This document provides an overview of Agile Scrum concepts including:
- The challenges of traditional software development that Scrum addresses like changing requirements and incomplete understanding at the start.
- The Scrum framework focuses on iterative development with 3 roles - Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team.
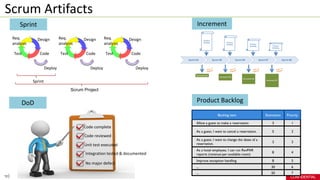
- Scrum uses artifacts like the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog and Burn Down Chart to track work.
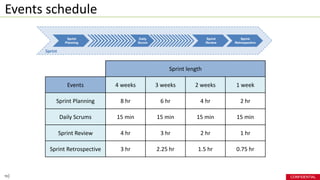
- Events in Scrum include Sprint Planning, Daily Scrums, Sprint Review and Retrospective which are timeboxed meetings.
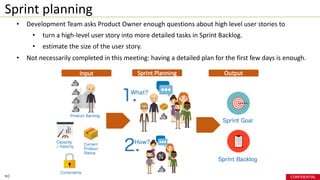
- Key techniques in Scrum are story point estimation, adjusting sprint length based on factors like uncertainty, maintaining a transparent backlog, and allowing some changes during