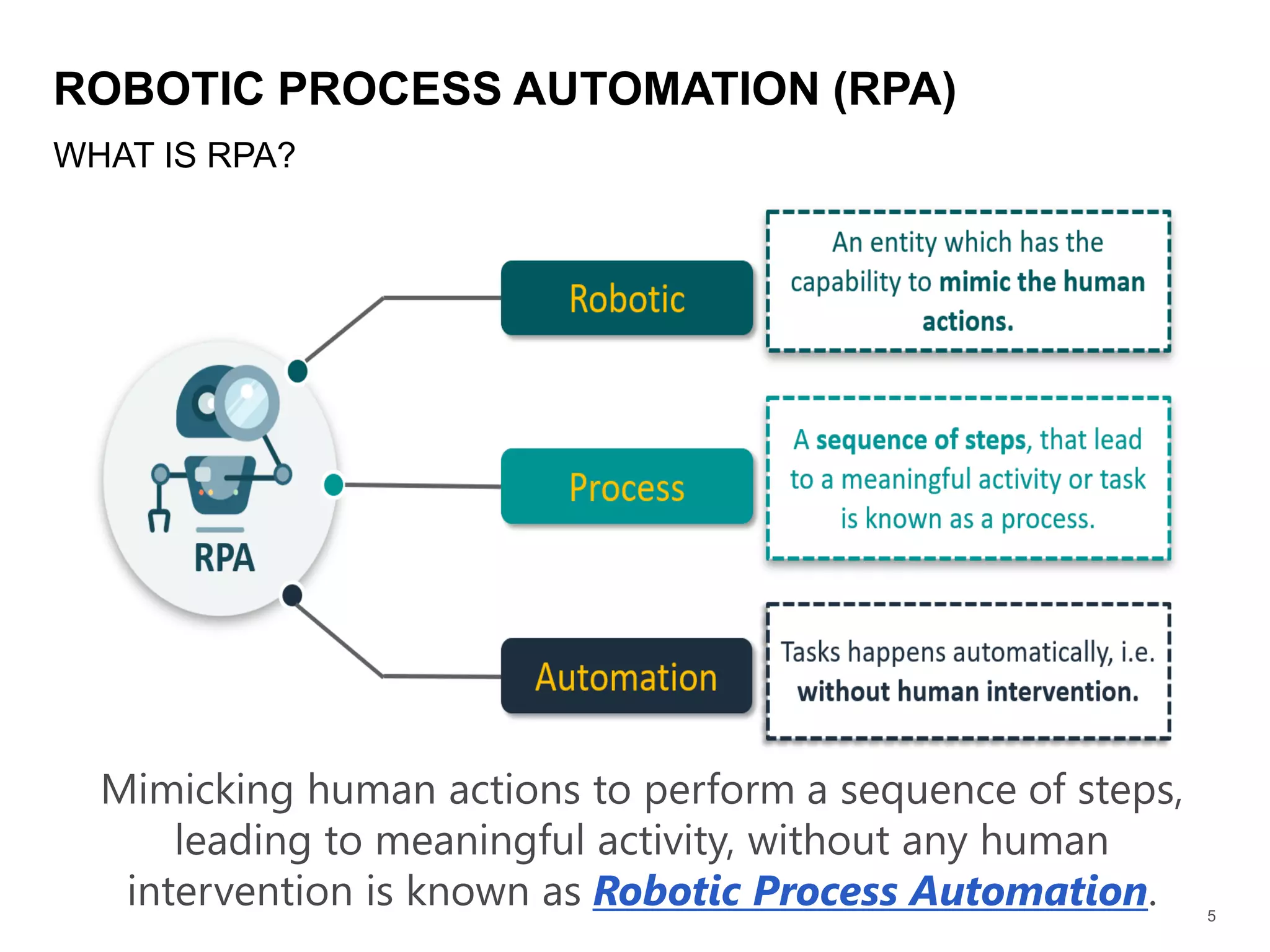
The document provides an overview of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), explaining its definition, features, benefits, and types. It emphasizes RPA's role in digital transformation by improving efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction across various industries. Additionally, it outlines the limitations of RPA and presents practical use cases in sectors such as banking, healthcare, HR, insurance, manufacturing, retail, telecom, and travel.