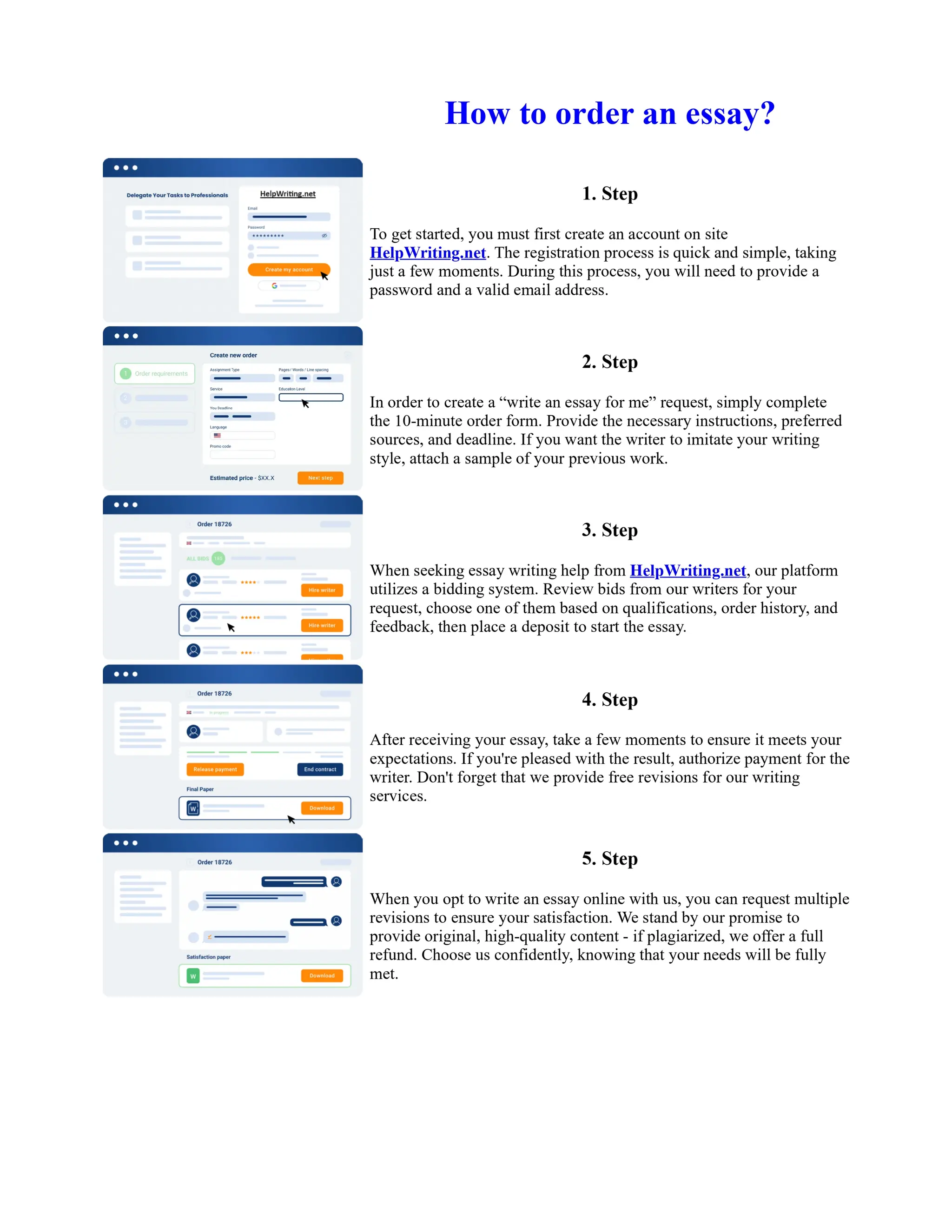
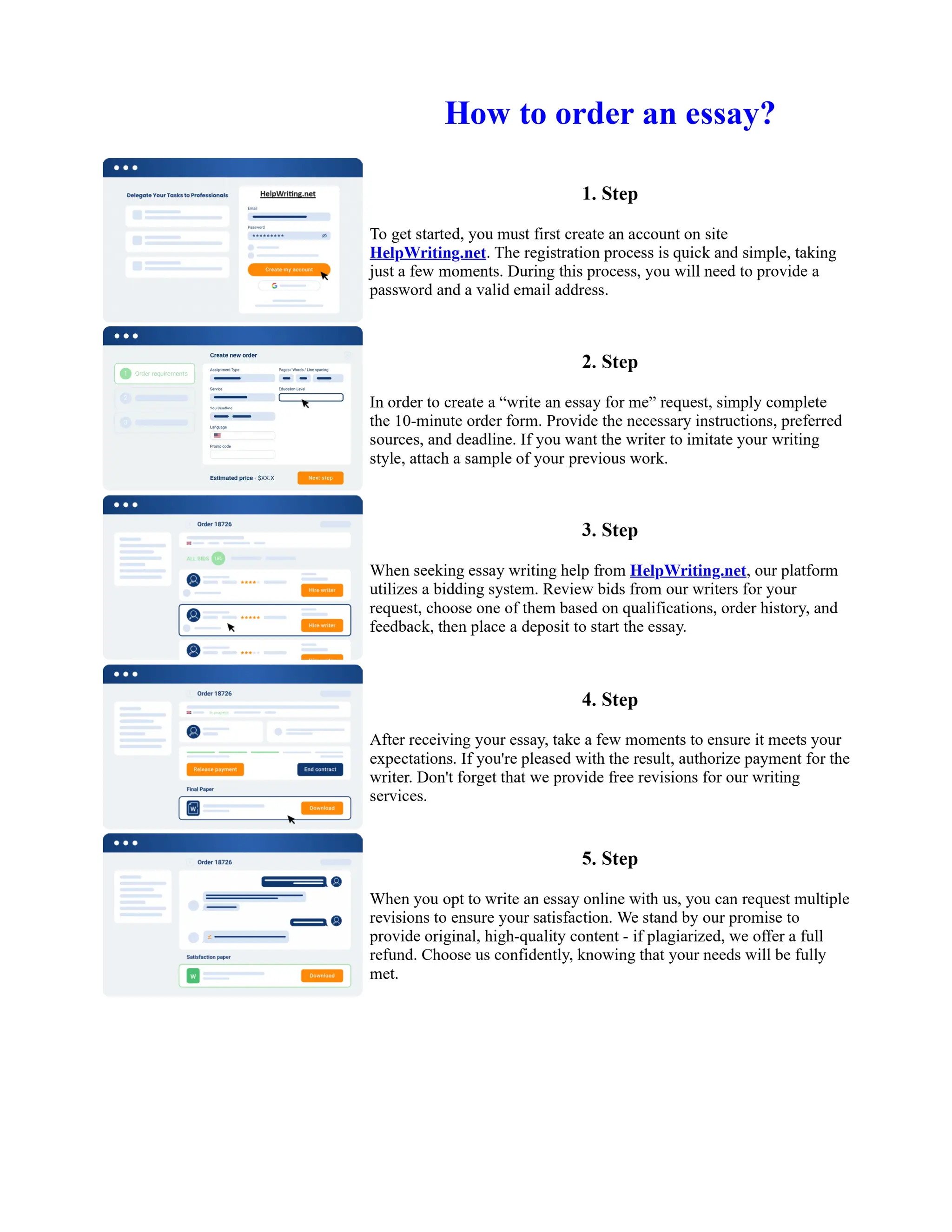
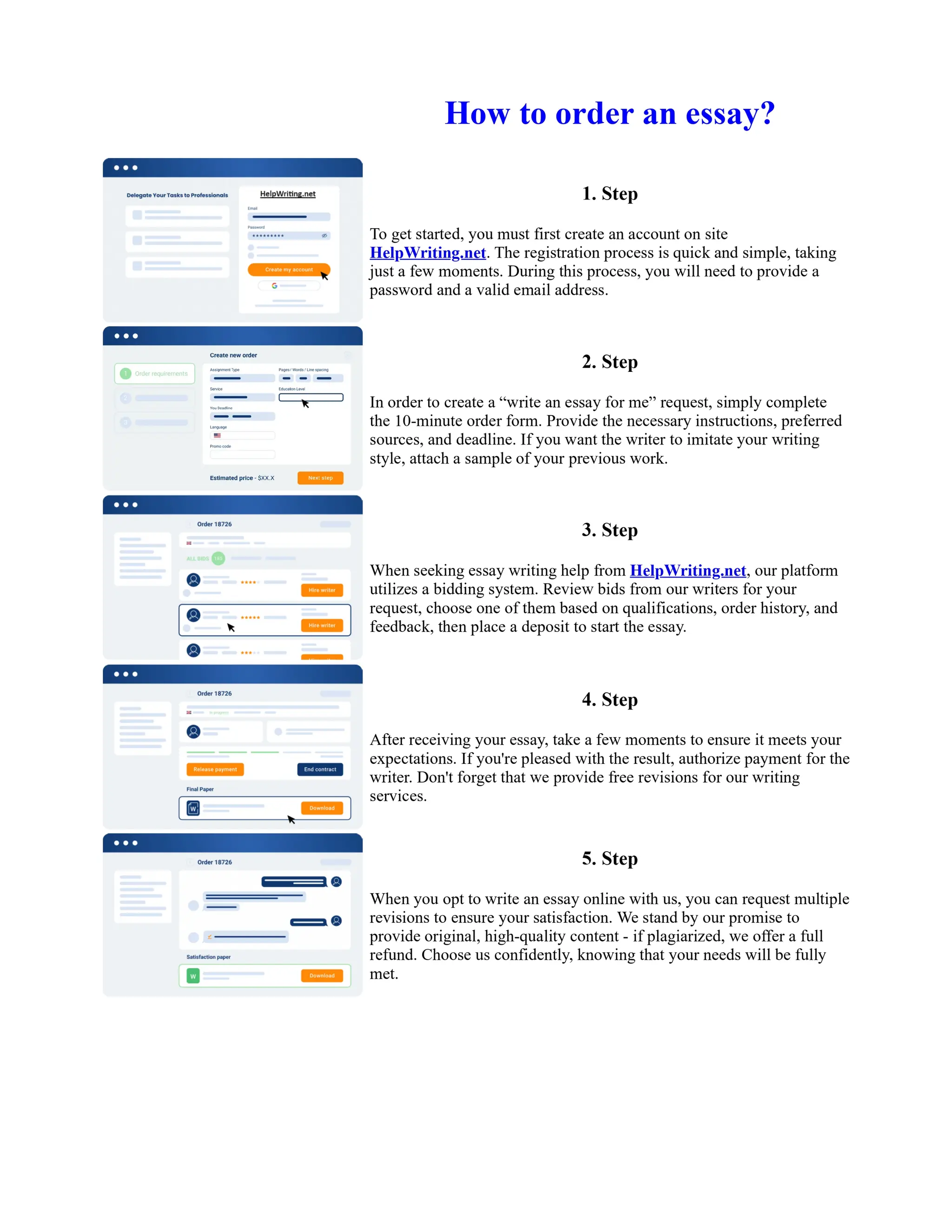
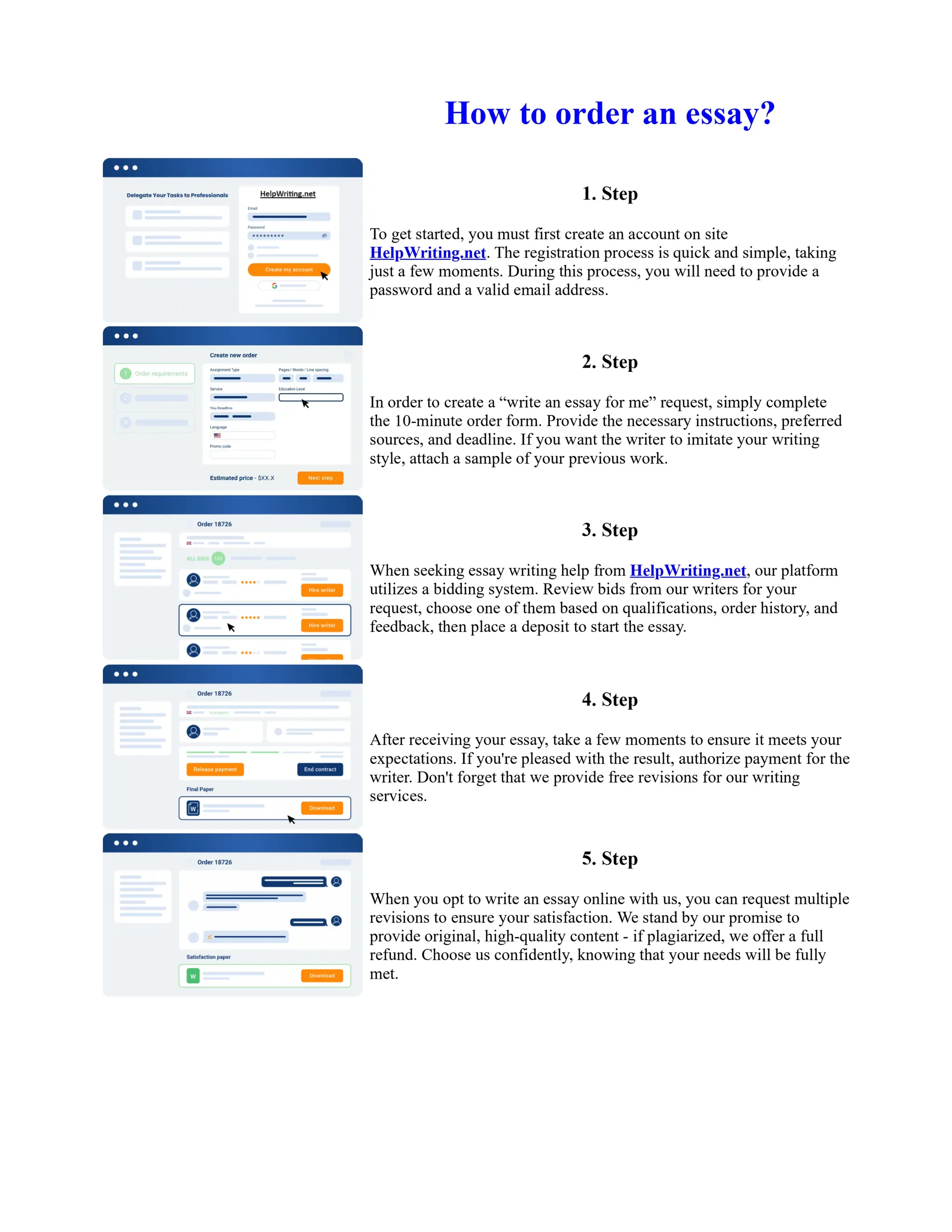
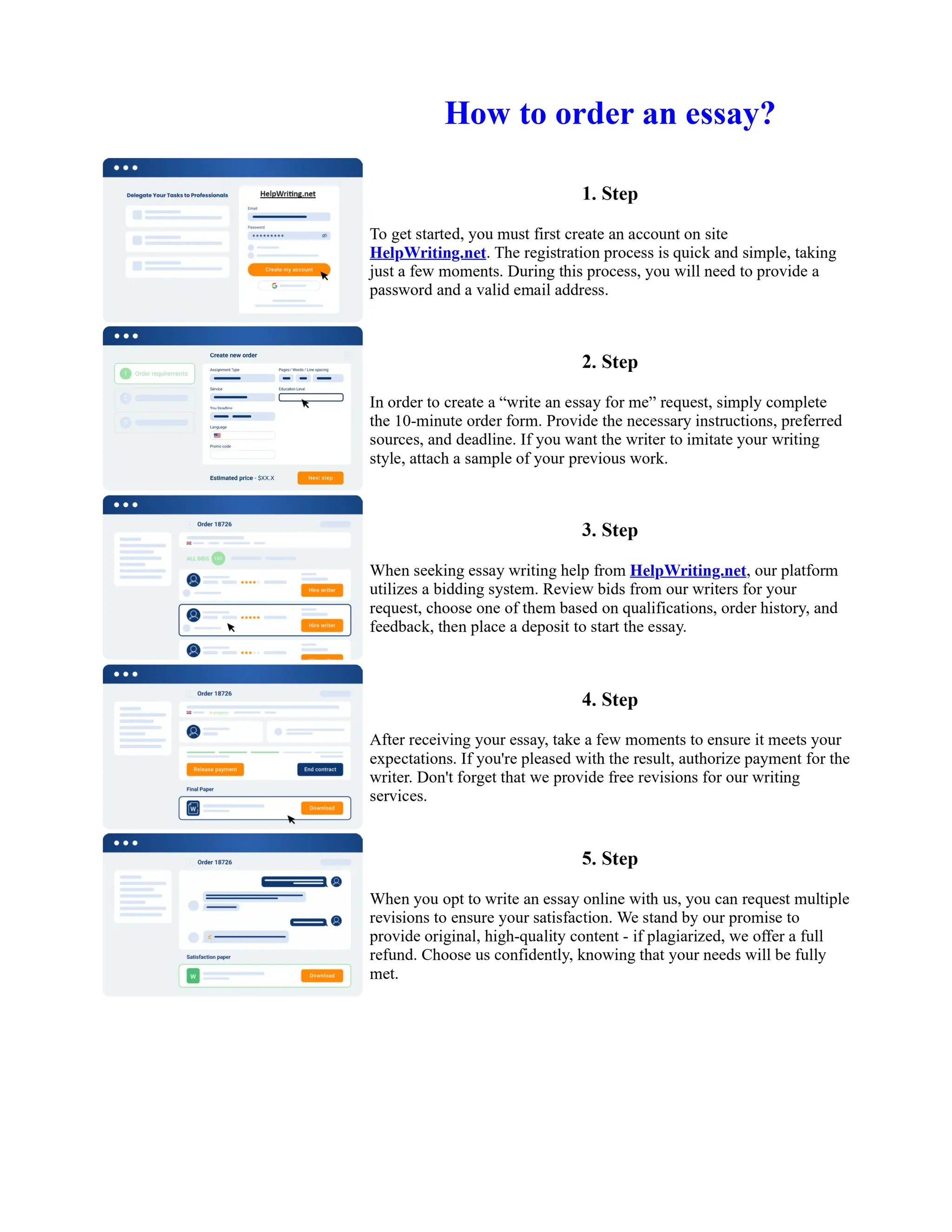
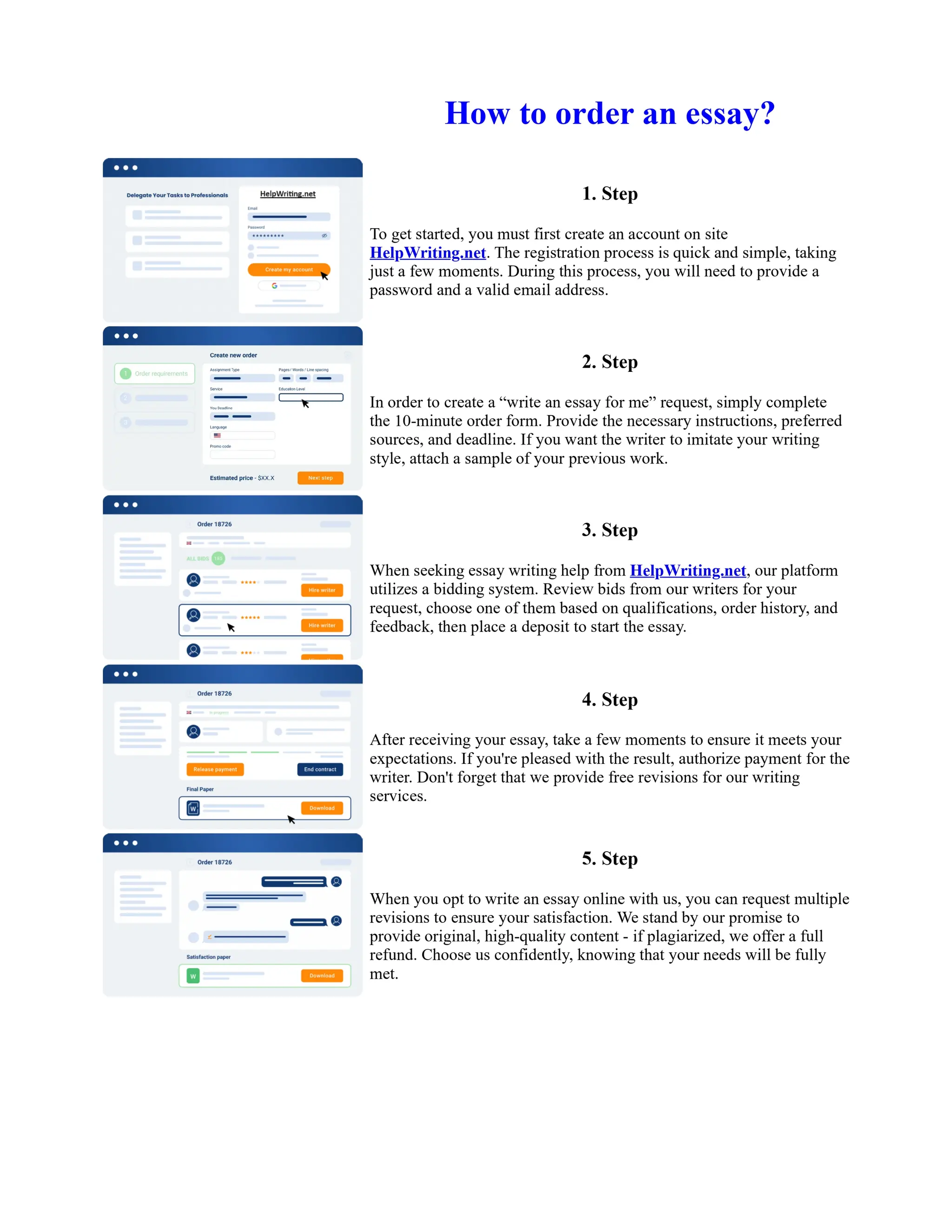
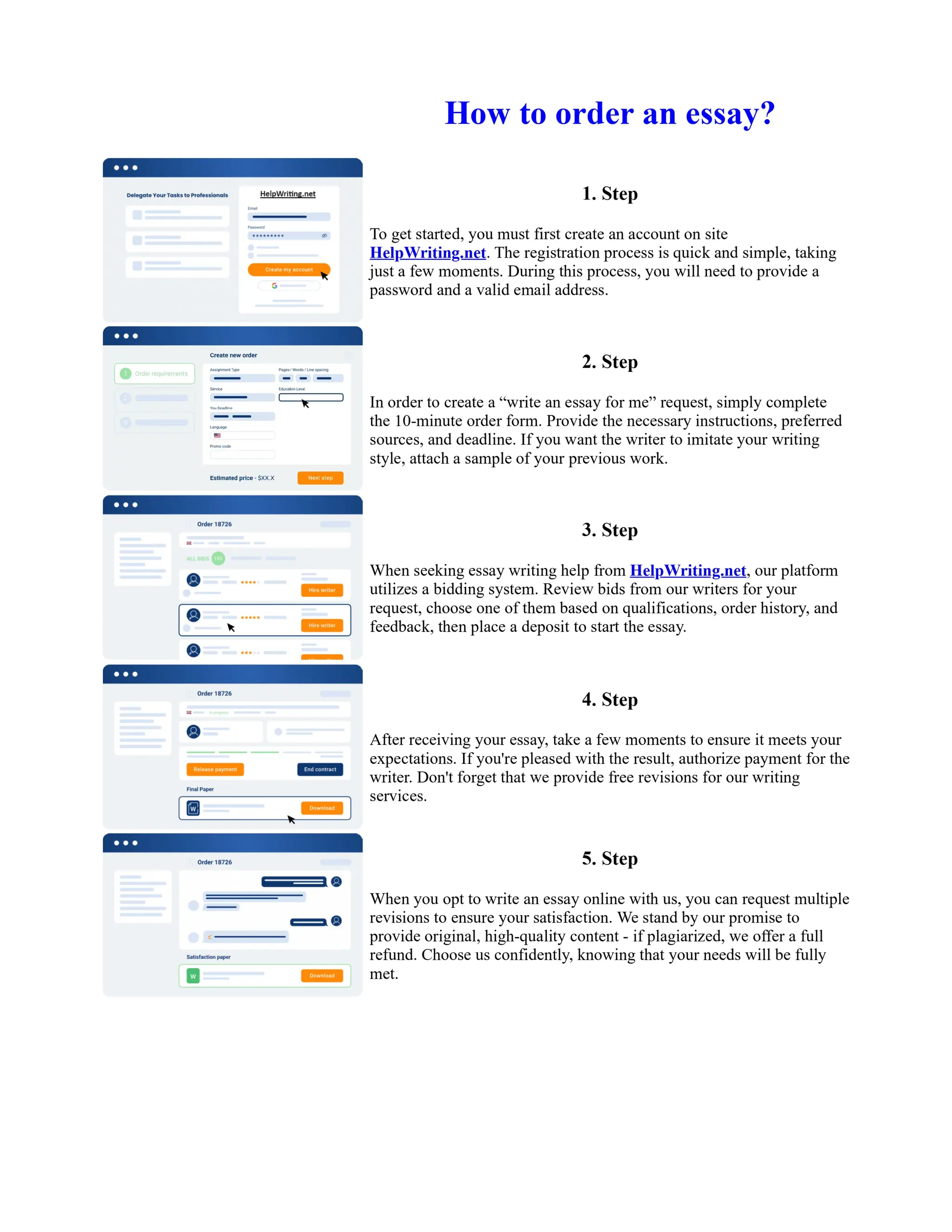
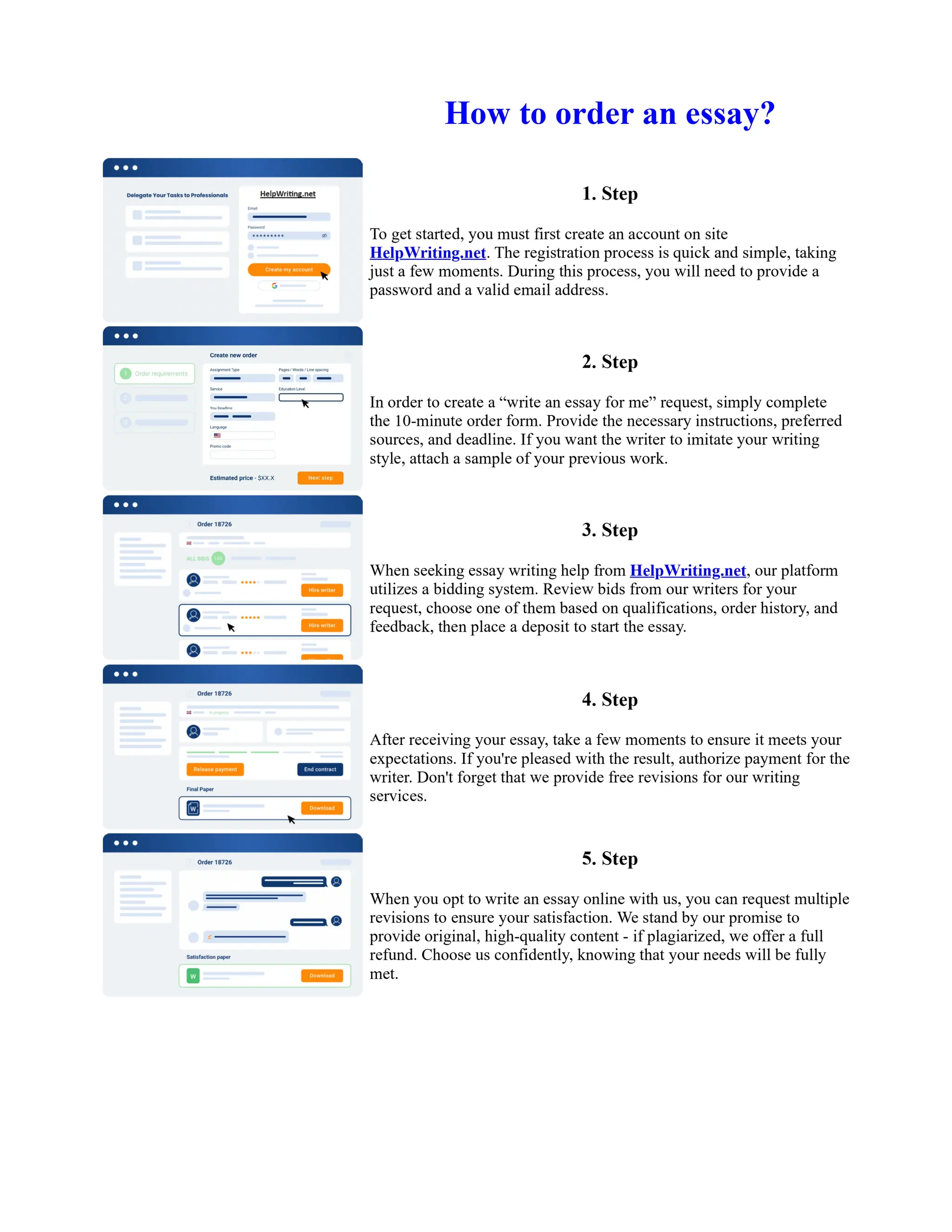
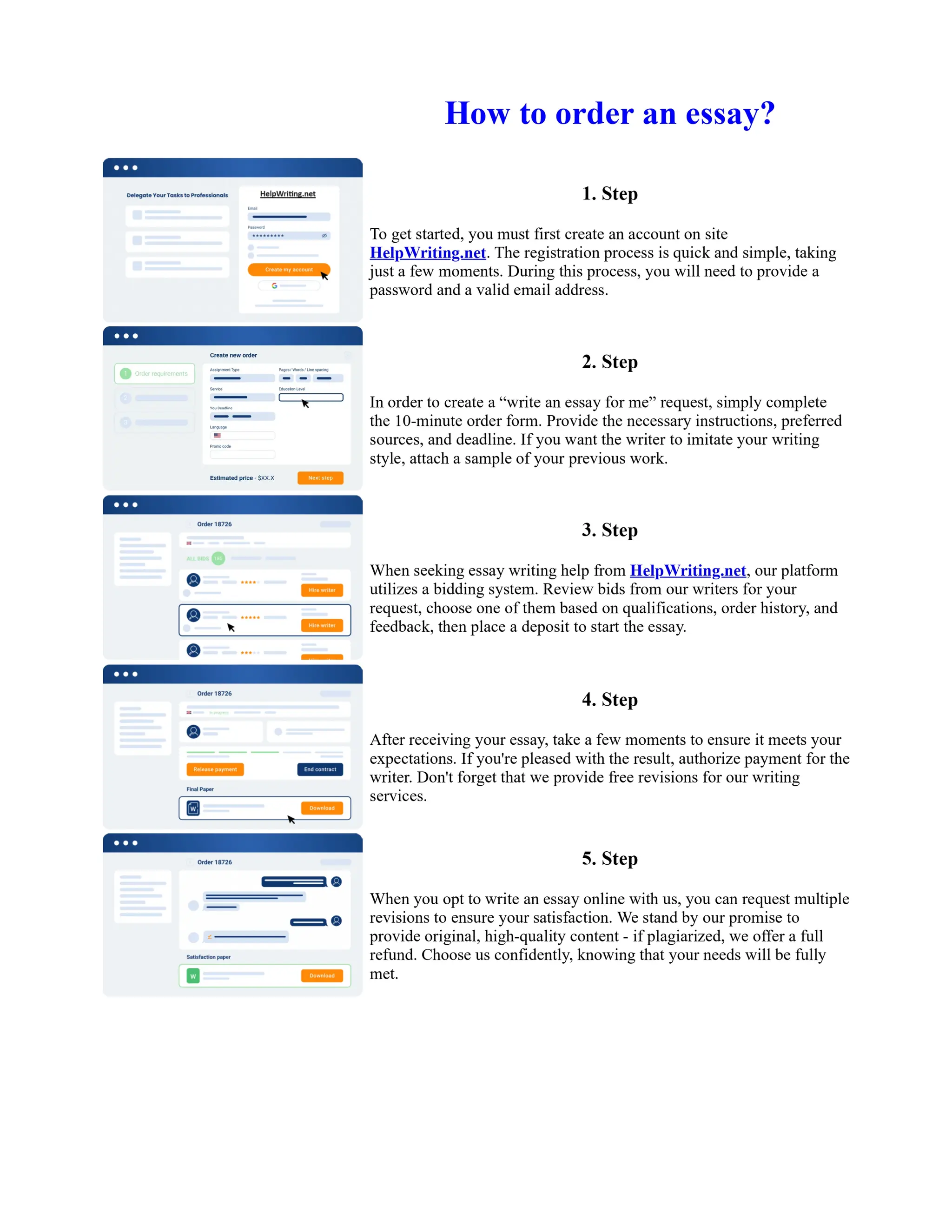
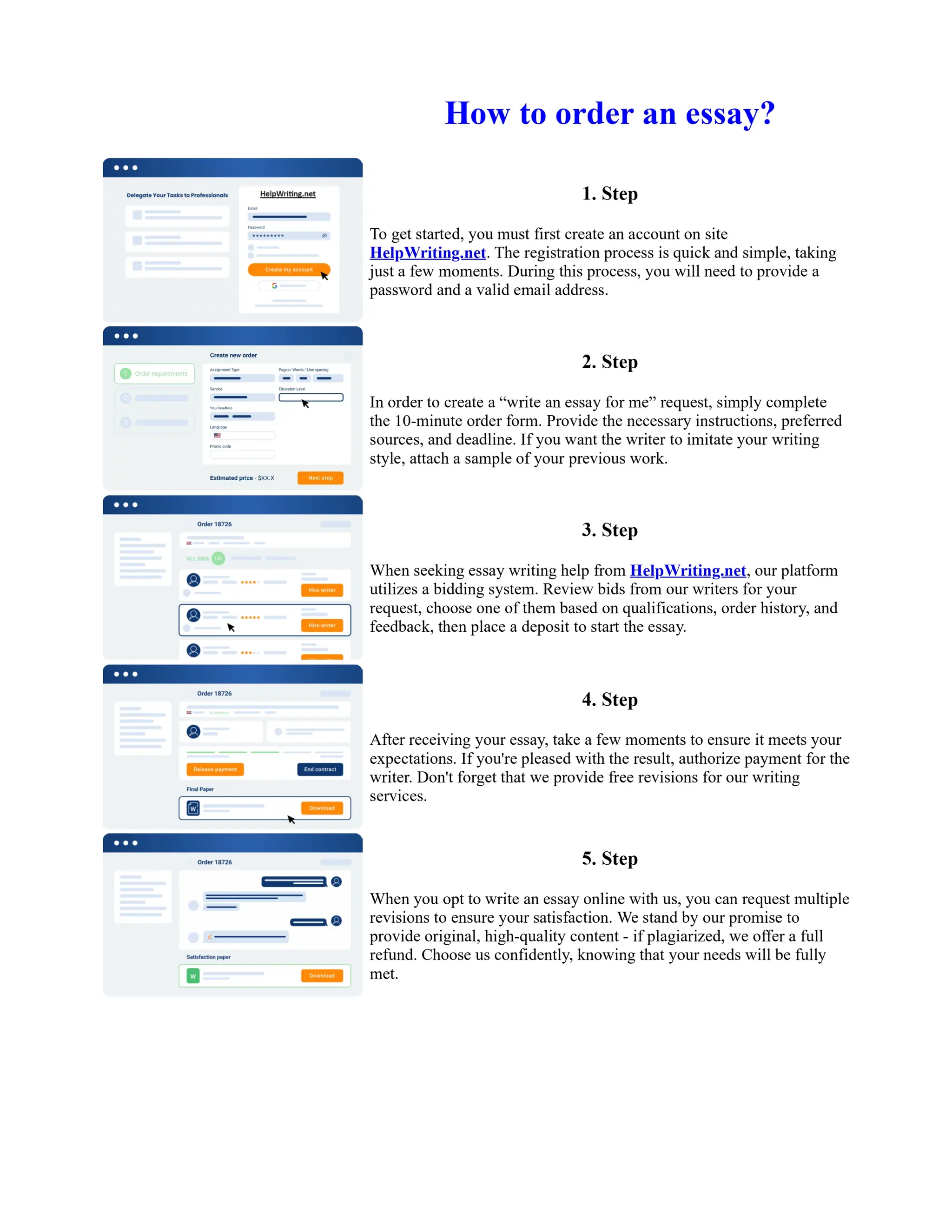
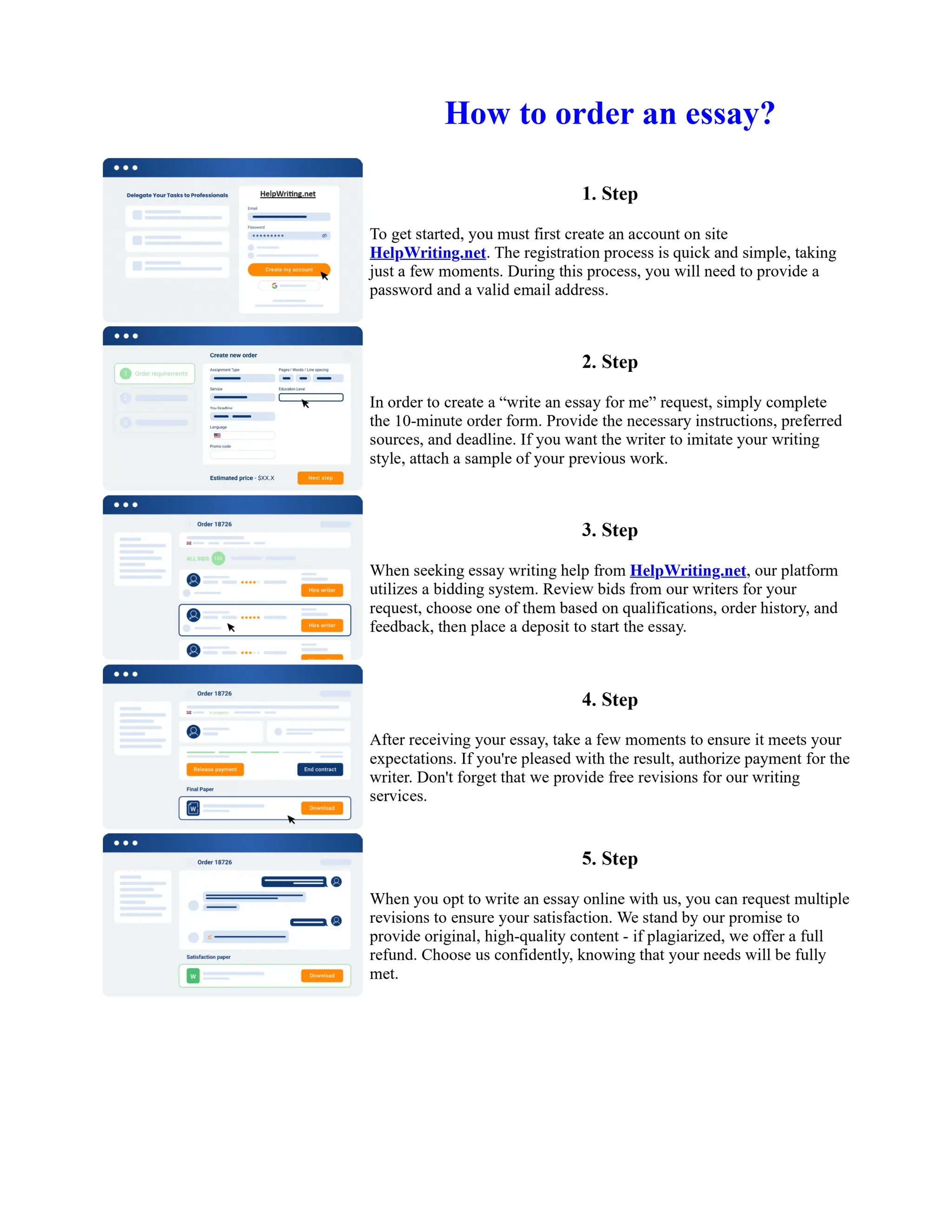
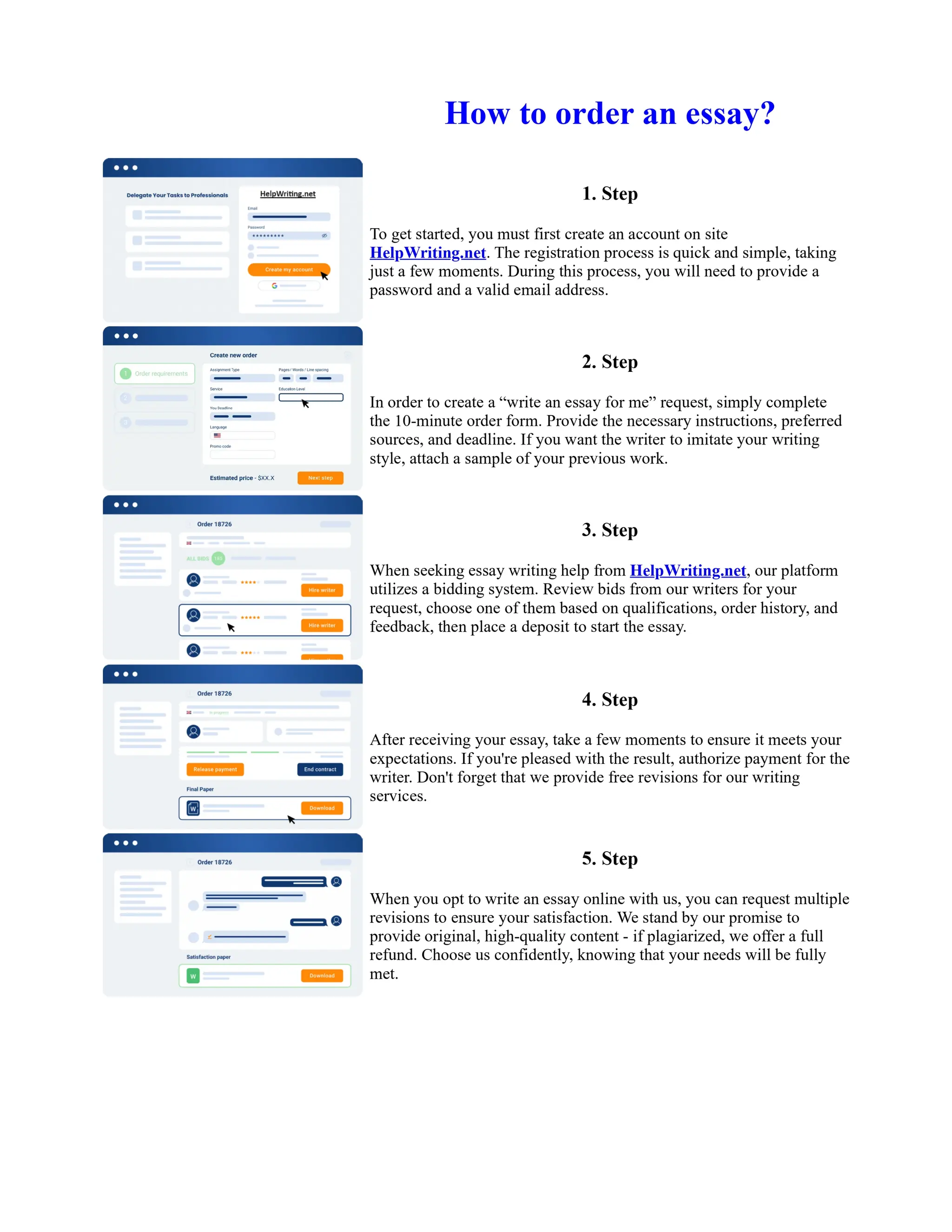
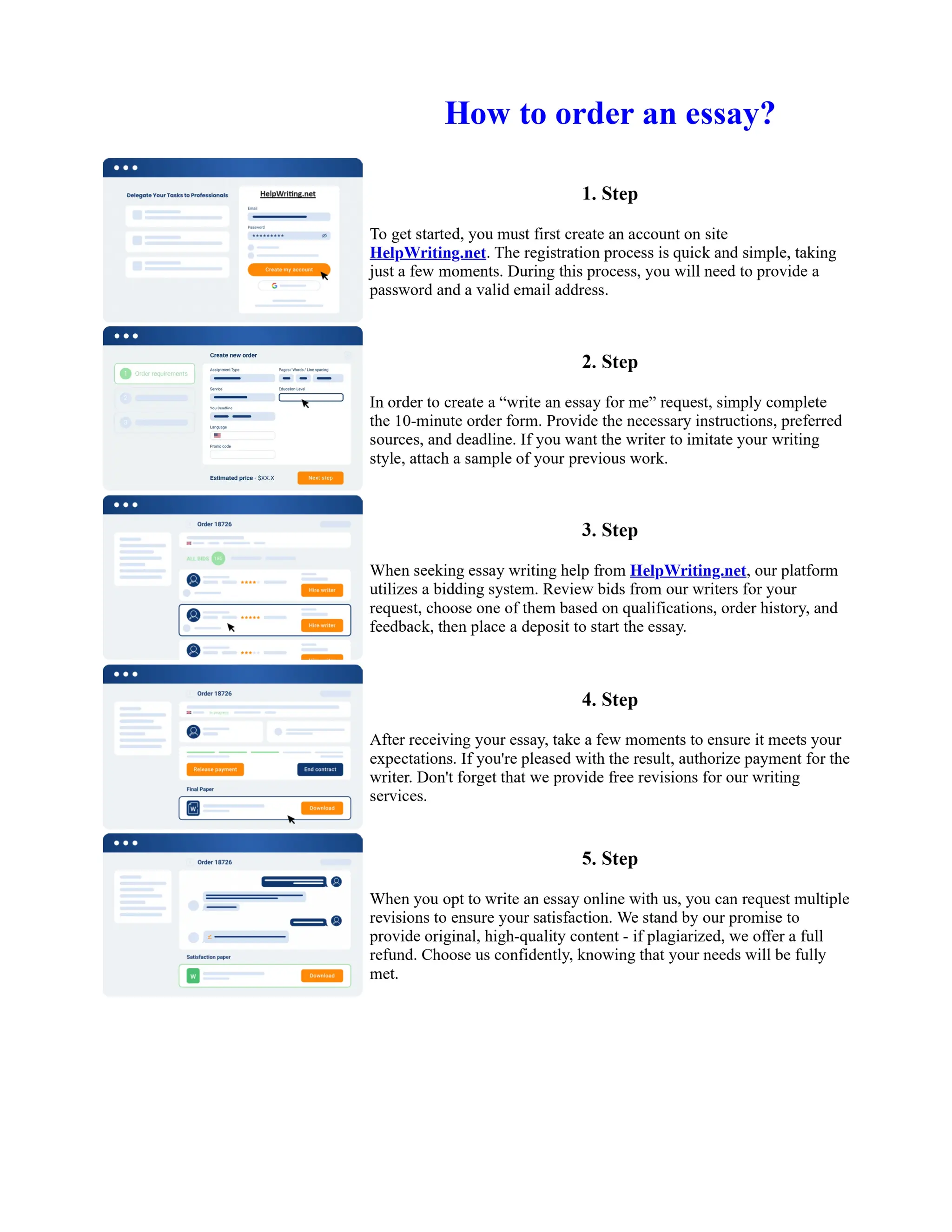
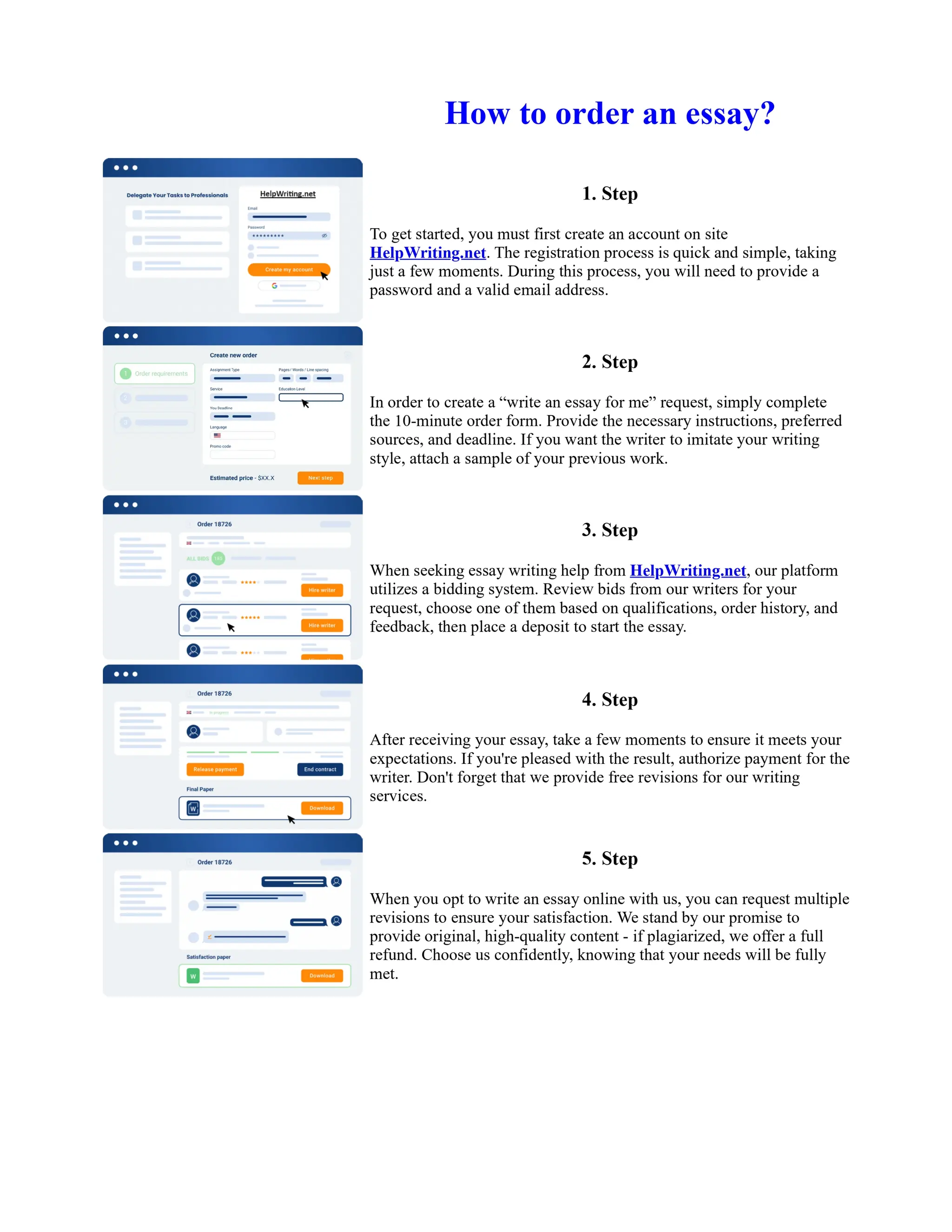
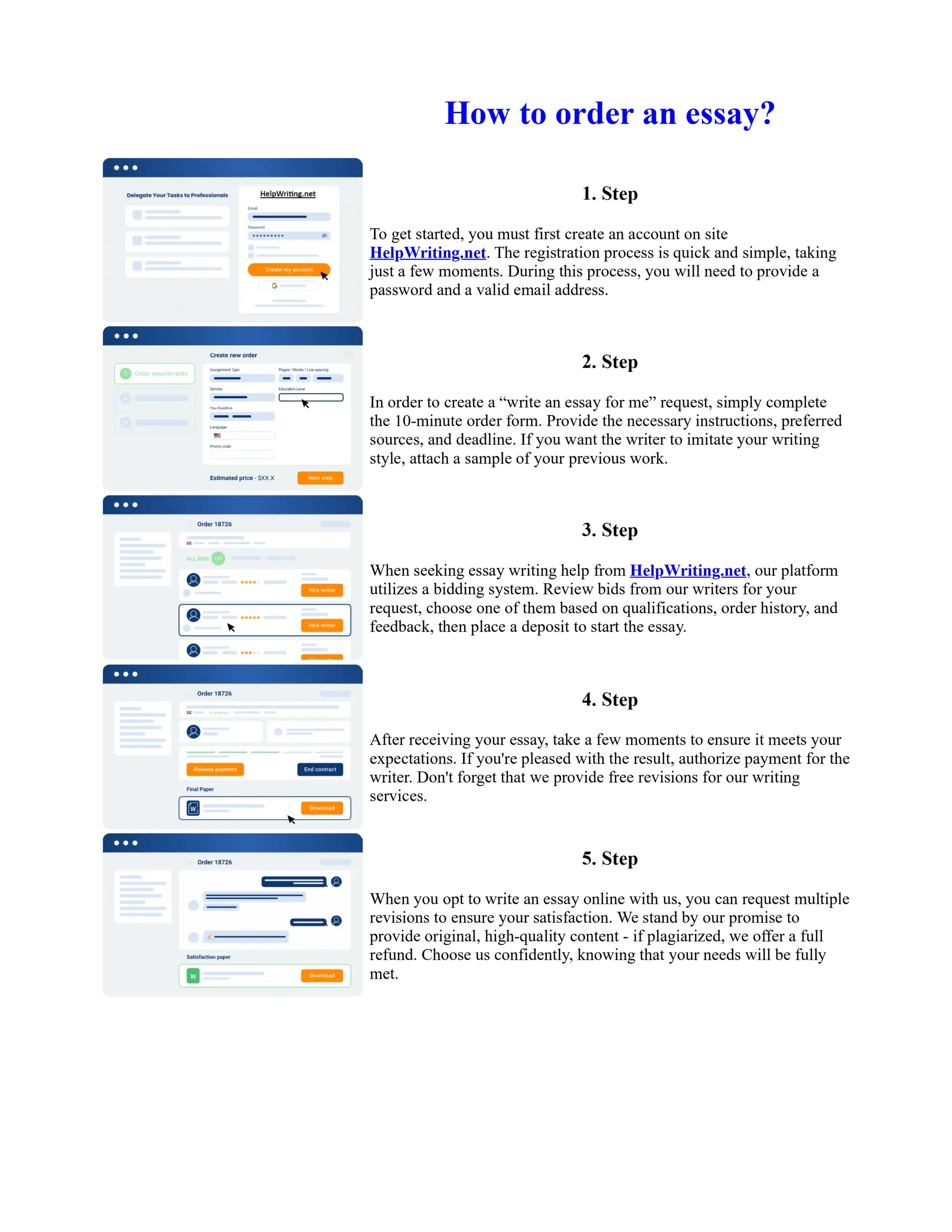
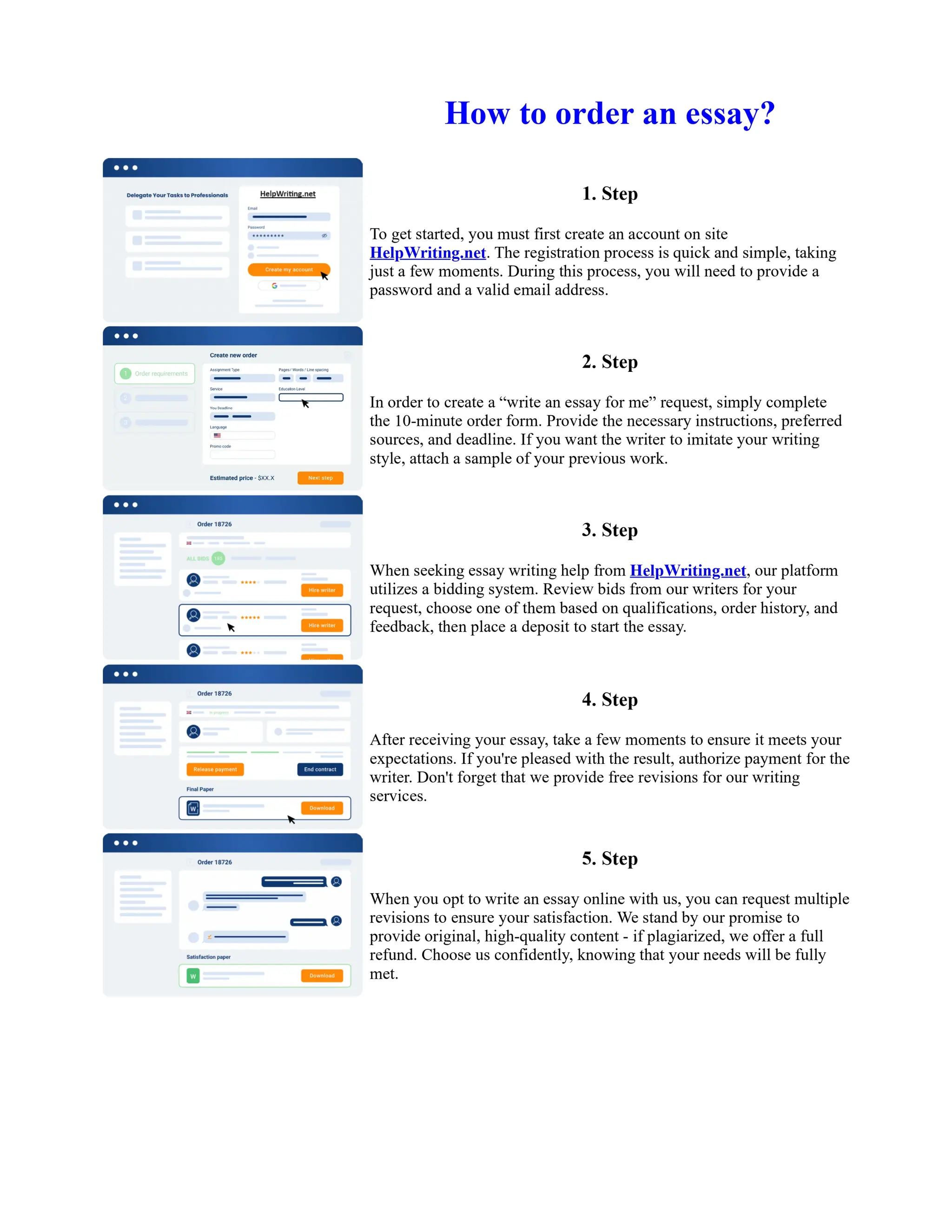
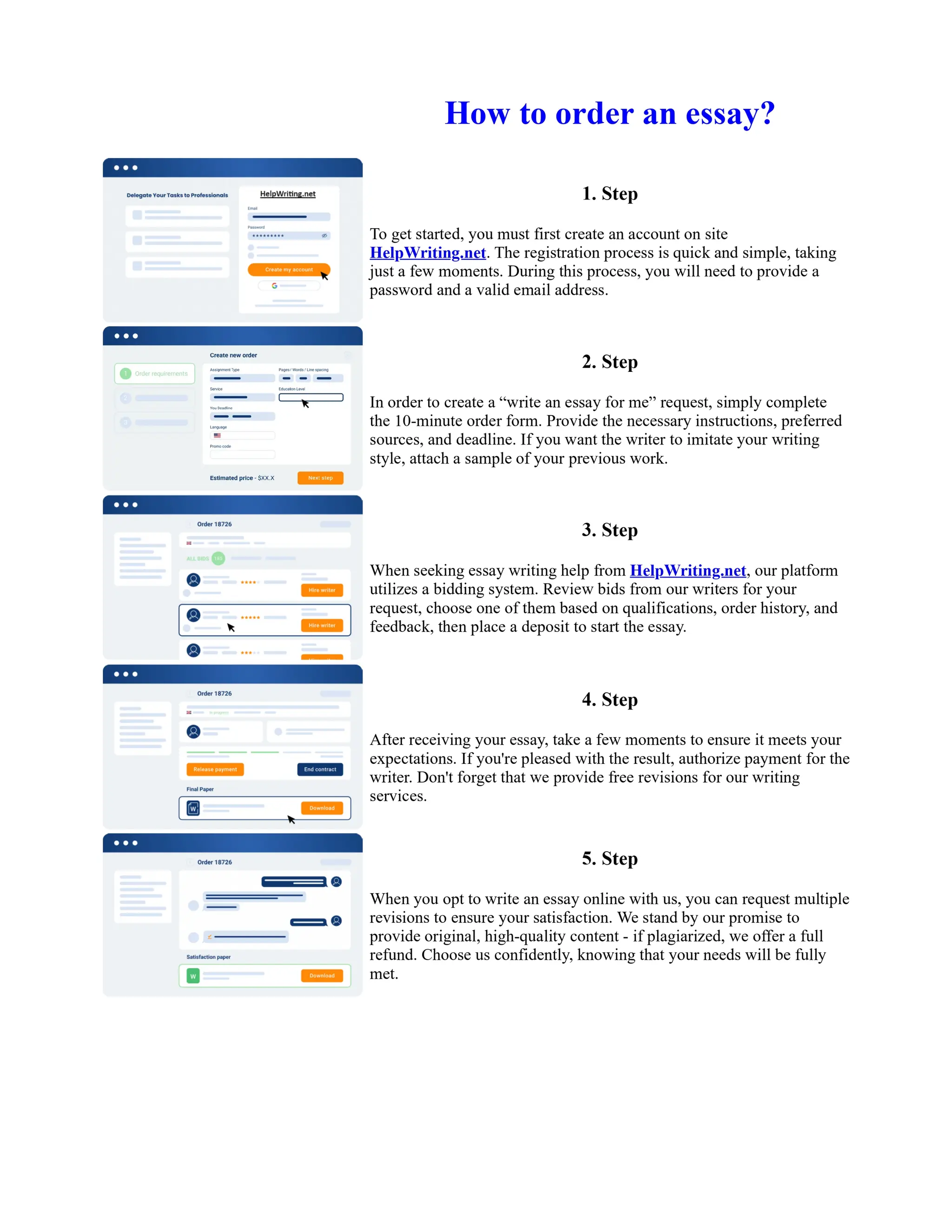
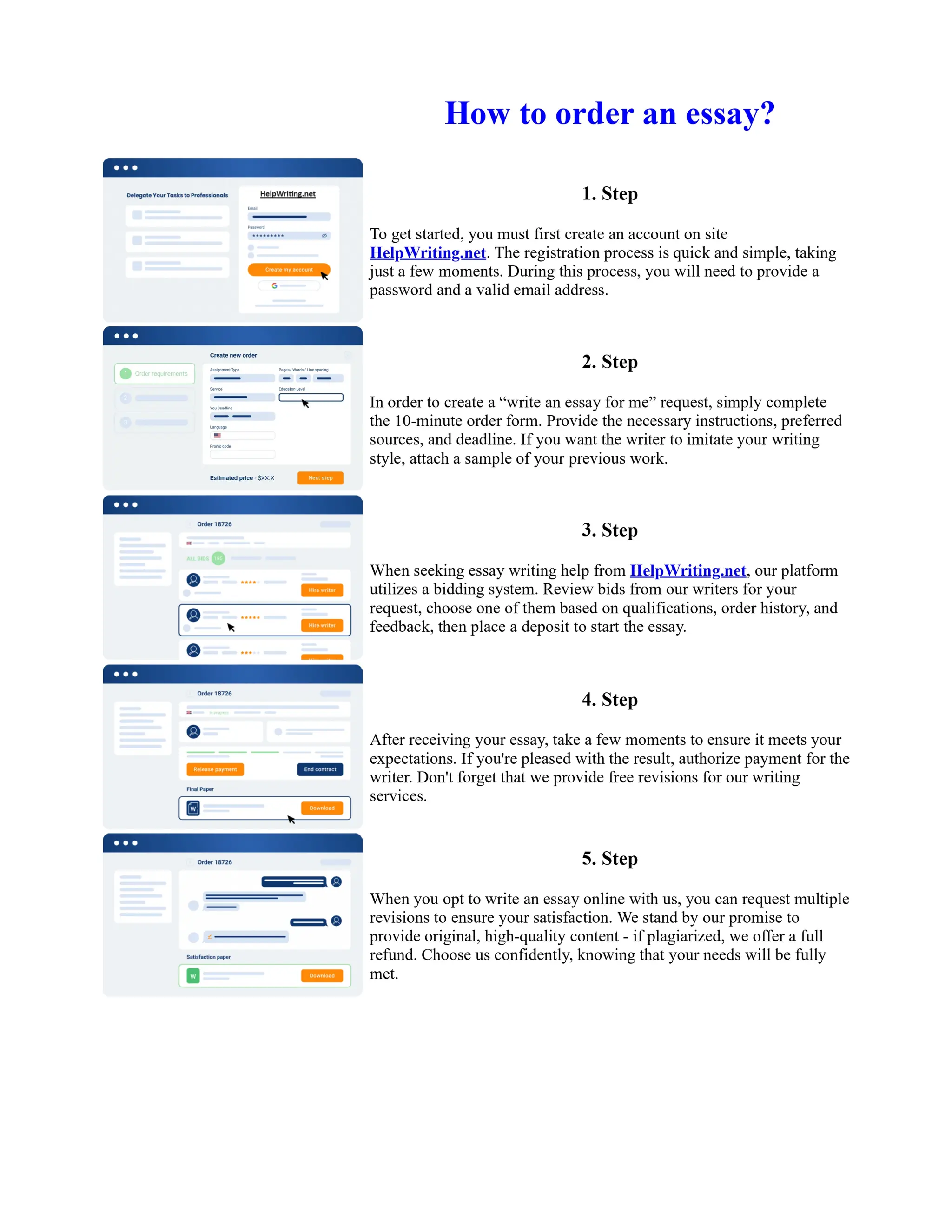
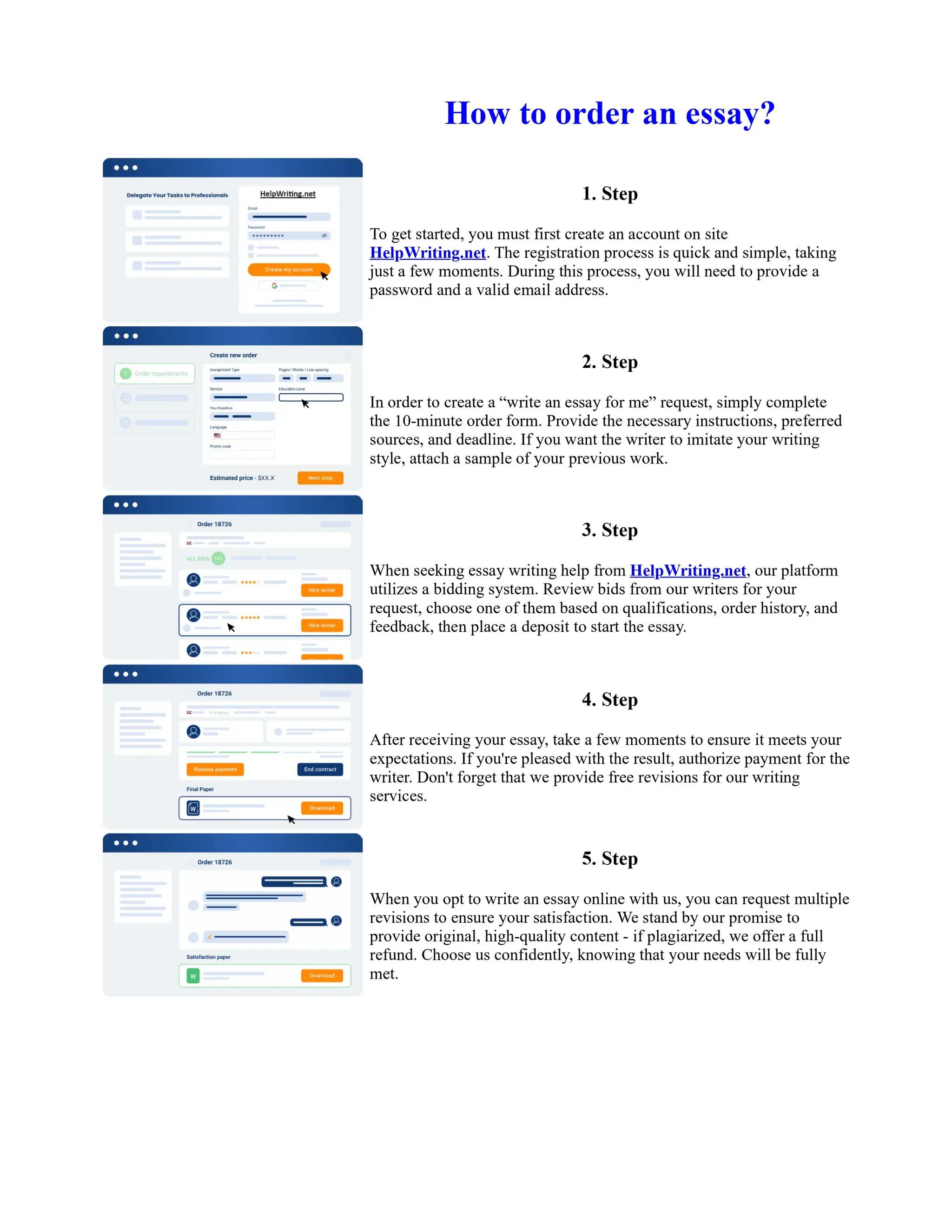
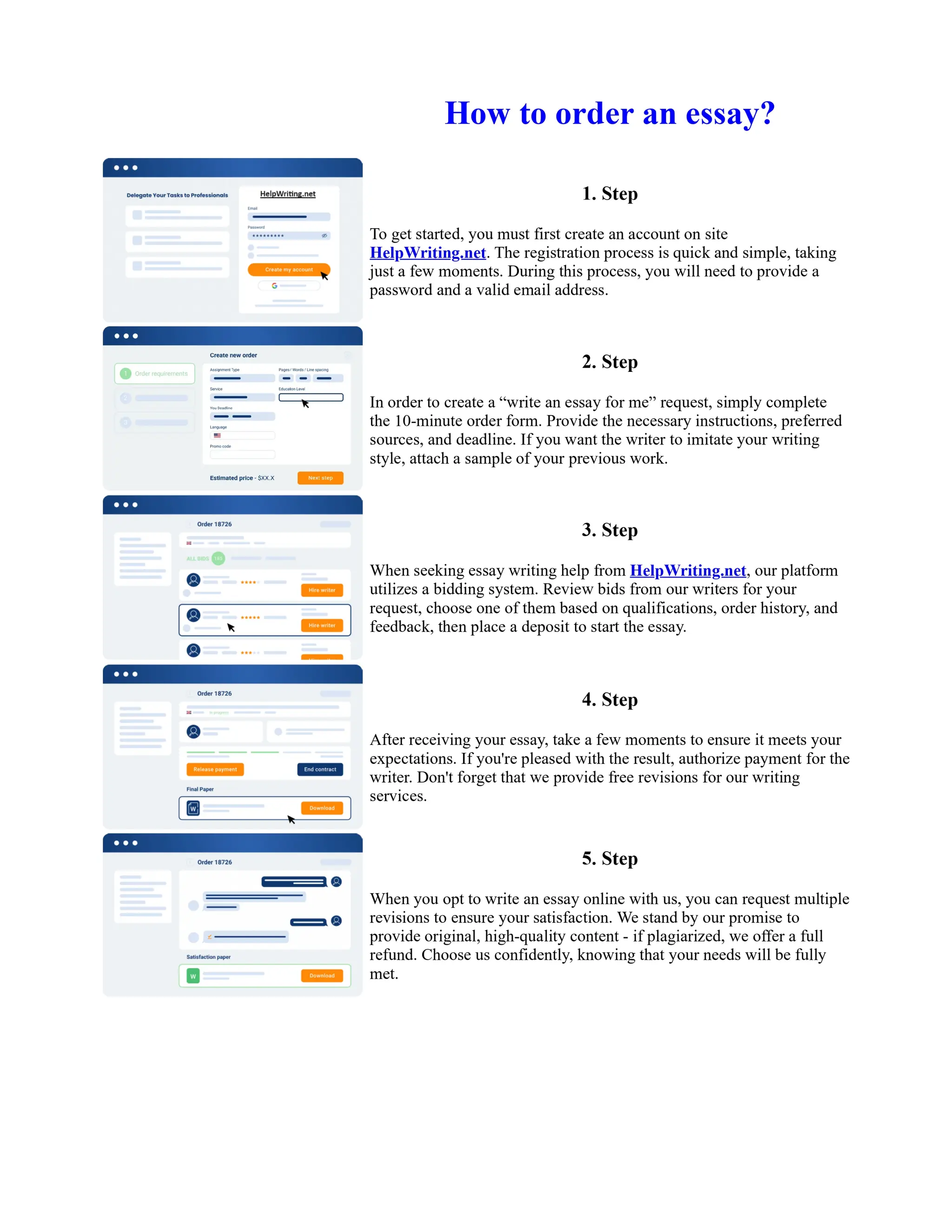
Tim Berners-Lee created HTML at CERN in the 1980s, laying the foundation for the modern internet. As a simple markup language, HTML allowed researchers to share documents over early computer networks by defining common tags to structure and format text-based content. Though limited in capabilities, HTML established a common language that could be understood by any computer or operating system. This open standard enabled the World Wide Web to rapidly expand and evolve into the vast digital network it is today, fundamentally transforming how people access and share information on a global scale.

![The Son of God in Milton’s Paradise Lost: Taking One for...
The Son of God in Milton's Paradise Lost: Taking One for the Team Among those familiar with the
Judeo–Christian belief system, Jesus is normally accepted as a selfless figure, one who became
human, suffered, and was put to death out of divine love for humanity. In his portrayal of the Son of
God in Paradise Lost, John Milton does not necessarily disagree with the devotion or love present in
the Son. His characterization of the Son does not oppose this tradition; rather, it is simply different.
By Milton's portrayal, the Son has an acute craving for attention, a desire for gory revenge over
Death, and an appetite for glory. Furthermore, while the Son, after accepting the task of becoming
mortal and dying to save Adam's descendants, ... Show more content on Helpwriting.net ...
That one exceptional individual, of course, is the Son. His acceptance implies, then, that his "love
and charity" surpass that of any of the angels. Perhaps to a Christian this is true, but for the Son to
see so readily in himself a previously impossible amount of love (as the Father's language suggests)
is not a particularly humble act.
It is possible, though, to see the Son's narcissism as being more apparent in the language he uses to
accept his responsibility than from the acceptance itself. As such, we ought to examine that
language: the manner in which the Son accepts the challenge is even more loaded and
selfreferential. He makes mention to himself six times in three lines of his acceptance speech (my
italics):
Behold me, then, me for him, life for life
I offer, on me let thine anger fall;
Account me man; I for his [man's] sake will leave
Thy bosom... (3.236–9)
In addition to mentioning himself repeatedly, the Son uses a key phrase: "Behold me." The first nine
lines (3.227–35) of his speech are about Grace's speed and universality; as soon as he mentions
himself, however, his rhetoric changes, describing the dread power of Death and how he plans to
vanquish Death. Grace, which comes from the Father, seems to come quite naturally ("finds her
way... unprevented, unimplored, unsought" (3.229–31), while to crush Death requires more of an
effort "'on me let Death wreak all his rage... Death his death's wound shall then
... Get more on HelpWriting.net ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advantagesoftheextensiblemarkuplanguagexml-231113203411-0c2ba1ae/75/Advantages-Of-The-Extensible-Markup-Language-XML-3-2048.jpg)

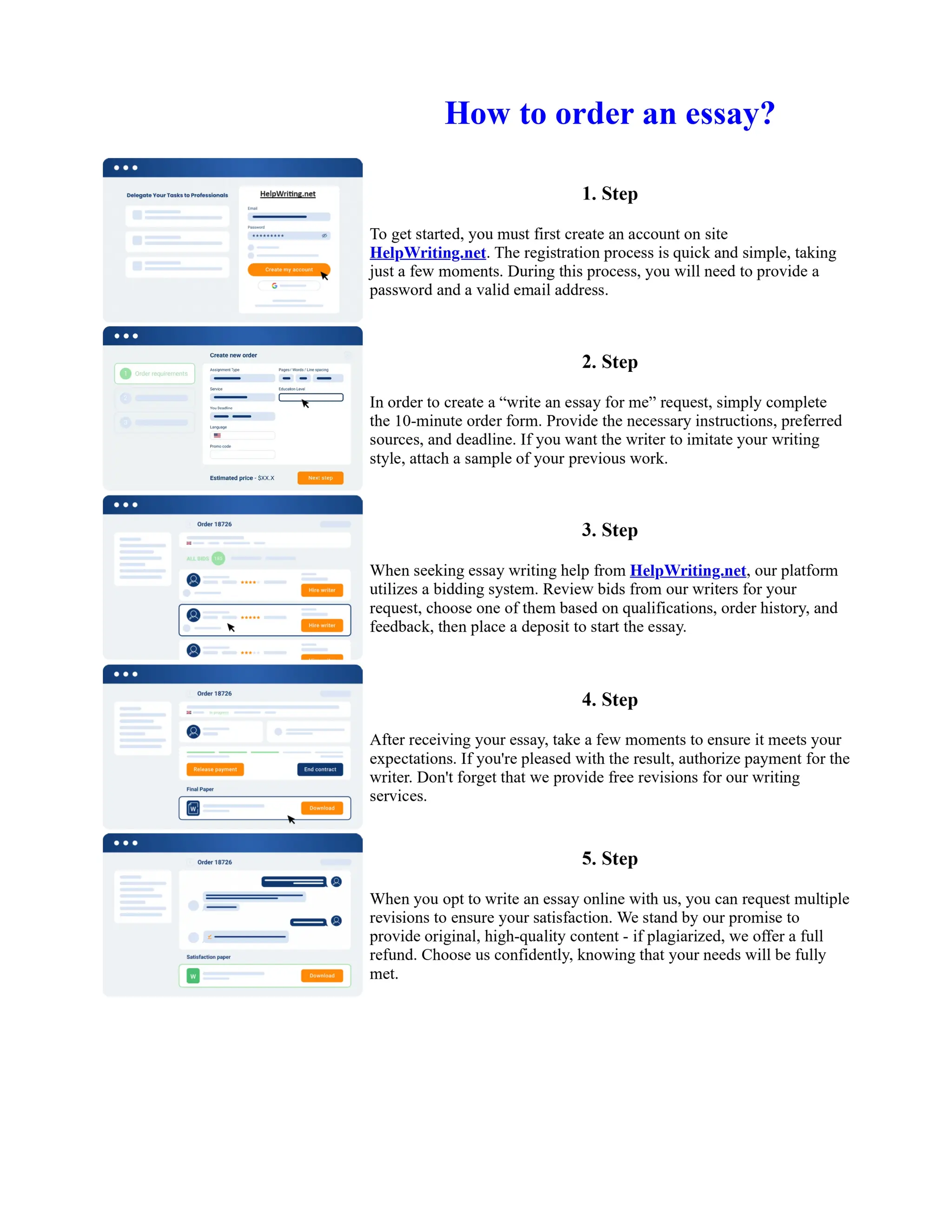

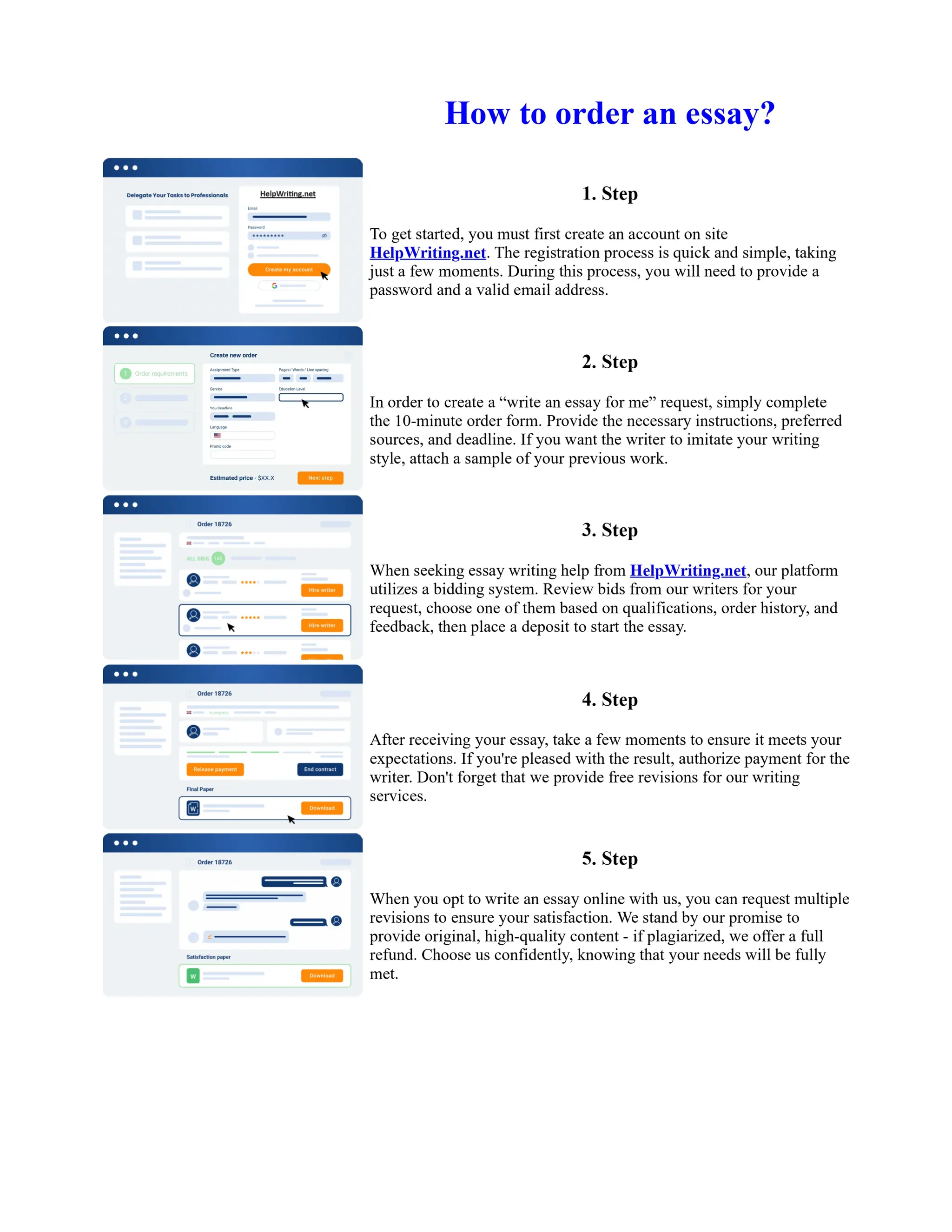

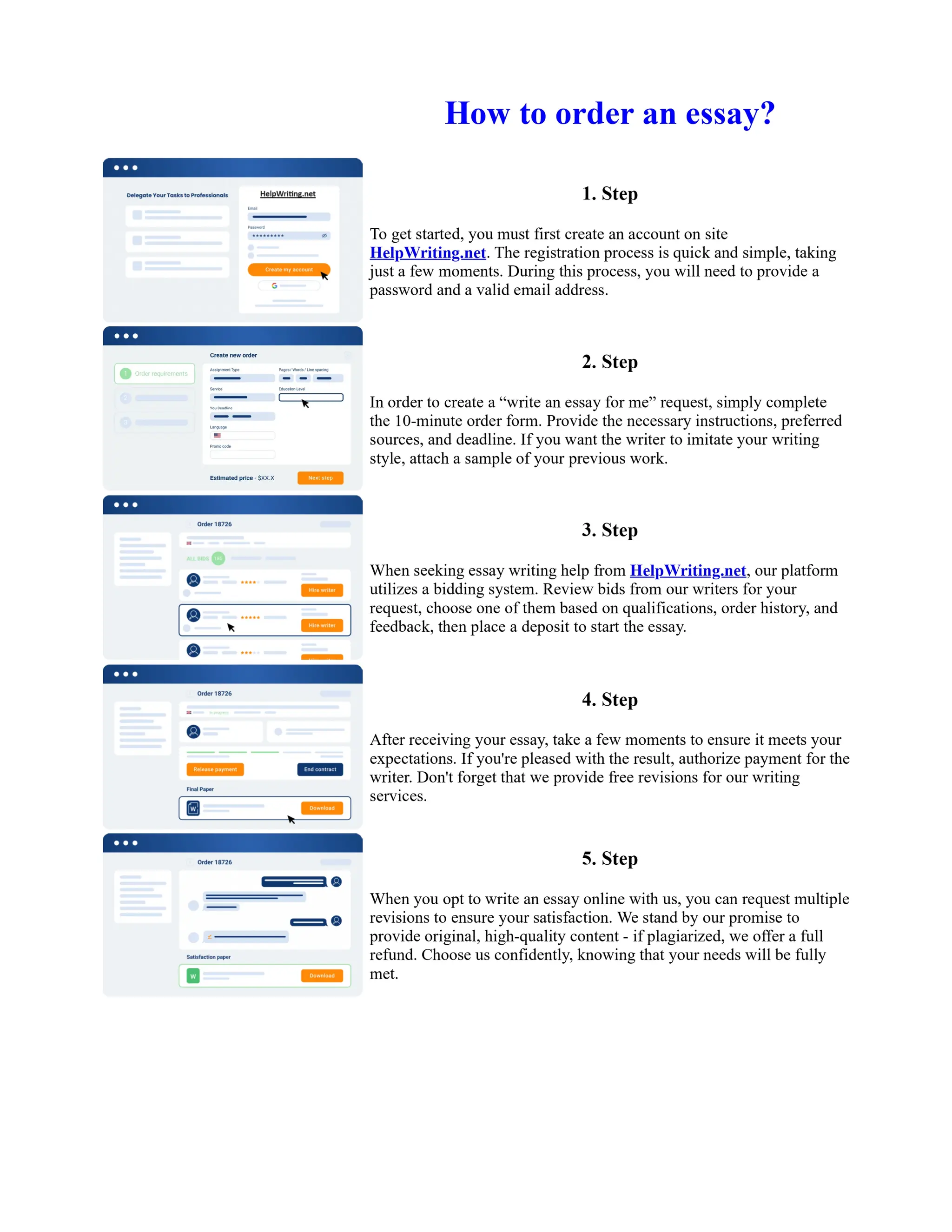

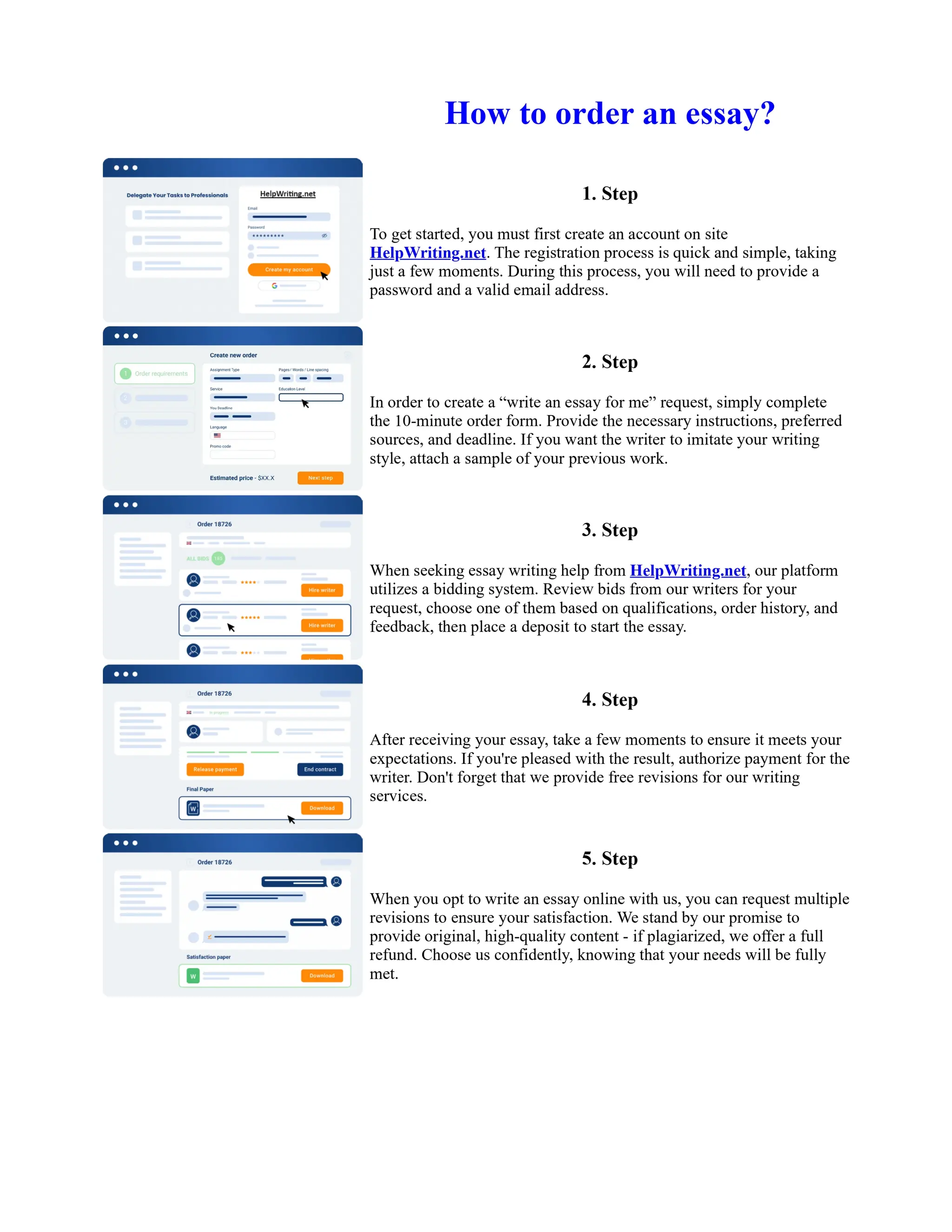

![Prepare for Sbi Po Exam 2013 in 60 Days
SBI PO Exam Preparation – 60 days Plan
By Varun Reddy
@ www.BankExamsIndia.com
[Get ready to crack the probationary officer exam in State bank of India with the help of very
detailed, topic wise, chapter wise materials prepared by a young aspirant.]
2
SBI PO Preparation Plan (60 days) by Varun reddy | Published @ http://www.BankExamsIndia.com
Materials Required for SBI PO exam preparations: The plan has been prepared by taking into
considerations the chapters present in the books given below. You may also refer similar books but
whether it would cover the chapters in–depth or not is unknown.(These books are available online as
well whose links are given below)
REASONING: Magical book series ANALYTICAL REASONING by M.k pandey – ... Show more
content on Helpwriting.net ...
Non Verbal reasoning–series: 5 figure series.
Number system.
Vocabulary (Norman Pratiyogita DarpanLewis: word power Nov2012 issue: Current made easy)
affairs. Revision (1–5). Grammar (By Wren and martin) – Parts of speech: Articles.
Number system.
Vocabulary (Norman Pratiyogita DarpanLewis: word power Dec2012 issue: News made easy) and
events. Revision (1–5). Grammar (By Wren and martin) – Parts of speech: Articles.
Number system.
Vocabulary (Norman Pratiyogita DarpanLewis: word power Dec2012 issue: Current made easy)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advantagesoftheextensiblemarkuplanguagexml-231113203411-0c2ba1ae/75/Advantages-Of-The-Extensible-Markup-Language-XML-15-2048.jpg)








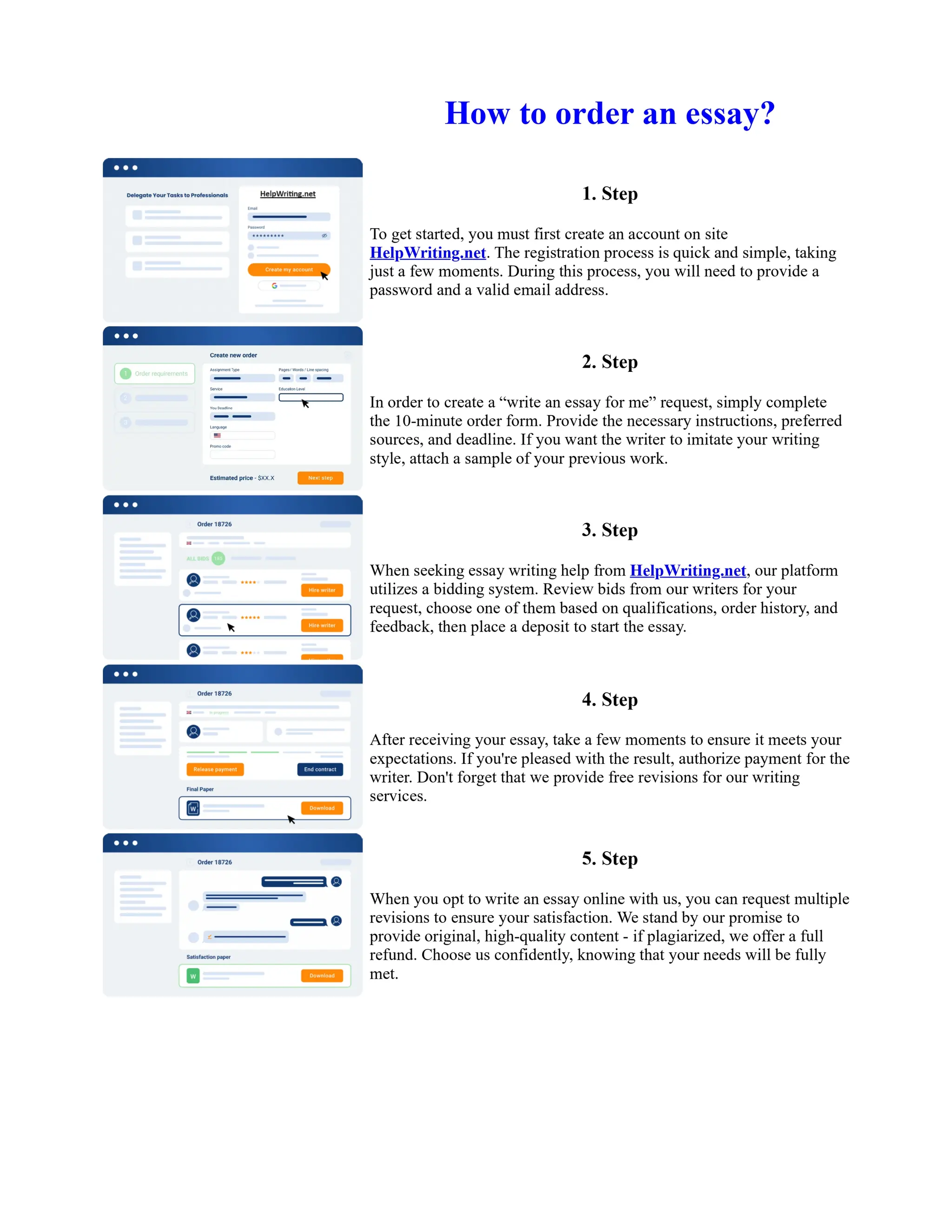

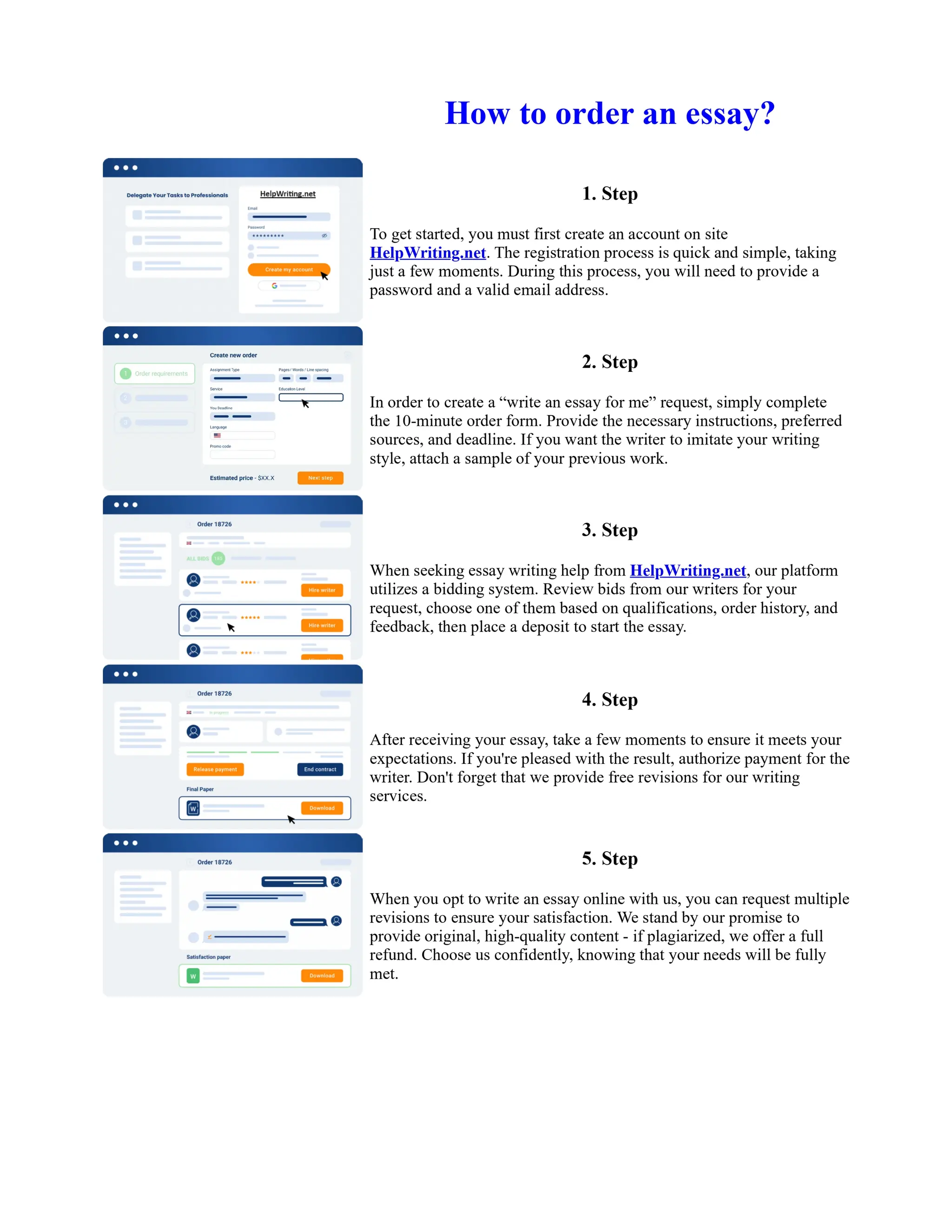

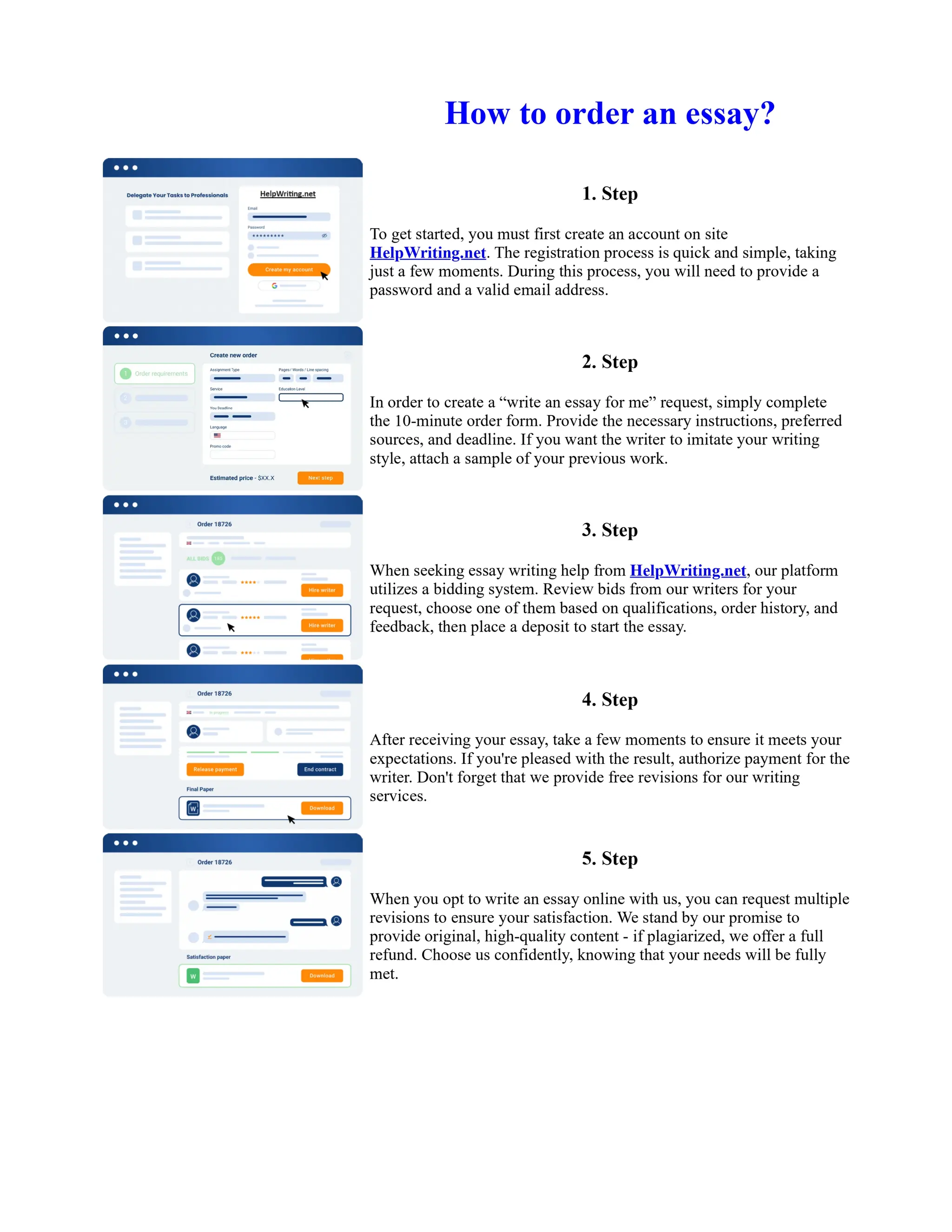

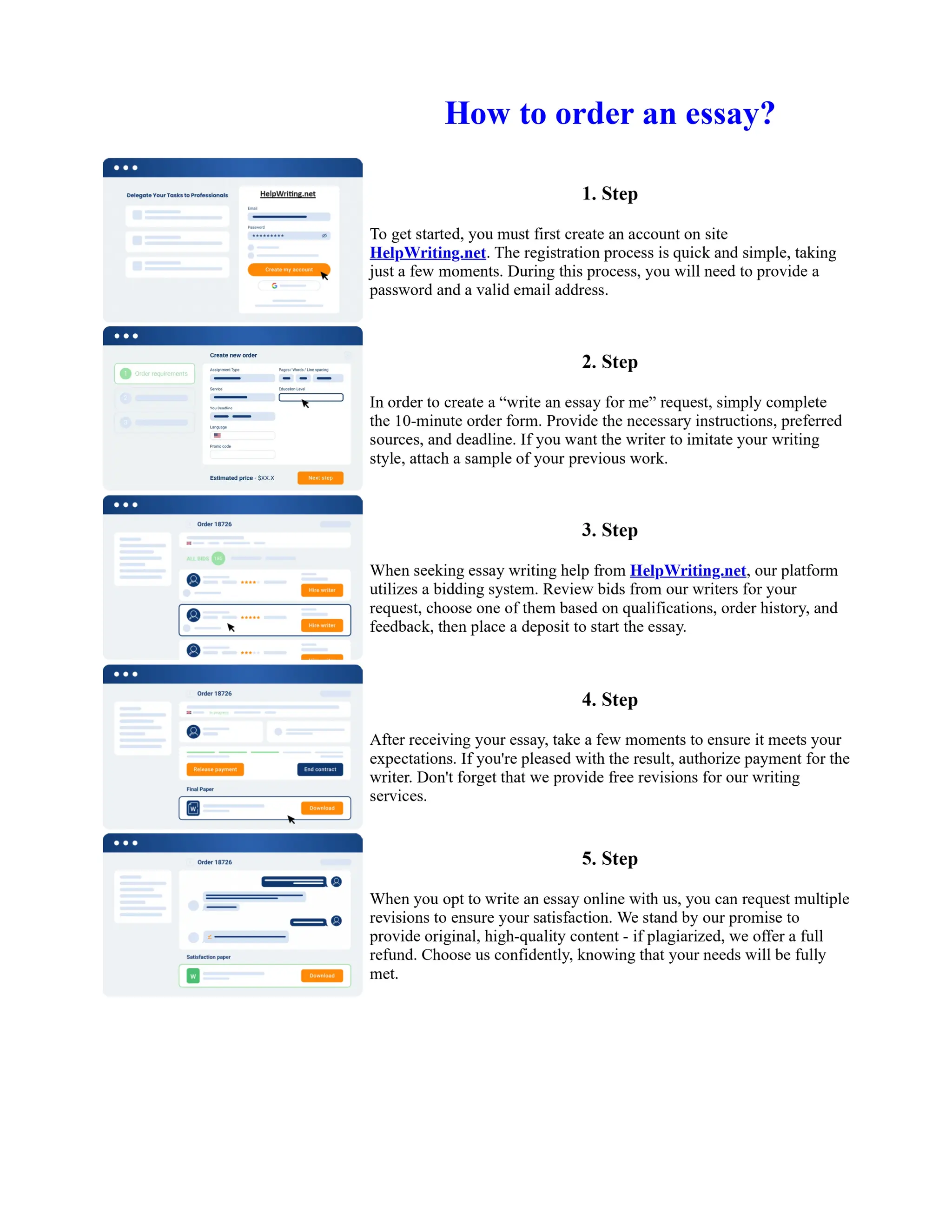



![The Sacred Language of Toni Morrison Essay
The Sacred Language of Toni Morrison
Toni Morrison makes a good point when, in her acceptance speech upon receiving the Nobel Prize
in Literature, she says, "Narrative . . . is . . . one of the principal ways in which we absorb
knowledge" (7). The words we use and the way in which we use them is how we, as humans,
communicate to each other our thoughts, feelings, and actions and therefore our knowledge of the
world and its peoples. Knowledge is power. In this way, our language, too, is powerful.
In her acceptance speech, Morrison tries to communicate the idea that we must be careful with how
we use our words. She analogizes the use of language to the life of a metaphoric bird in a tale of a
wise, old, blind ... Show more content on Helpwriting.net ...
Throughout her speech, Toni Morrison works towards defining and supporting this thesis of
responsibility. It is our responsibility, as users of words, to make language thrive. Elizabeth Fox–
Genovese has a similar goal, but takes a different approach in her essay "The Claims of a Common
Culture: Gender, Race, Class and the Canon." She speaks on the use and composition of the canon
taught in humanities classes. Her idea is that the canon of today is much too one–sided and does not
include the influence of the several different cultures, peoples, and ideas that make up our society.
She says that "with respect to representativeness, the canon fails woefully. It represent[s] a small,
sometimes minute, portion of the elite, which itself constitute[s] a statistical minority of the
population" (Fox–Genovese 19). In this abstract way, Fox–Genovese is reiterating Morrison's words
that what we say, and how we say it (or teach it), or what we fail to say (as in the canon taught
today) is monumentally influencing and impactful upon others.
If we are not aware of the words that come out of our mouths due to lack of thought or attention, we
all suffer and we are all at fault: "When language dies, out of carelessness, disuse, indifference, and
absence of esteem, or killed by fiat, . . . all users and makers are accountable for its demise"
(Morrison 14–15). The standards of society are changing and with them the
... Get more on HelpWriting.net ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advantagesoftheextensiblemarkuplanguagexml-231113203411-0c2ba1ae/75/Advantages-Of-The-Extensible-Markup-Language-XML-44-2048.jpg)


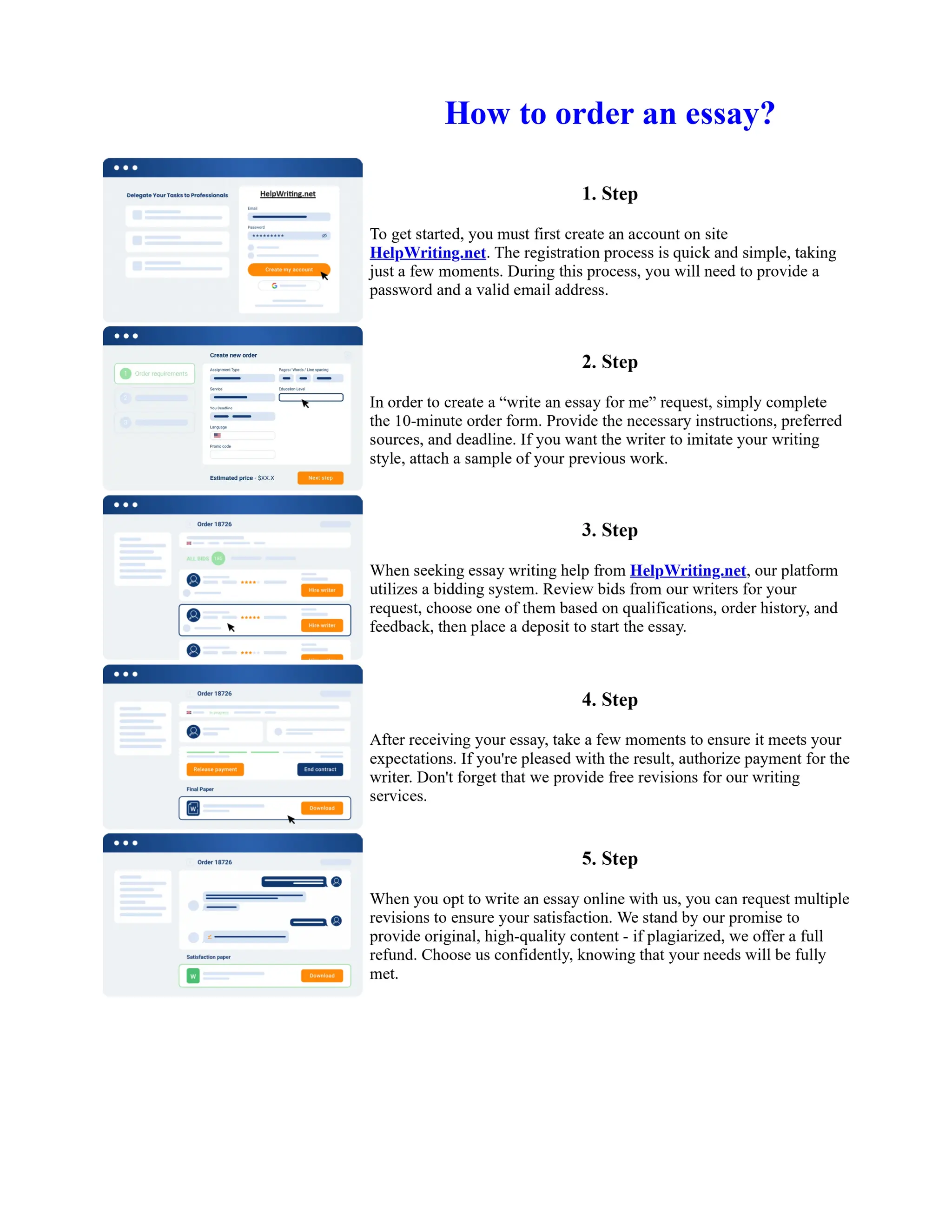

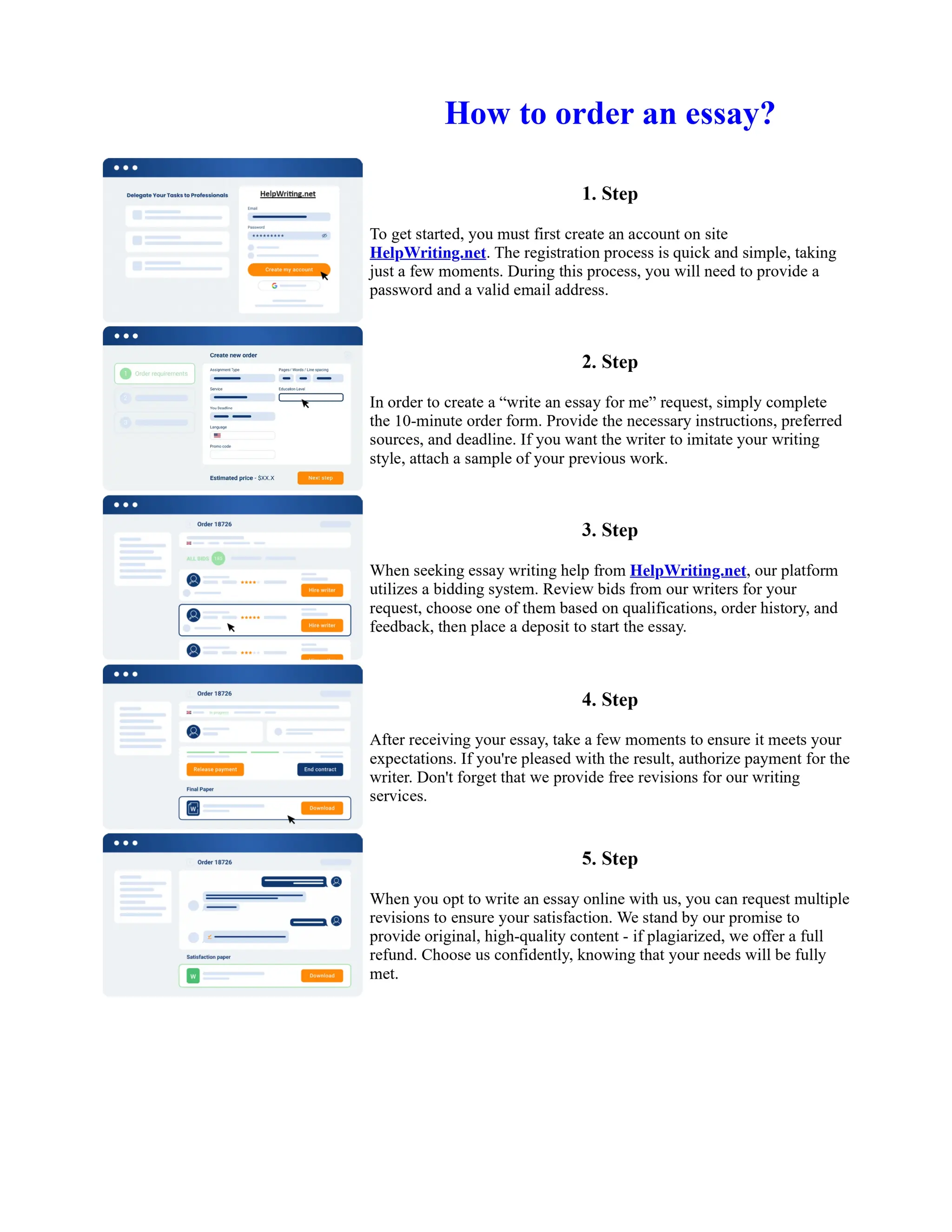

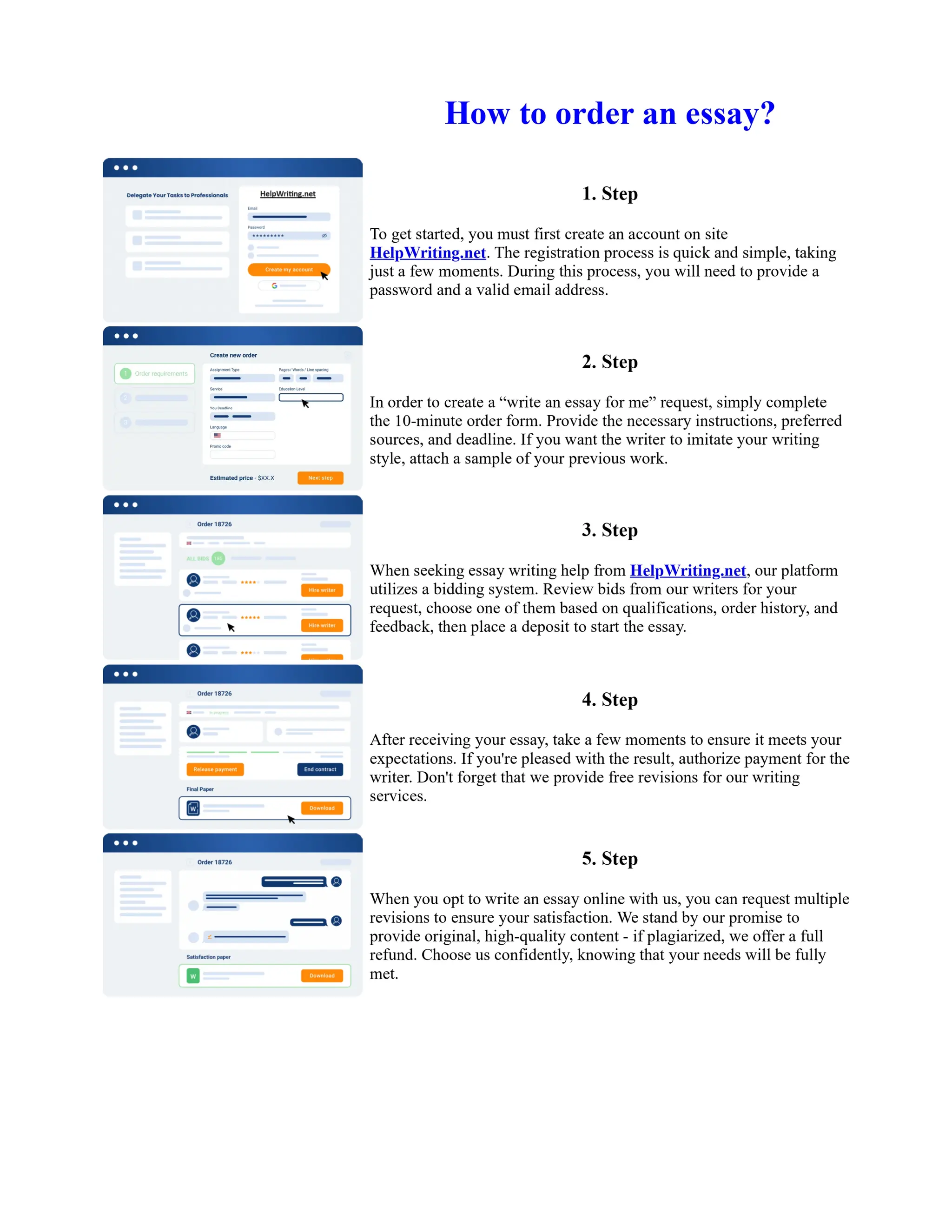

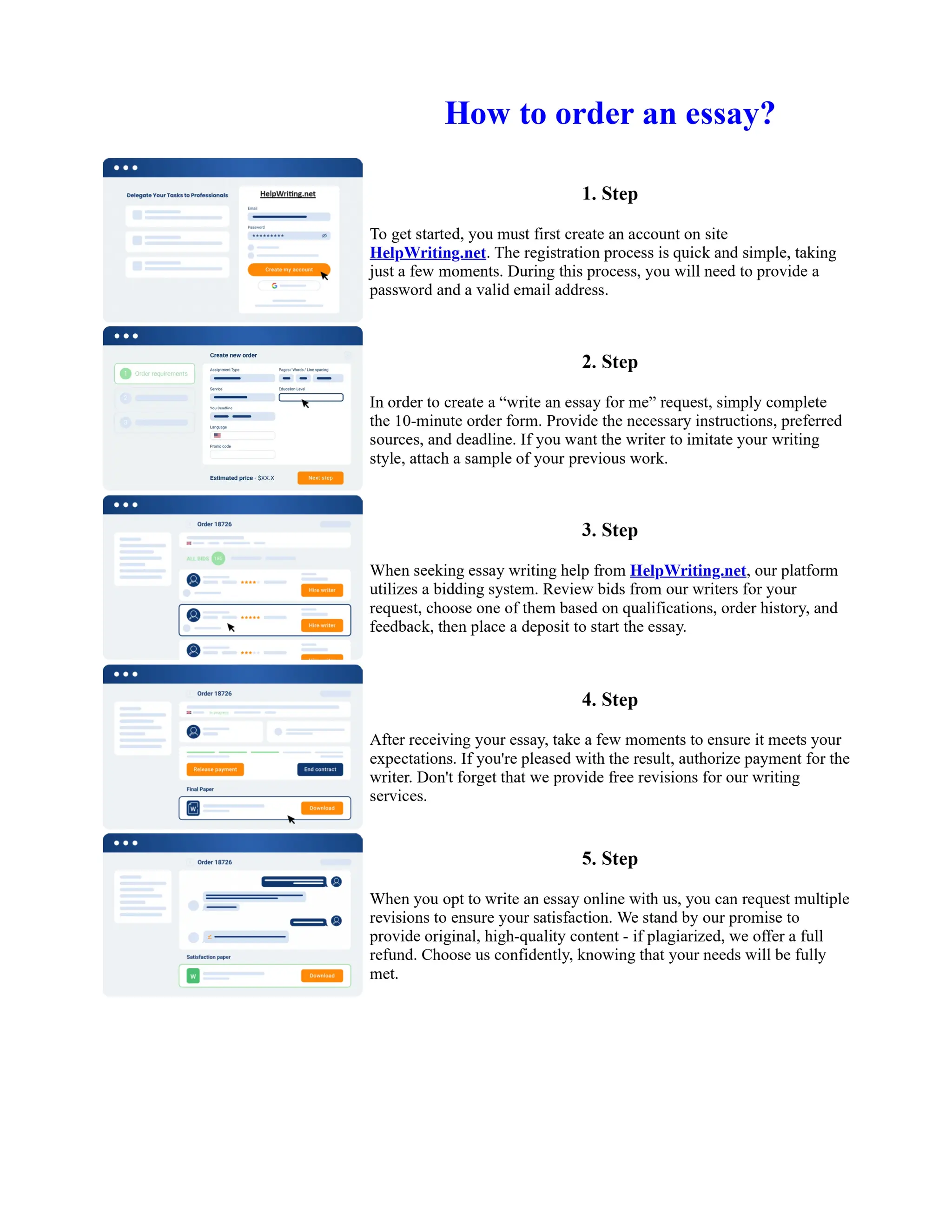

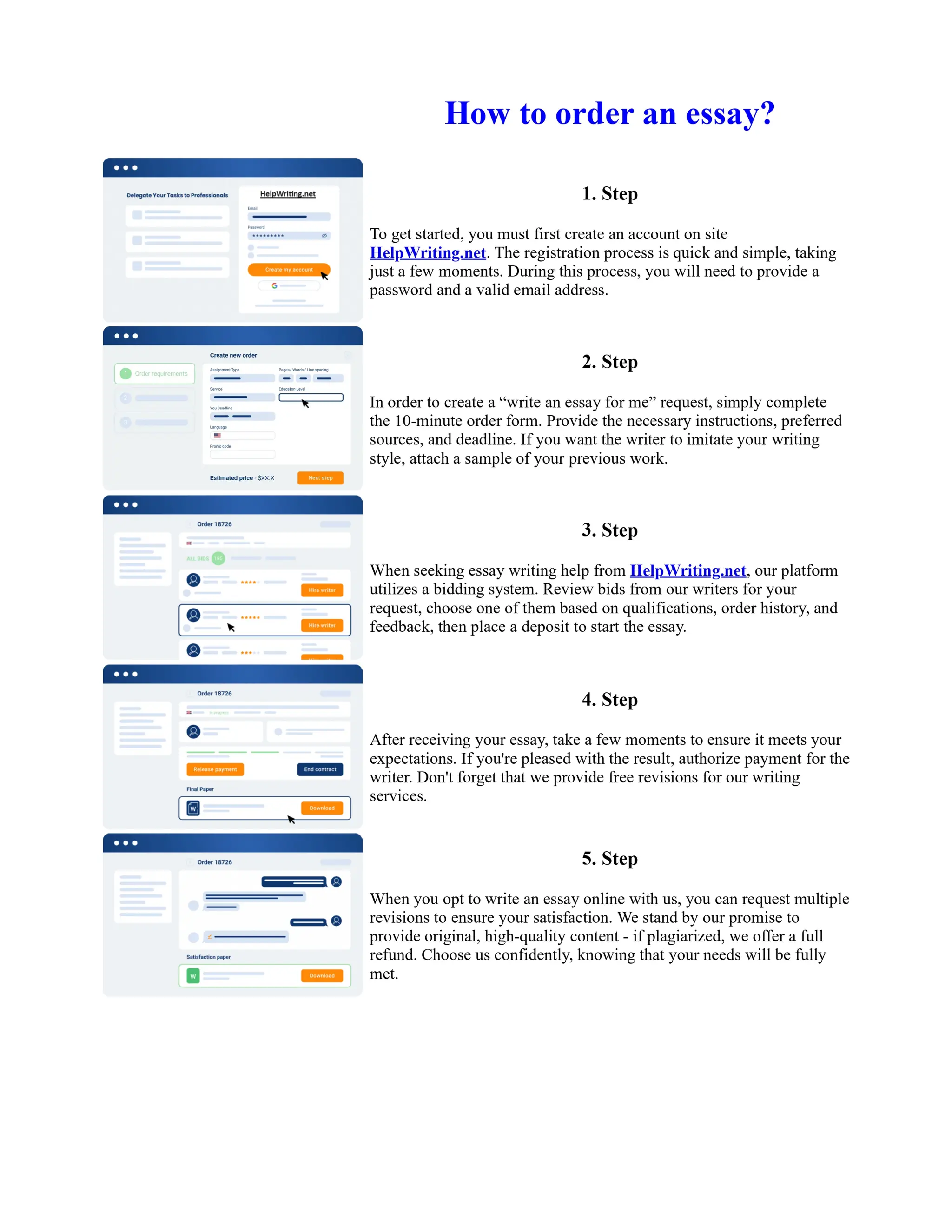

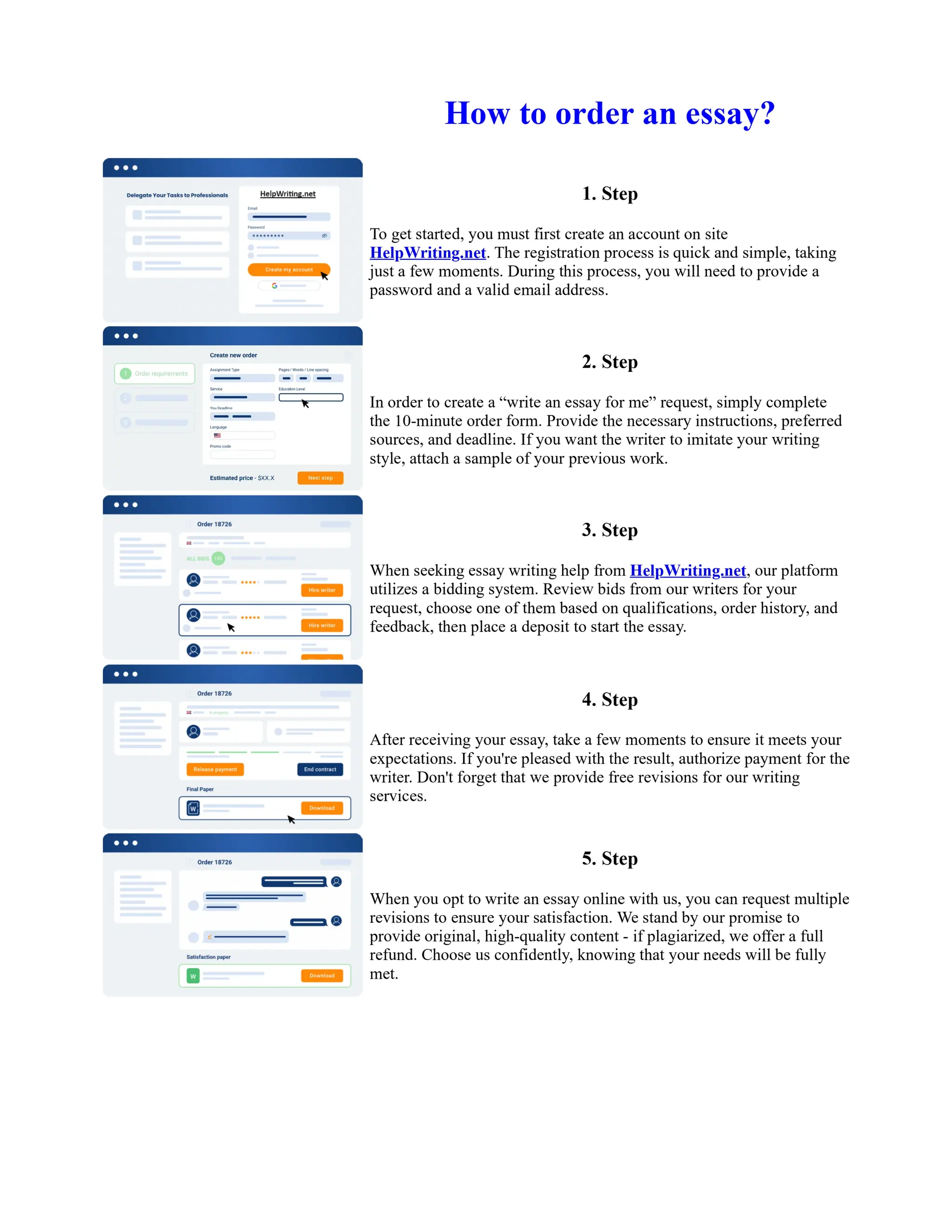

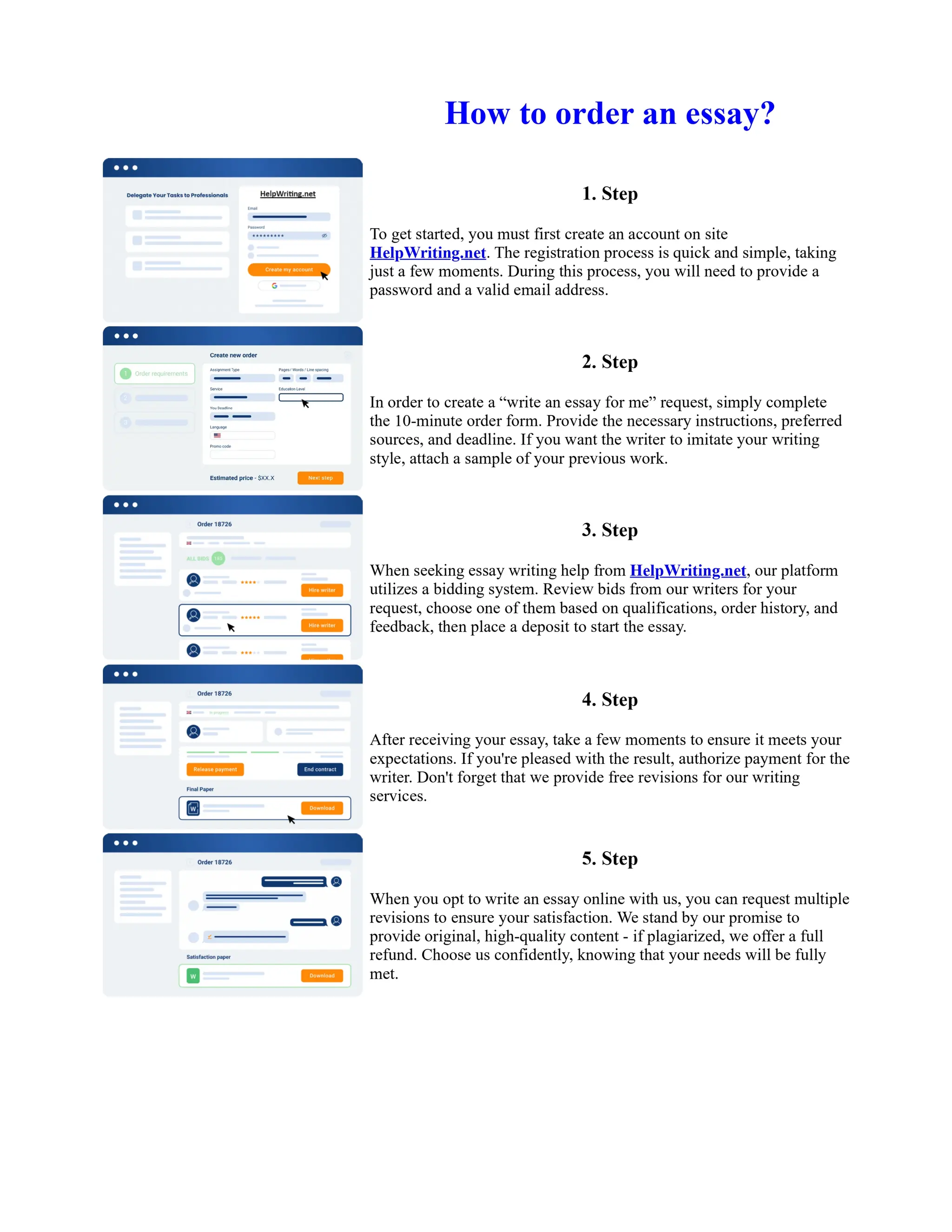

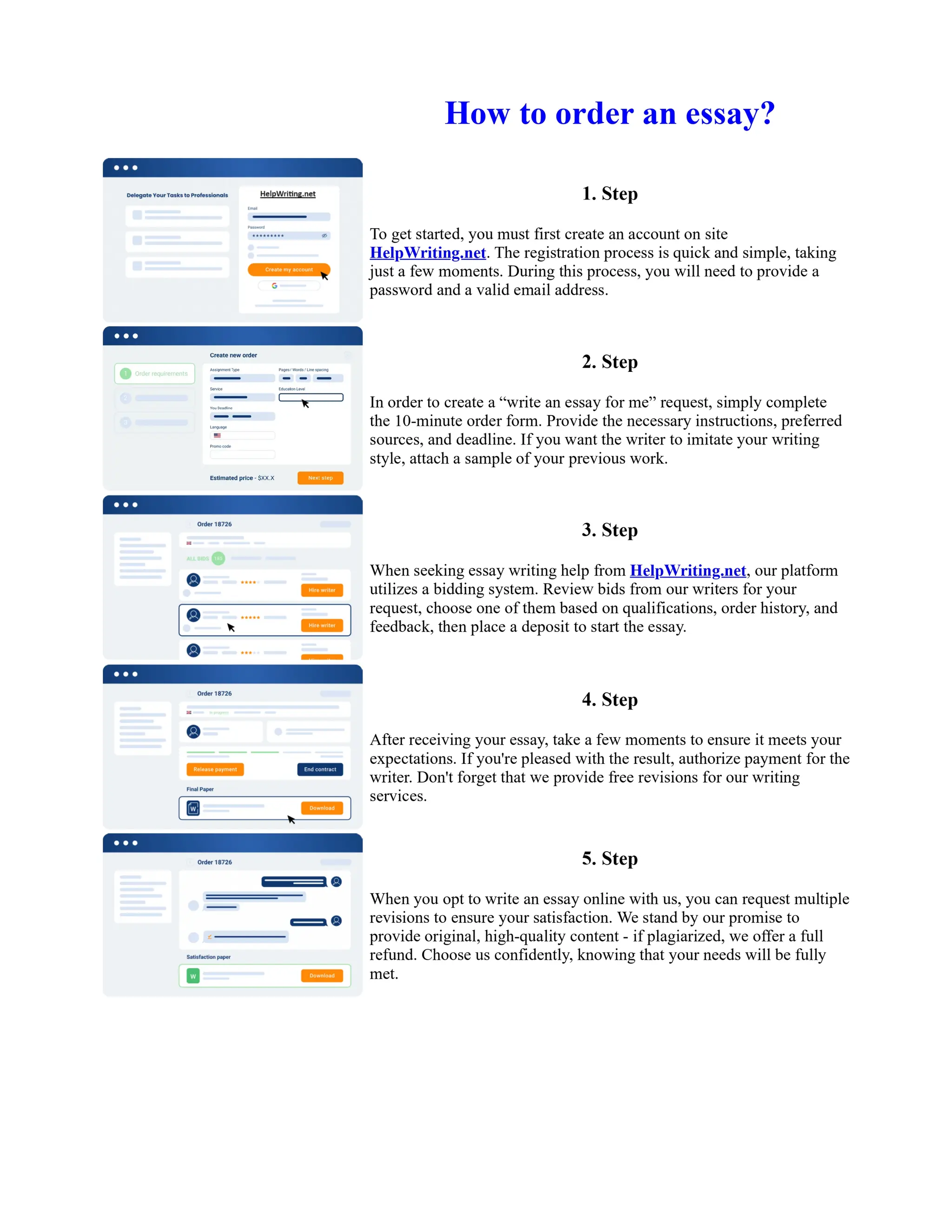


![Twelfth Night Essay
In Shakespeare's play, Twelfth Night or What you Will, the characters are involved in a plot
complete with trickery, disguise, and love. Each character is defined not by his or her gender or true
identity, but by the role they are forced to take because of the complicated situation that arises.
Unlike their gender, the speech the characters give an insight to their true personalities. In the
Twelfth Night, the character Duke Orsino uses flowery and over–dramatic language, long poetic
sentence structure, and melodramatic metaphors to display his overemotional romantic nature
despite the different emotions in his various speeches. Duke Orsino's repeated usage of poetical
verse and poetic devices to describe his woes from love set him ... Show more content on
Helpwriting.net ...
Enough no more!" (1.1.6–7). He accentuates his original metaphor by personifying music and
comparing it to a breeze that carries the flowers odor with it. Until line 8, Orsino does not mention
his love explicitly. Instead, he establishes the feeling of yearning by referring to symbols of love
such as music and flowers. Orsino ends his long speech with, "Even in a minute, So full of shapes is
fancy./ That it alone is high fantastical." (1.1.14–15). By stating that love is a wonderful figment of
imagination, Orsino reinforces the previous metaphorical and vague language he uses in the
beginning of the speech. "That it [love] alone is high fantastical" (1.1.15) also shows that he is a true
romantic because he is in love with the concept of love rather than the person themselves.
Furthermore, he line, "...Enough no more!" (1.1.7) contradicts with the previous line, "Give me
excess of it, that, surfeiting," (1.1.4) which proves that Orsino is very dramatic in character because
he constantly vacillates in his actions and desires. He is emotionally unstable at times in the play and
thus acquires a dramatic behavior.
In Act 5, Orsino delivers a speech to Olivia in order to express his broken heart and pine over his
unreciprocated feelings. However, by drawing out the speech with allusions, excessive language,
and metaphors, Shakespeare portrays Orsino as an overemotional and romance–driven character.
Compared to Orsino's first
... Get more on HelpWriting.net ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advantagesoftheextensiblemarkuplanguagexml-231113203411-0c2ba1ae/75/Advantages-Of-The-Extensible-Markup-Language-XML-67-2048.jpg)