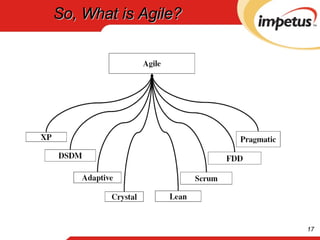
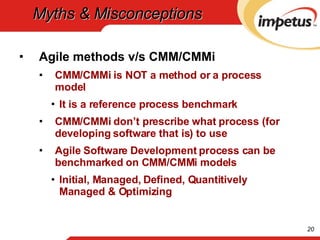
The document outlines an introduction to Agile software development, highlighting the evolution of software practices, the Agile manifesto, and common myths about Agile methodologies. It emphasizes Agile's focus on responding to change, early delivery of valuable software, and collaboration between developers and business stakeholders. The content also dispels misconceptions about Agile being unplanned or undisciplined, explaining its adaptive nature compared to predictive methods.

![Who am I? Software Practitioner & Evangelist 13 years of building software and learning Certified Scrum Master Lead Impetus Labs, Consulting and Research I am available for Speaking on Technology & Agile Help & Support your Agile journey (e) [email_address] (m) 931 310 2111](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-agile-agilencr-1214995433561594-9/85/Introduction-To-Agile-2-320.jpg)