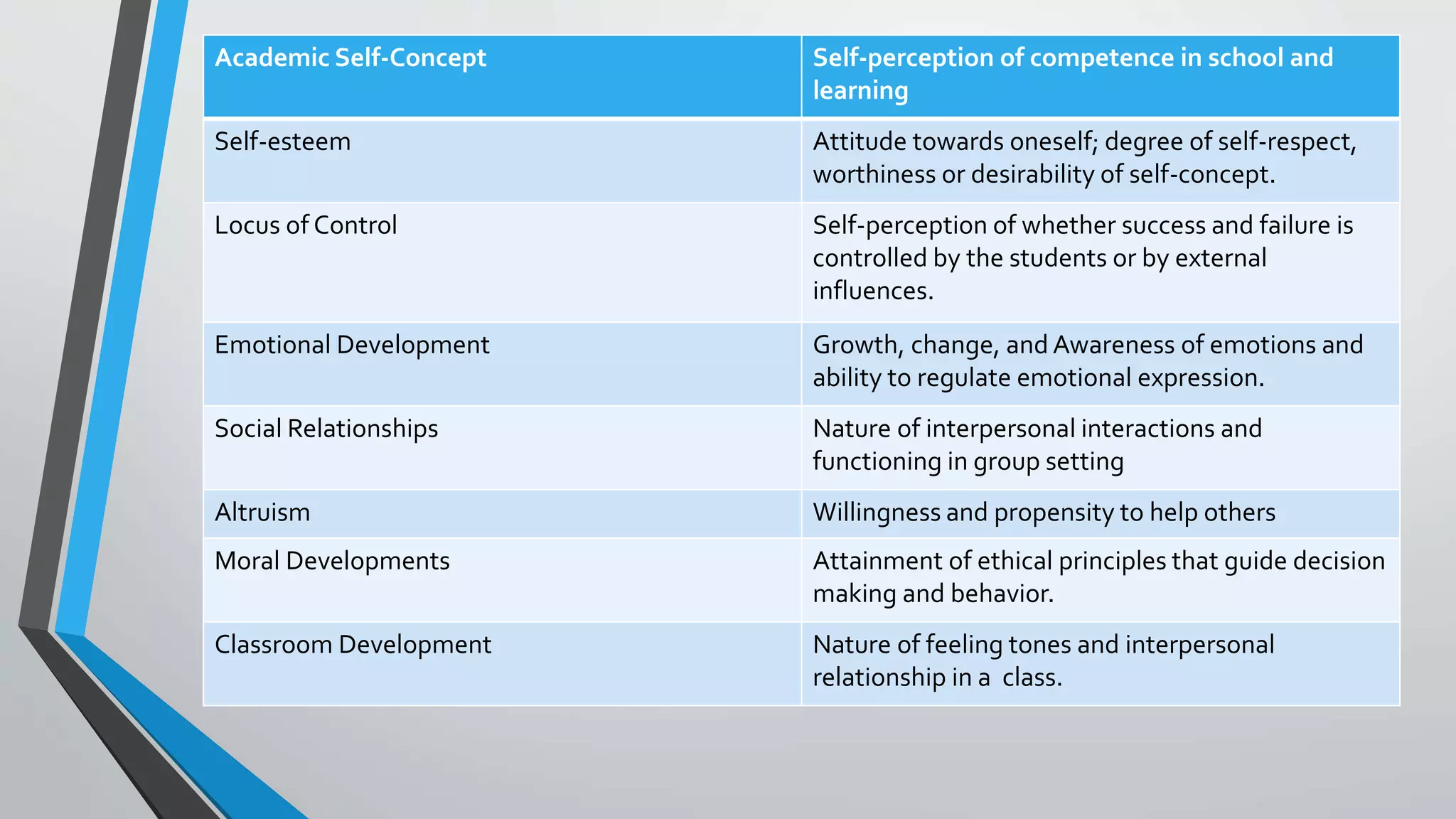
The document discusses affective learning competencies essential for teachers in managing the emotional and social development of exceptional students. It emphasizes the importance of motivation, engagement, and attitudes in learning through various interactive activities aimed at enhancing students' problem-solving skills, self-awareness, and social relationships. Key components discussed include attitudes, values, self-concept, and classroom environment, all critical for fostering a positive educational experience.