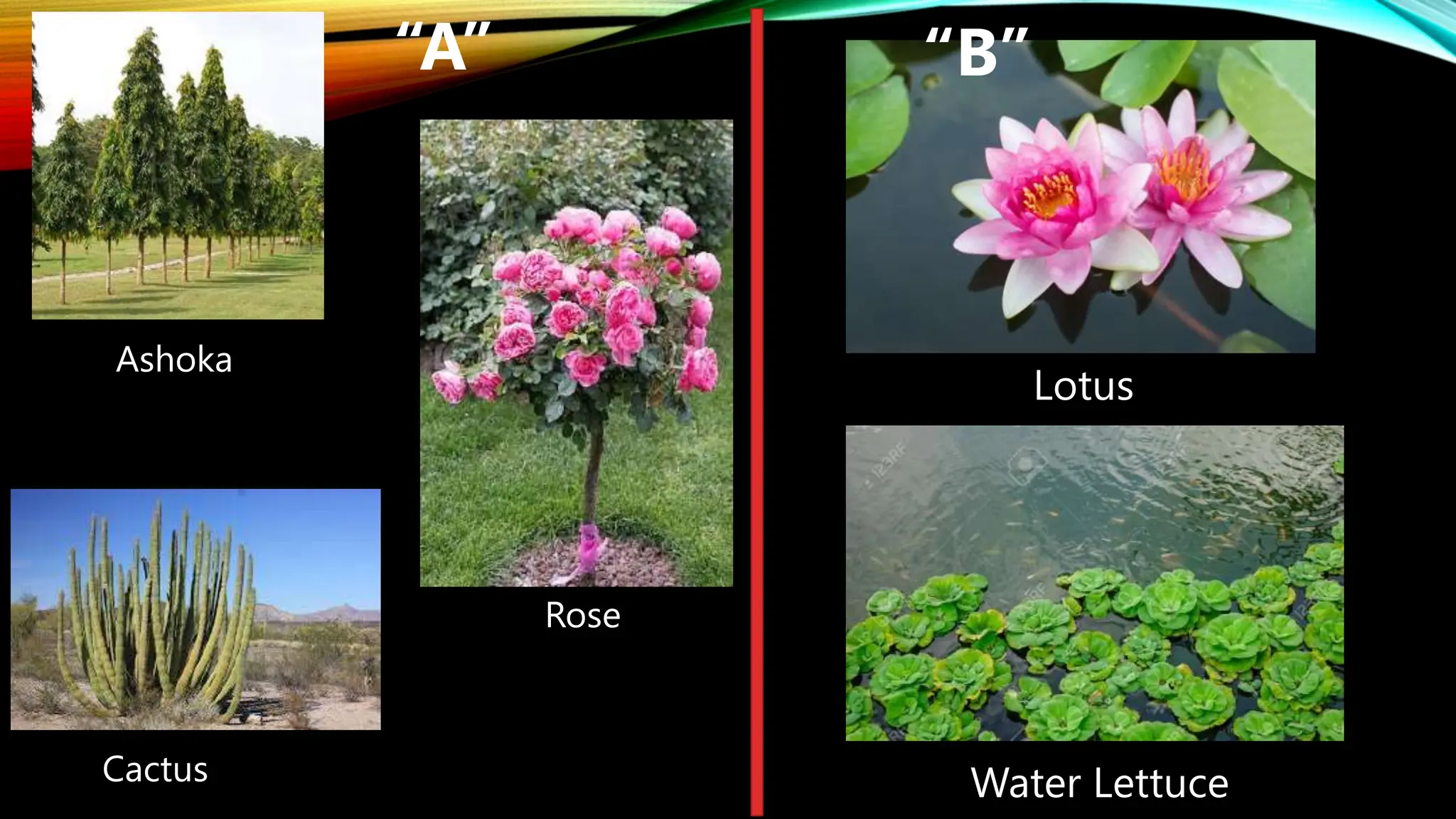
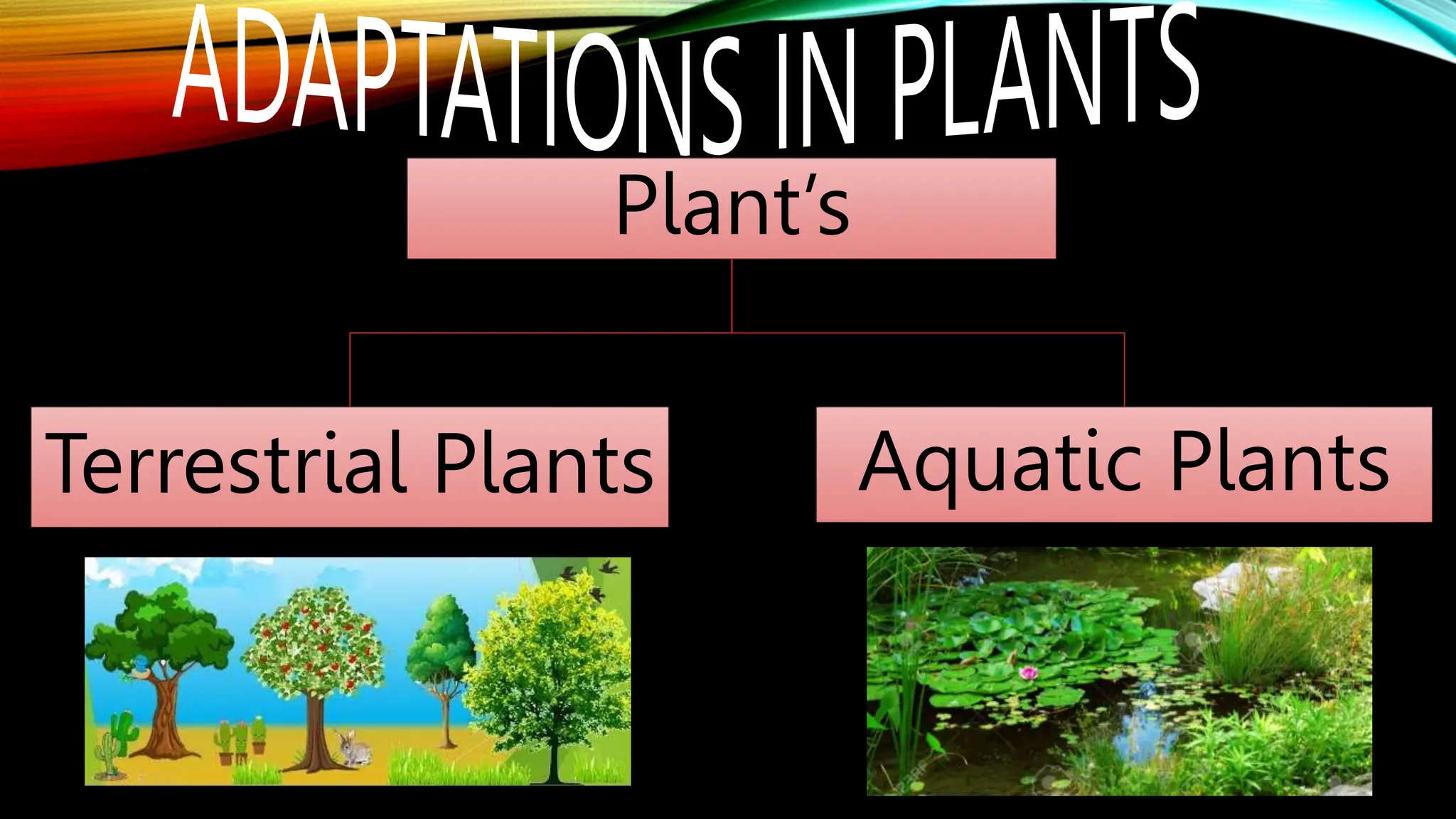
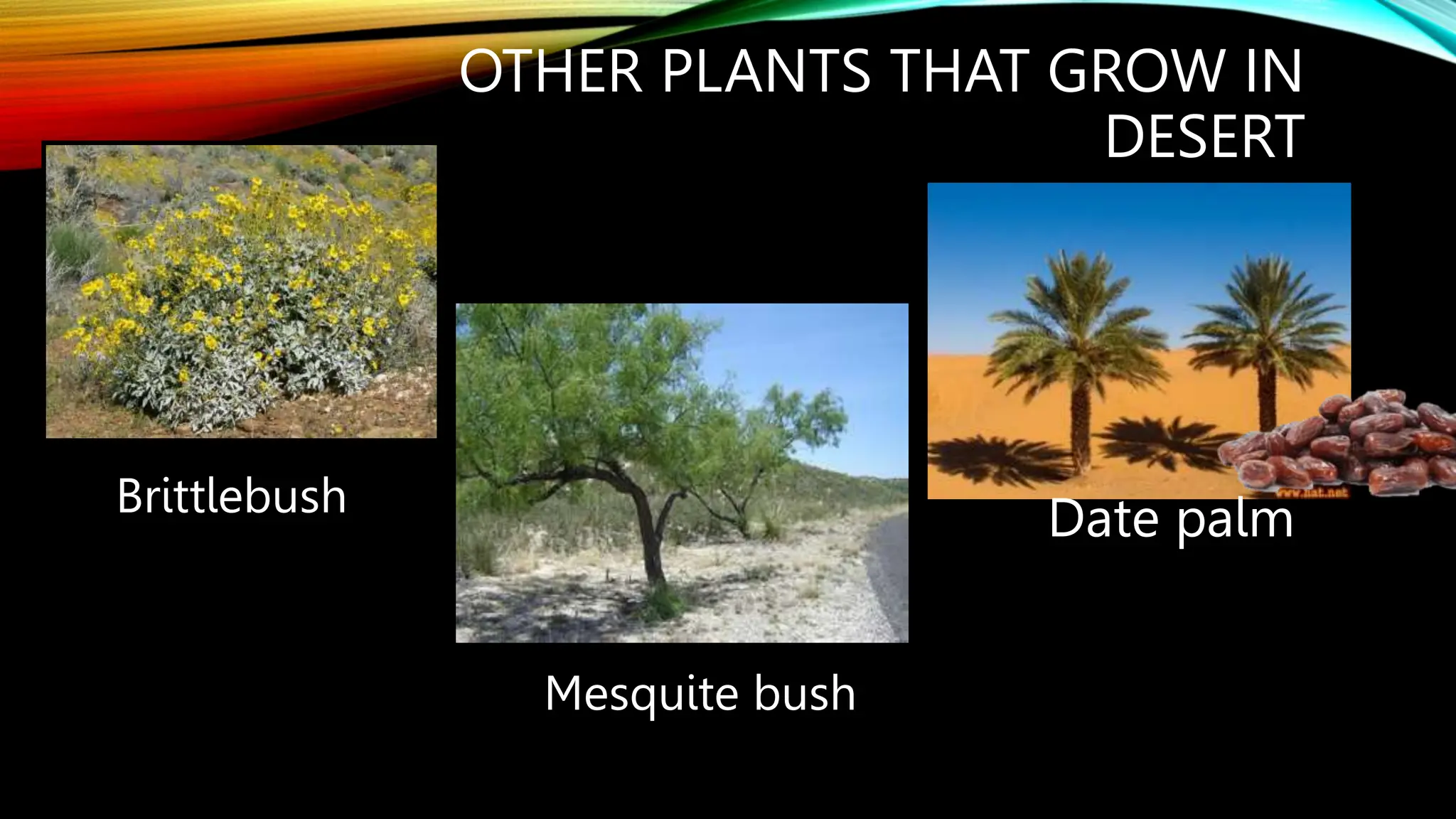
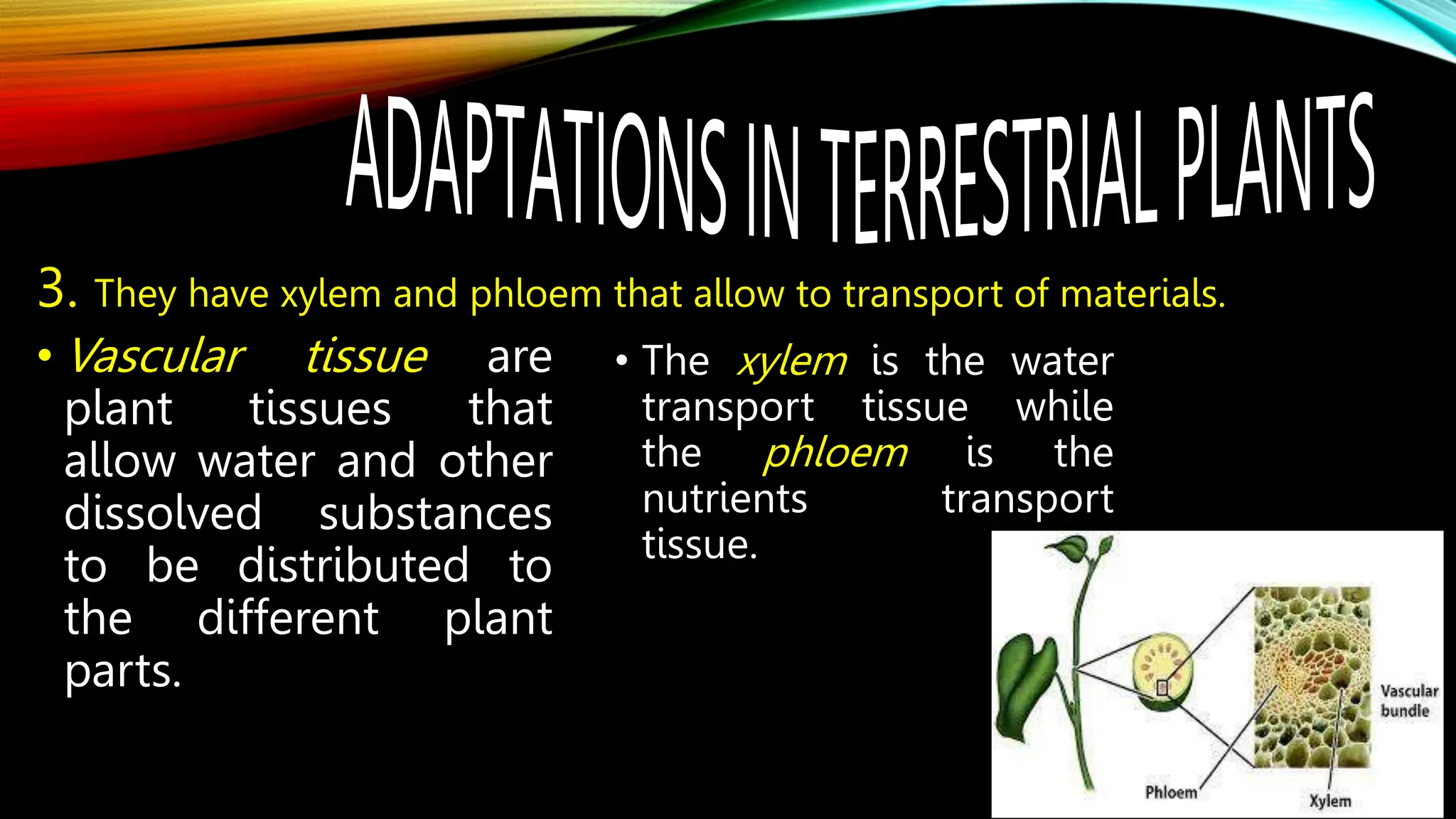
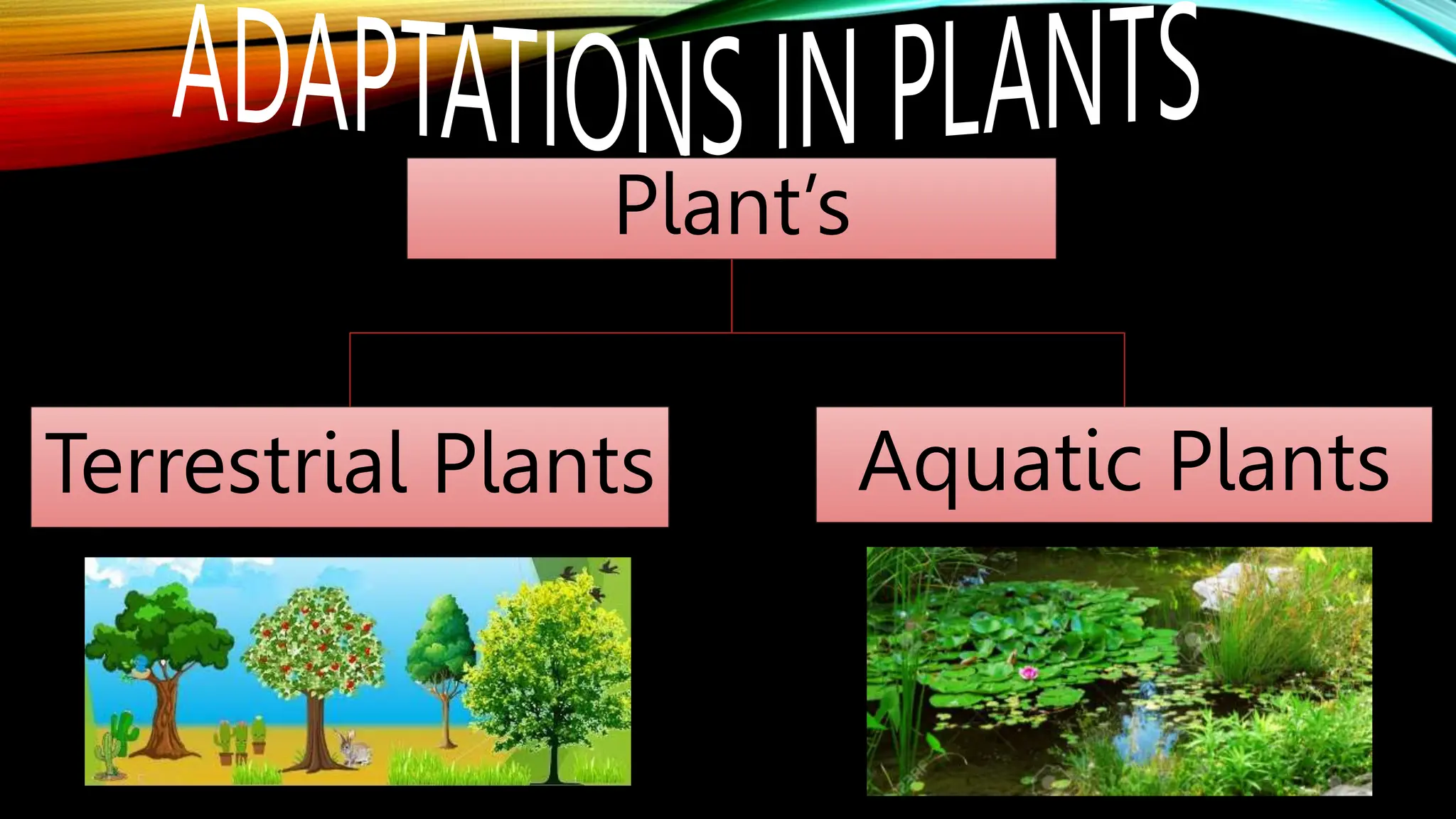
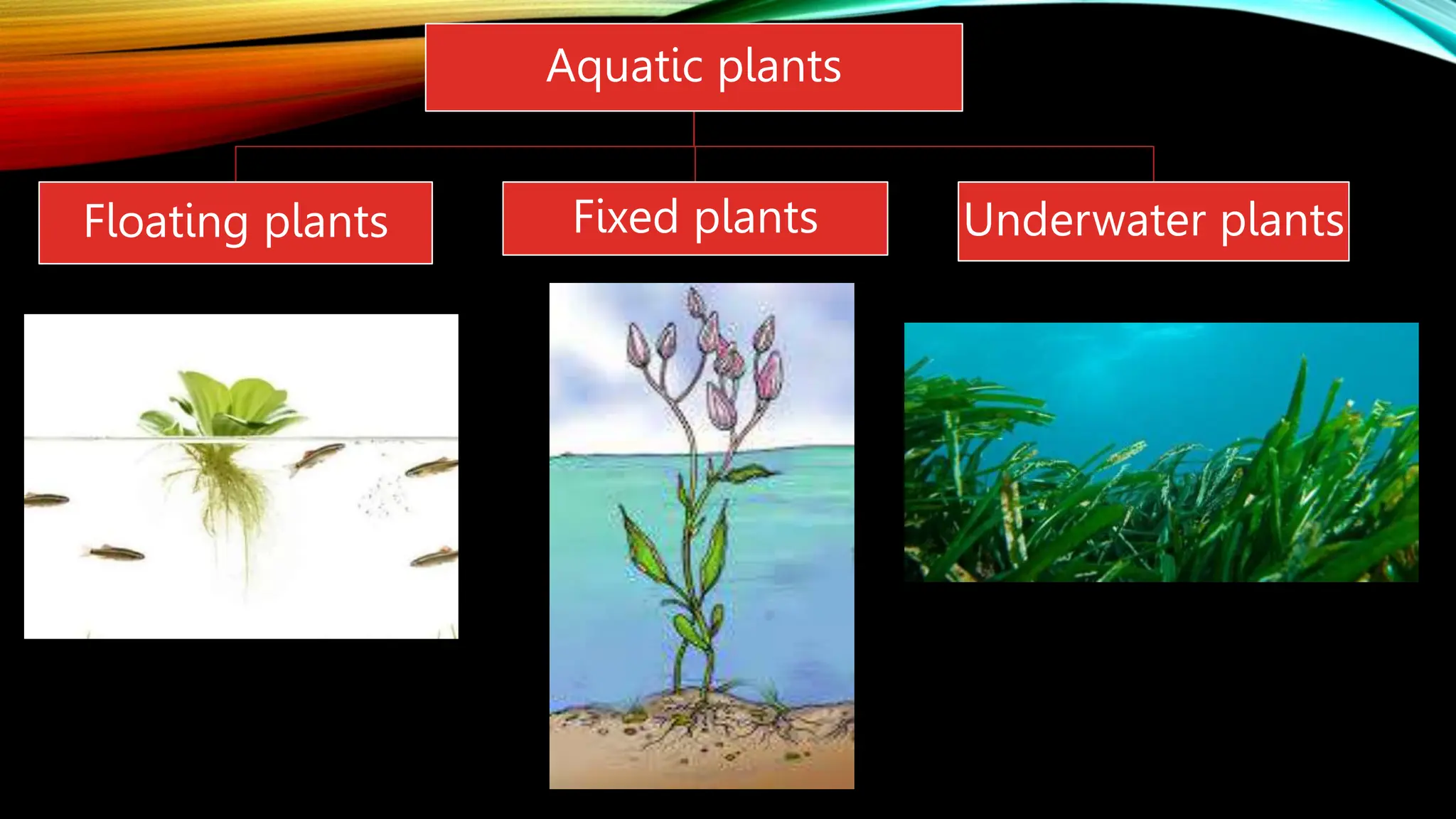
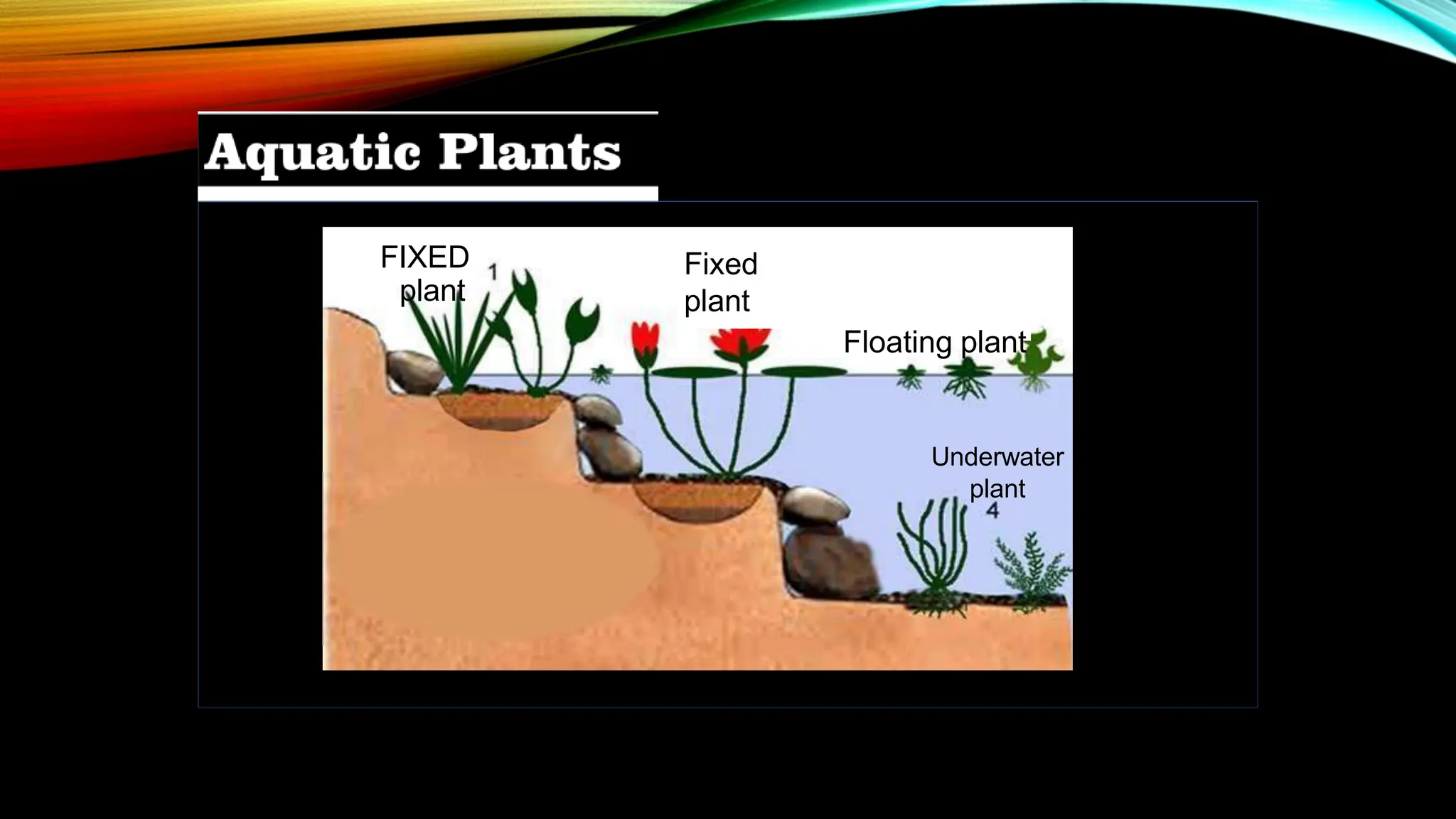
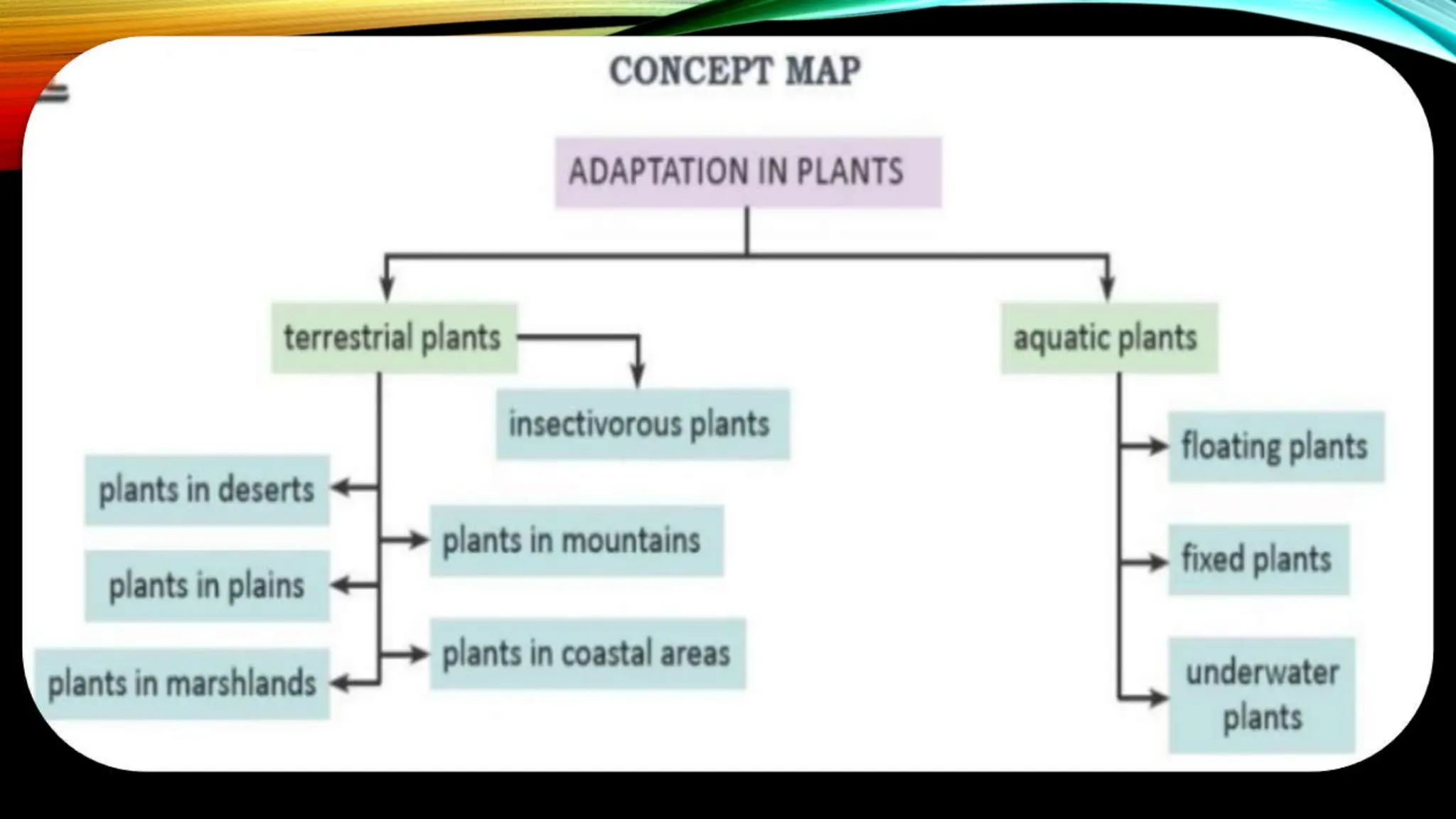
This document discusses the adaptations of terrestrial and aquatic plants. It divides plants into two groups: terrestrial plants that grow on land, and aquatic plants that grow in water. Terrestrial plants are further divided based on their habitats, such as deserts, mountains, plains, coastal areas, and marshlands. Each habitat has different conditions that plants adapt to through features like waxy coatings, spines, thick bark, and deciduous or evergreen leaves. Aquatic plants include floating plants, fixed plants, and underwater plants. Their adaptations allow them to survive being completely or partially submerged in water.