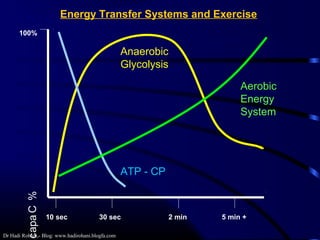
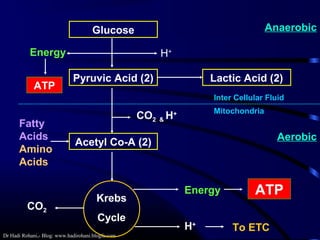
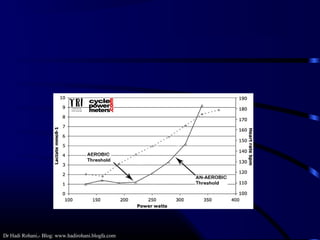
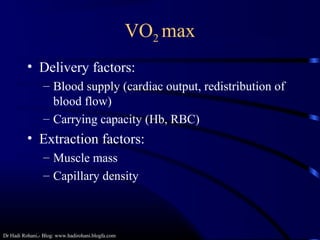
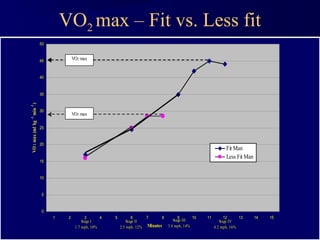
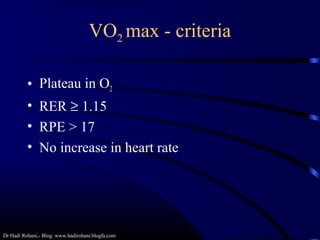
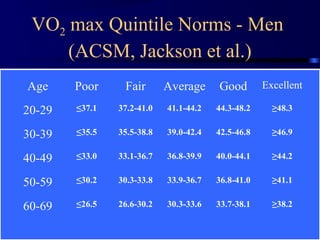
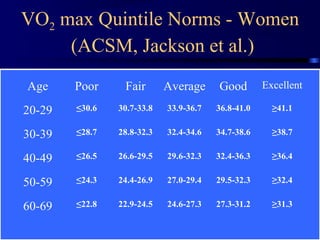
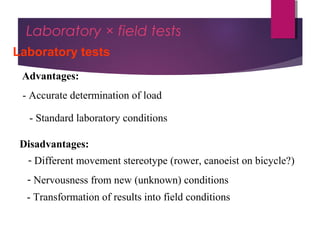
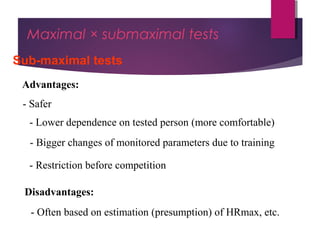
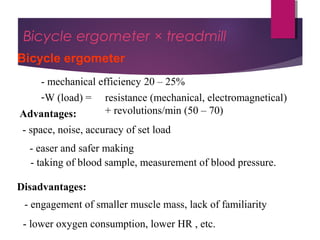
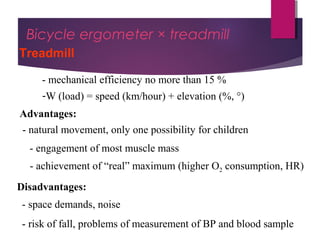
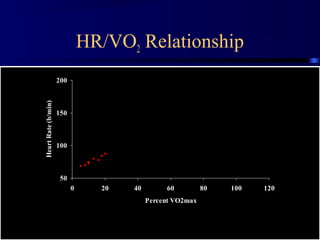
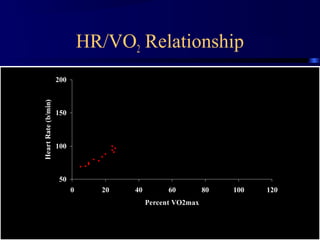
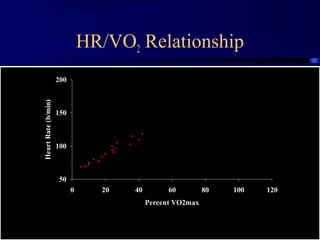
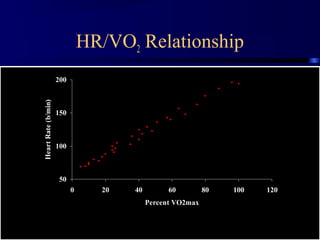
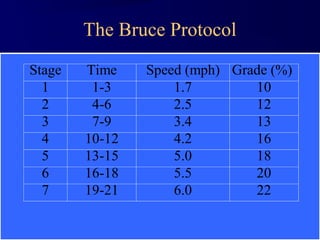
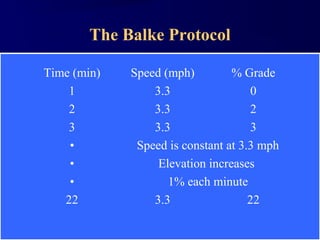
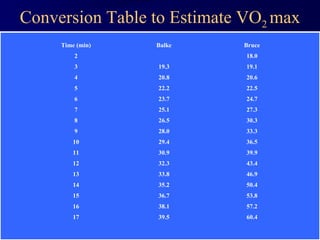
This document discusses aerobic and anaerobic fitness. It defines aerobic fitness as the ability to meet energy demands during sustained submaximal work through oxygen delivery and utilization. Aerobic respiration breaks down glucose to produce energy in the presence of oxygen, while anaerobic respiration does so in the absence of oxygen through fermentation. The document also discusses various tests used to evaluate aerobic and anaerobic fitness, including maximal tests like the Bruce and Balke protocols to estimate VO2 max, and the Wingate test to evaluate anaerobic power.