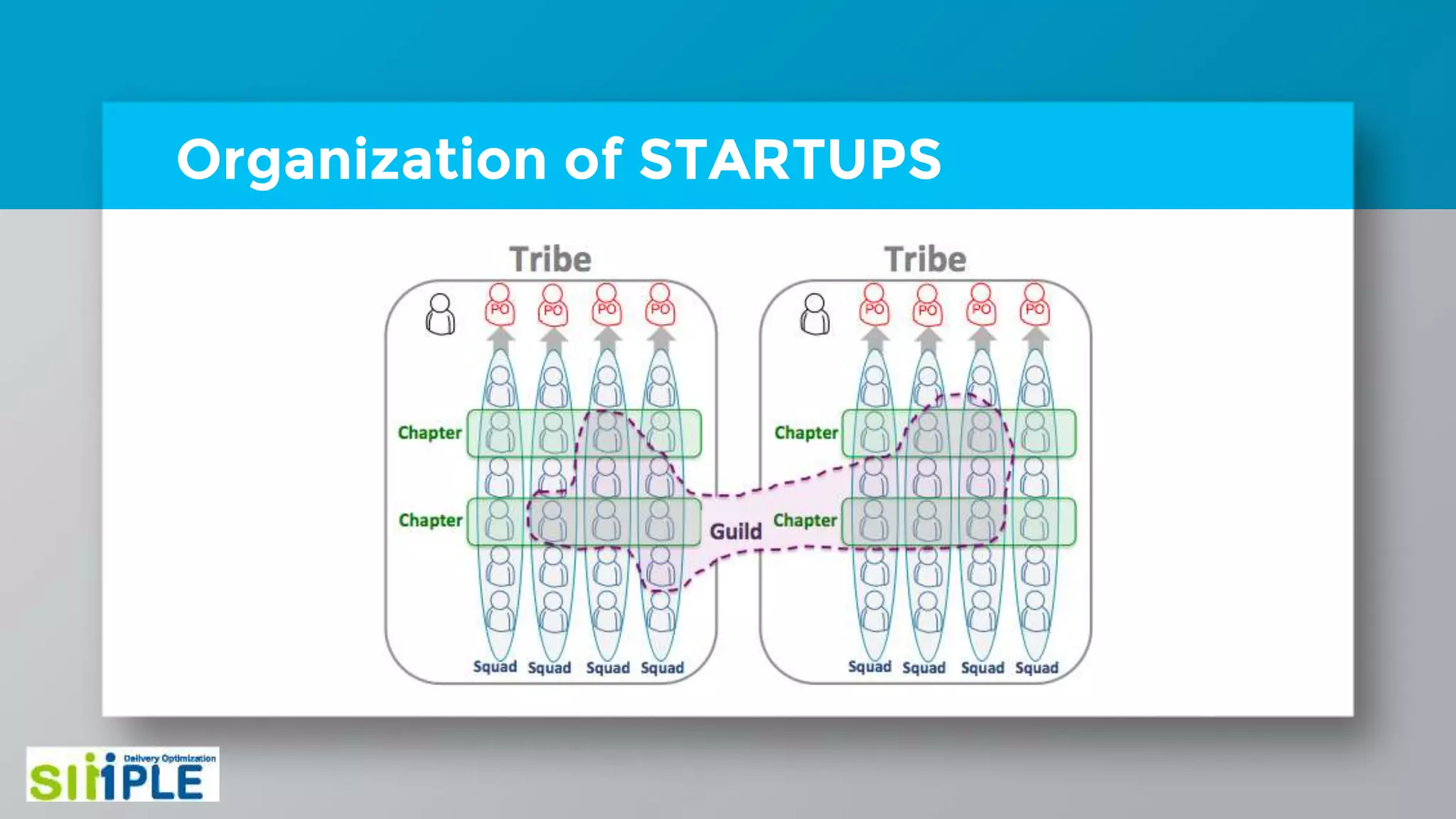
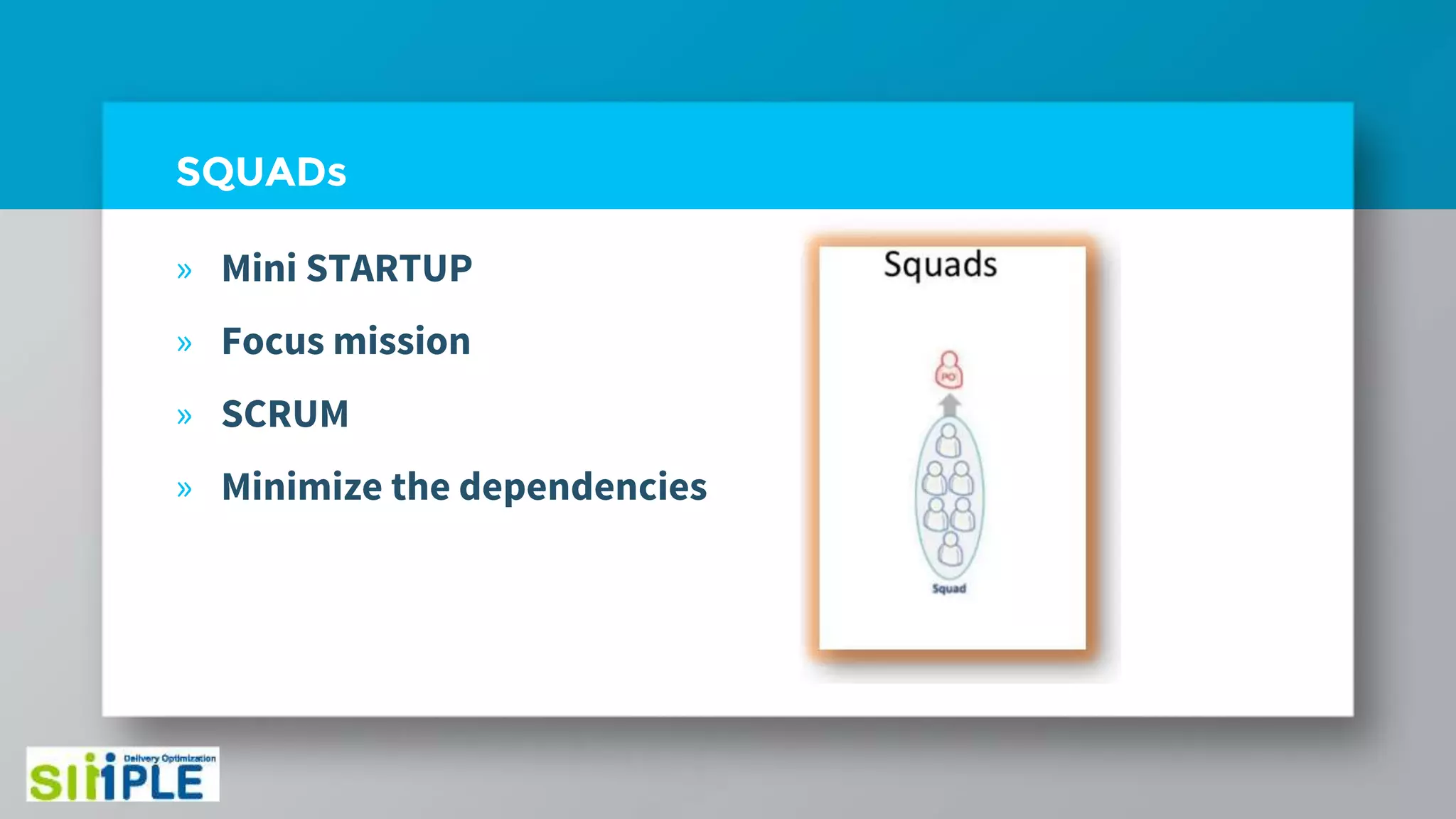
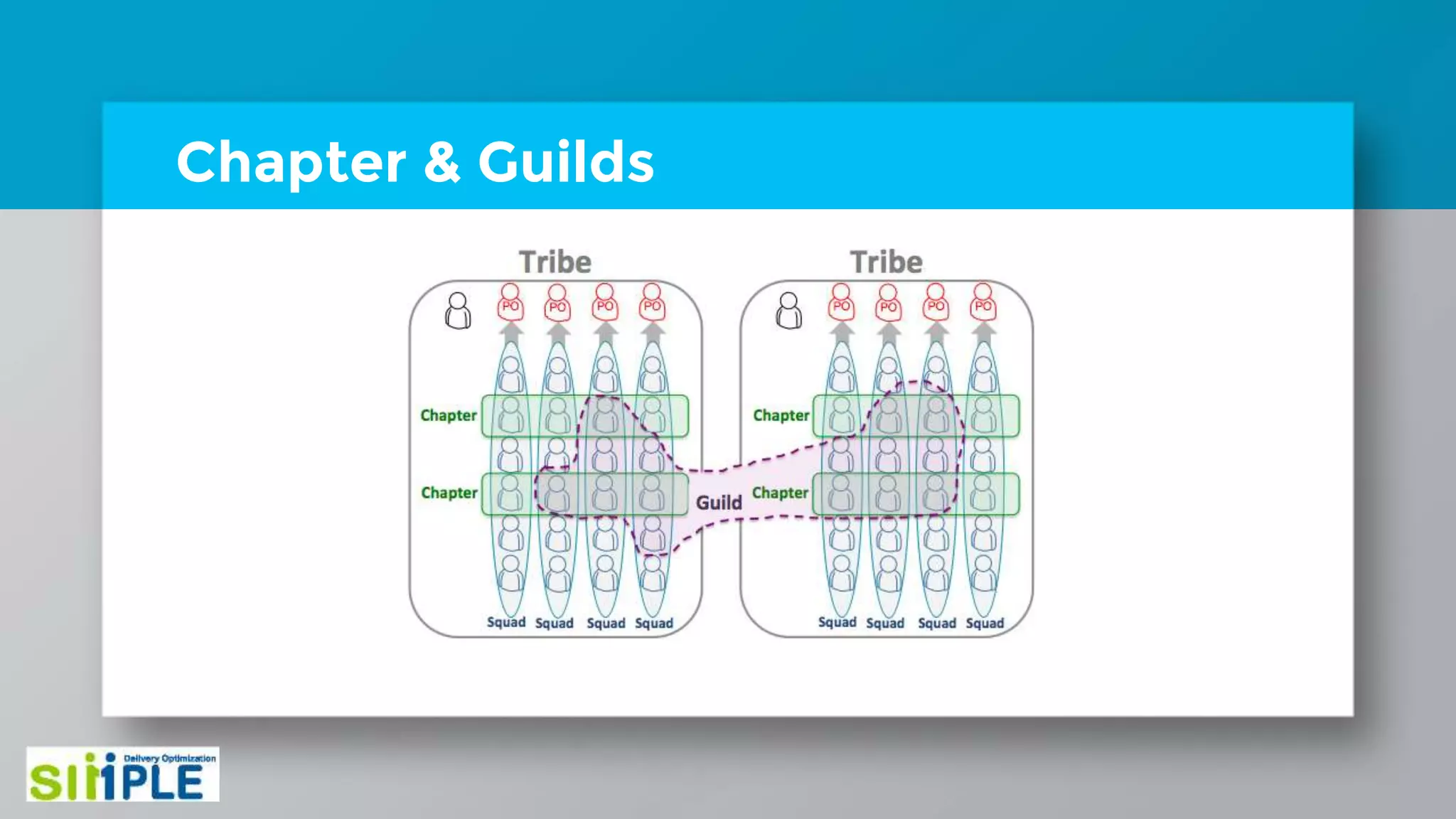
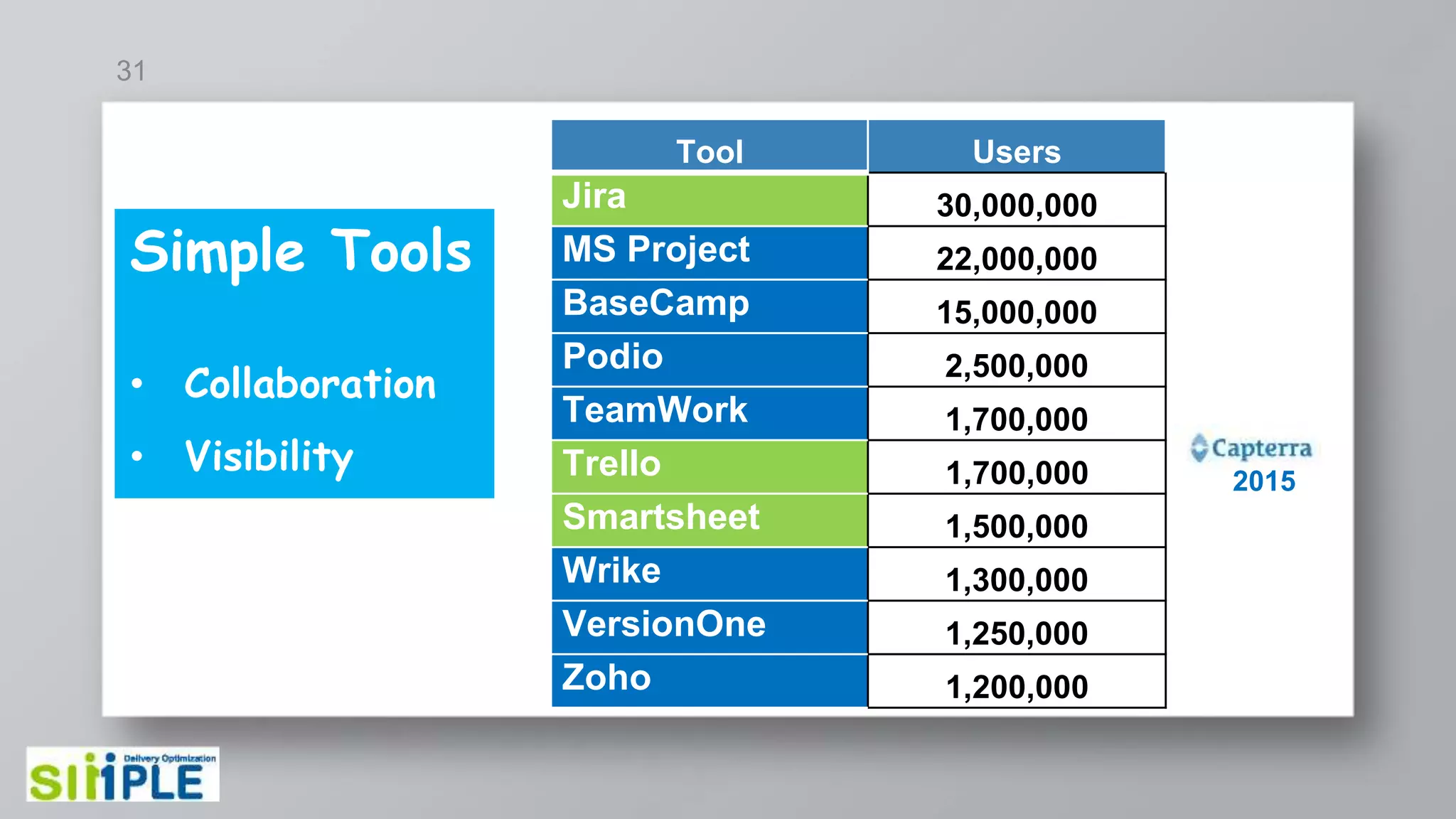
The document discusses different project management methodologies like Waterfall, Agile, and hybrid approaches. It provides details on frameworks for scaling Agile like SAFe and LeSS. Studies have shown that Agile projects have a higher success rate of delivering on time and on budget compared to Waterfall. Scaling Agile involves frameworks to coordinate large programs involving multiple Agile teams through elements like program increment planning and aligning teams.