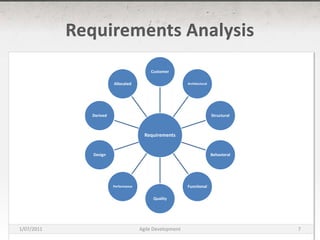
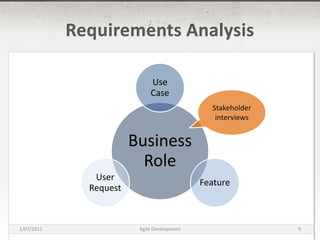
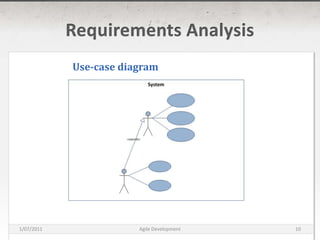
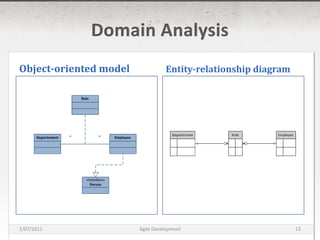
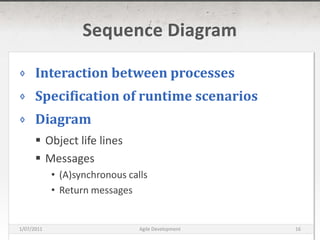
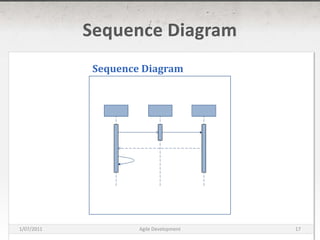
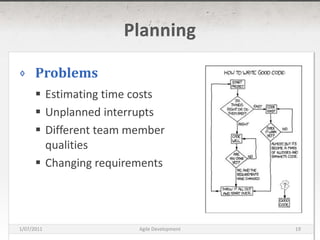
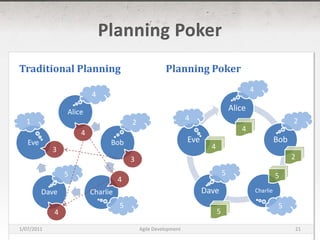
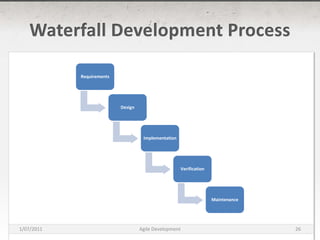
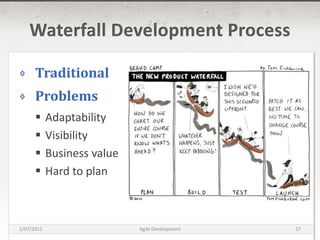
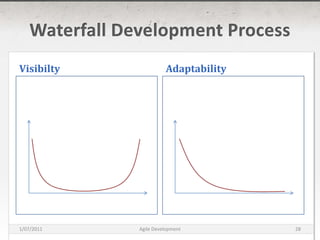
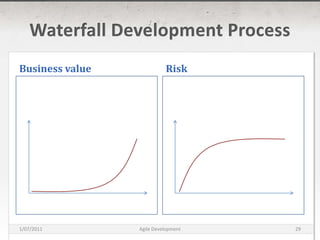
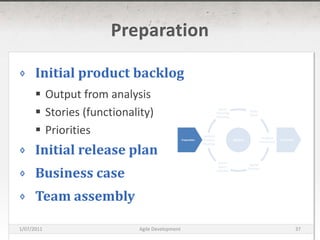
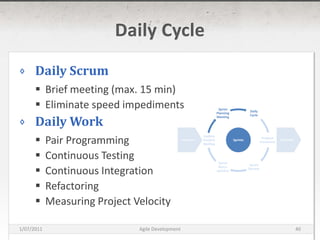
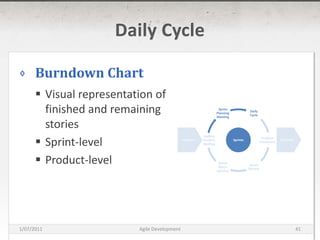
The document discusses agile development methods like Scrum and Extreme Programming (XP). It covers topics like iterative planning, continuous integration, pair programming, and refactoring code. The goal of agile methods is to provide visibility, adaptability, and business value through a flexible iterative process compared to traditional waterfall development.