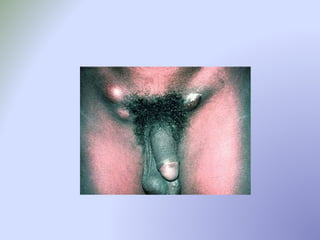
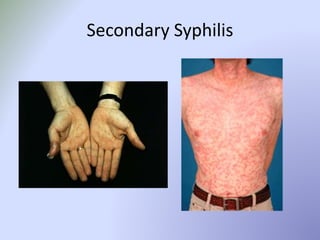
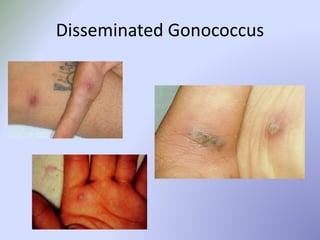
This document discusses sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It lists reportable STIs in South Carolina and provides statistics on STIs in the US, including that adolescents experience high rates of infection. It then covers specific STIs like chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes, syphilis, and human papillomavirus. It discusses symptoms, treatments, and considerations for adolescents. Overall, the document is an informative overview of common STIs, reporting requirements, and management strategies.
















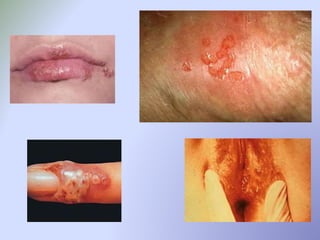


![Chancroid/Lymphogranuloma
Venereum/Granuloma Inguinale
• Chancroid
– Haemophilus ducreyi, very uncommon in the US
– Papule pustule PAINFUL ulcers with fluctuant buboes (lymph nodes can
spontaneously rupture)
– Tx: Azithromycin 1g po x 1 OR Ceftriaxone 250mg IM x 1
• Lymphogranuloma Venereum
– L1, L2, and L3 serovars of Chlamydia; tropical and subtropical areas of the
world
– Spontaneously healing PAINLESS genital ulcer extension to regional lymph
nodes (groove sign) fibrosis and stricture of anogenital tract
– Tx: Doxycycline 100mg po BID x 21 days OR Erythromycin/Azithromycin
• Granuloma Inguinale (Donovanosis)
– Uncommon, caused by Klebsiella granulomatis (PAINLESS ULCER[S])
– Tx: Doxycycline, Azithromycin, Cipro, Erythromycin, or Bactrim x 3 weeks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adolescentstiucaya-150219105028-conversion-gate01/85/Adolescent-sti-ucaya-20-320.jpg)