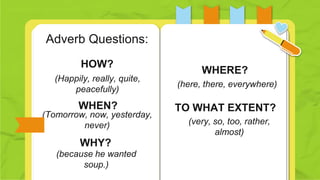
An adverb modifies verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs by answering questions about manner, place, time, frequency, or degree. Examples are provided that show adverbs answering how, when, where, why, and to what extent questions. There are five main types of adverbs: degree, frequency, manner, time, and place.
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses a sudden feeling like joy, sorrow, or excitement. There are six types of interjections: primary, secondary, volitive, emotive, cognitive, and greetings/parting words. Examples are provided for each type of interjection.