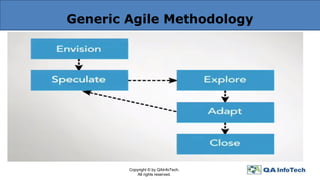
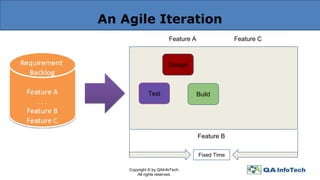
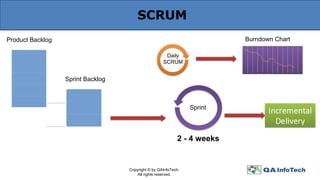
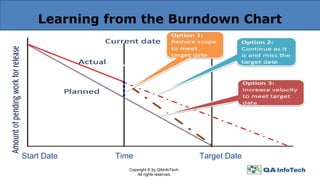
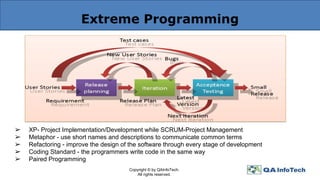
The document outlines agile methodology, defining it as an iterative and incremental approach to software development emphasizing collaboration and adaptability. It discusses key agile principles, various models such as Scrum and Extreme Programming, and stresses the importance of communication, customer involvement, and responsiveness to change. The conclusion highlights the diversity of agile methodologies and their applicability depending on the project environment.