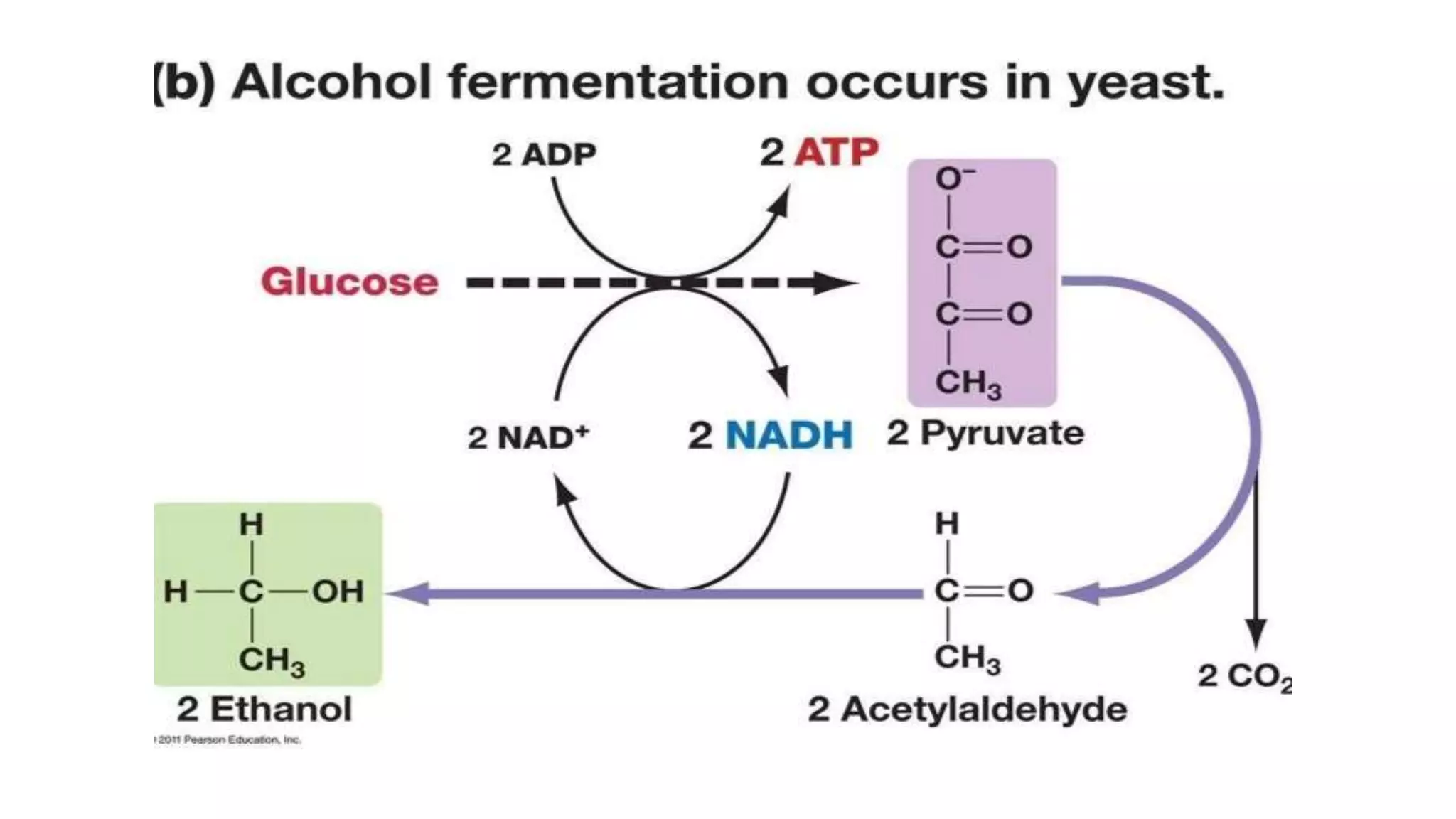
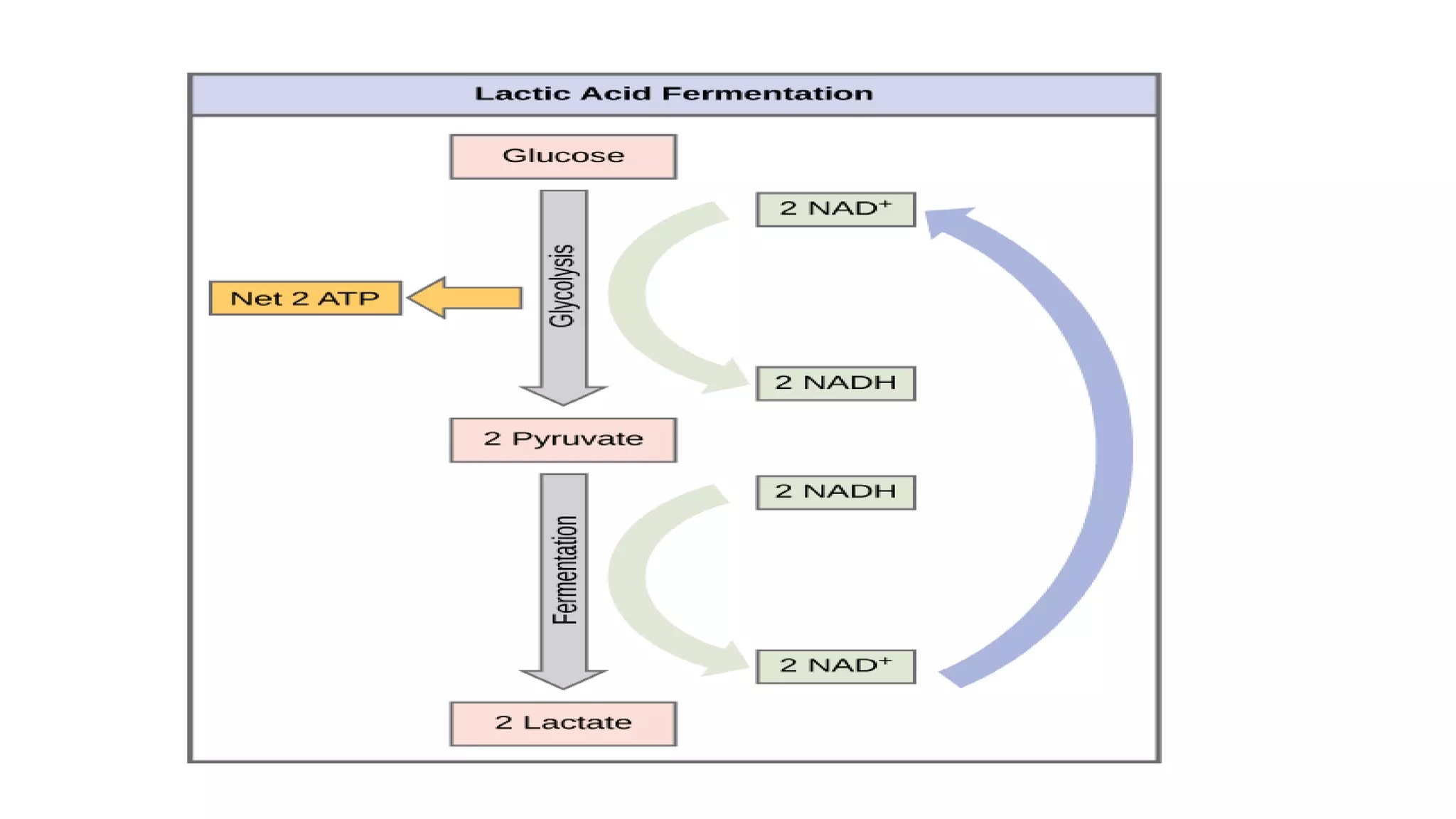
This document discusses aerobic and anaerobic fermentation. It defines fermentation as a metabolic process catalyzed by enzymes that produces chemical changes in organic substrates. Aerobic fermentation uses oxygen and includes surface and submerged cultures. Anaerobic fermentation does not use oxygen and involves glycolysis producing ethanol or lactic acid to regenerate NAD+. The advantages are producing energy when oxygen is limited, but disadvantages include potential toxicity of products, slower production, and high costs.