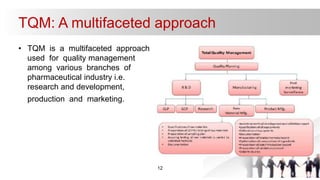
This document discusses Total Quality Management (TQM) in the pharmaceutical industry. TQM is a multifaceted approach that involves building quality into every step of the pharmaceutical process from research and development to manufacturing to marketing. It utilizes various quality management techniques like quality risk management, quality by design, good manufacturing practices, and ISO standards. TQM ensures quality is maintained through all stages of production from raw materials to finished drugs. It is important for the pharmaceutical industry given many drugs are life saving and quality defects could pose health hazards.









![• 1. Research and development: TQM also plays very vital role in quality
management of research and development process.
• It involves following points:[ a]. GLP: It is also called as ‘Good Laboratory
Practices’. It involves strict control over use of animals in the laboratory for
experimentation.
• TQM in GLP involves following points:
• 1] Preparation of protocol or master schedule sheet for the study,
Maintenance of copy of protocol in the laboratory in which study is to be carried
out, 2]• Periodic inspection of facility in which study is to be carried out,3] • If any
change in approved protocol of the study then there should be documentation
and approval of the change along with the reason for carrying out the
change, and Documentation.
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/affrintqm-220626052530-fe50e2e1/85/TQM-Modern-pharmaceutics-12-320.jpg)
![• [b]. GCP: It is also called as ‘Good Clinical Practices’. It
involves strict control over use of human beings in clinical trials.
The regulations for GCP are almost similar to that of GLP. The
major difference being that before starting study or involving any
subject or human being into the clinical trials. A complete duly
filled informed consent form should be taken from subjects along
with their signature to make sure that subject is known he/she
is involved in clinical trials. These records should be
maintained. If patient dropout involve during the study then
number of dropouts along with reason of dropout from study
should be documented. 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/affrintqm-220626052530-fe50e2e1/85/TQM-Modern-pharmaceutics-13-320.jpg)

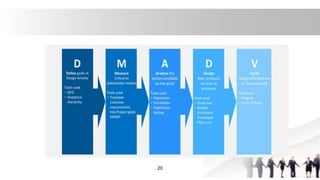
![Approaches for TQM
[1]Six Sigma Technique
Six Sigma involves two methods:[A]DMAIC [B]DMADV
[2]Quality Risk Management (QRM)
[3]Quality by Design (QbD)
[4]ISO Series
[5]Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP)
[6]International Conference on Harmonization (ICH)
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/affrintqm-220626052530-fe50e2e1/85/TQM-Modern-pharmaceutics-15-320.jpg)
![• Various approaches as practiced by
industries in TQM of pharmaceutical
process
• [1]Six Sigma Technique: Six Sigma
technique can improve the quality of
process outputs by identifying and
removing the causes of defects (errors)
and minimizing variability in manufacturing
and business processes
• two methods:1. DMAIC: It is an
abbreviation used for an improvement
cycle, which involves 5 Phases
17
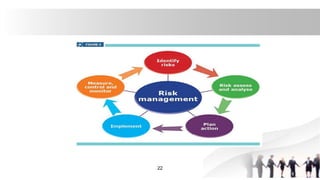
• understand or define what the
problem is,
• then it is measured to receive
existing data at unaltered state,
• once it has been measured the
problem and data is analyzed to
understand the root cause,
• after analyzing improvement
strategies are developed to address
the root cause,
• and lastly is to control the
improvements and look for future
improvements.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/affrintqm-220626052530-fe50e2e1/85/TQM-Modern-pharmaceutics-16-320.jpg)