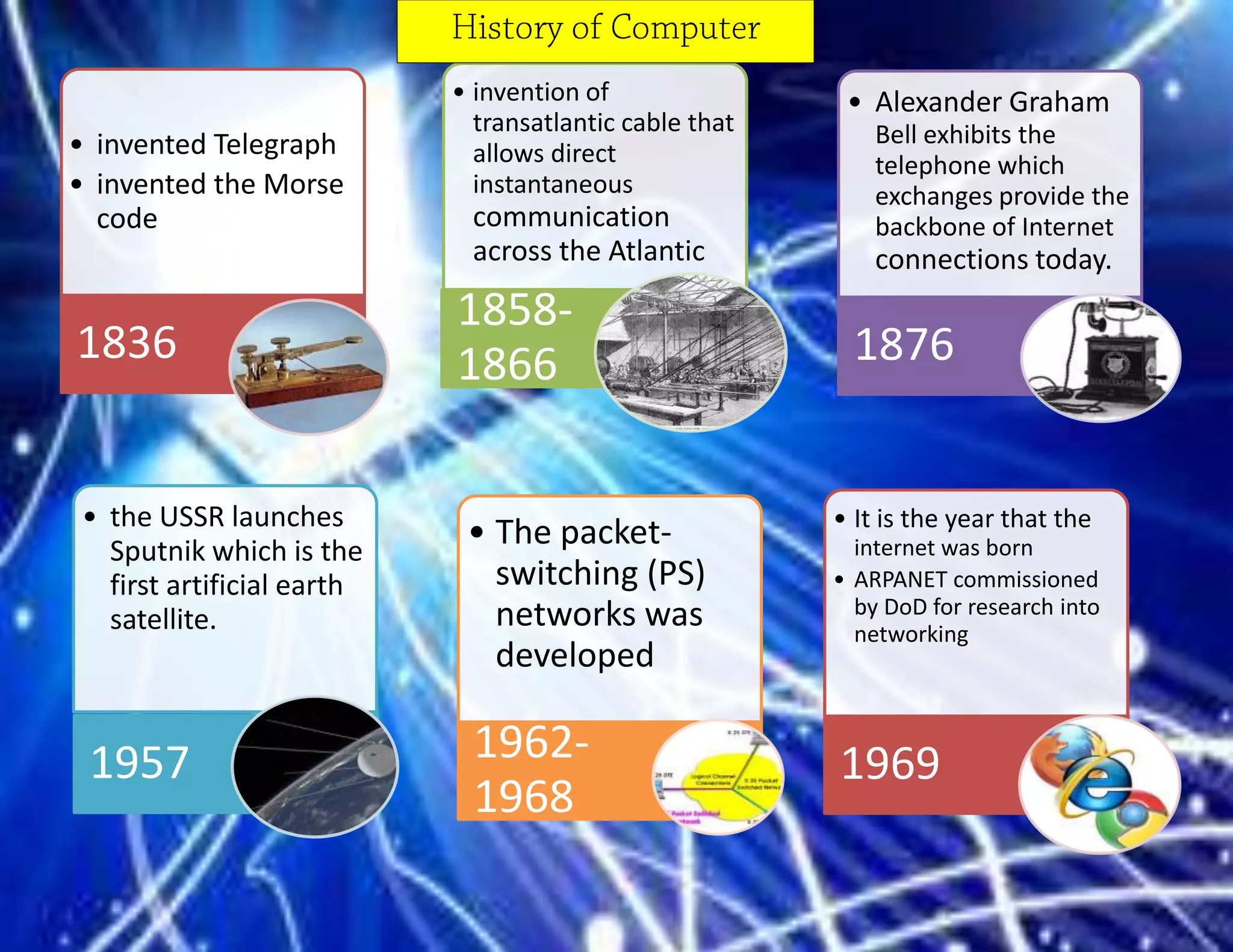
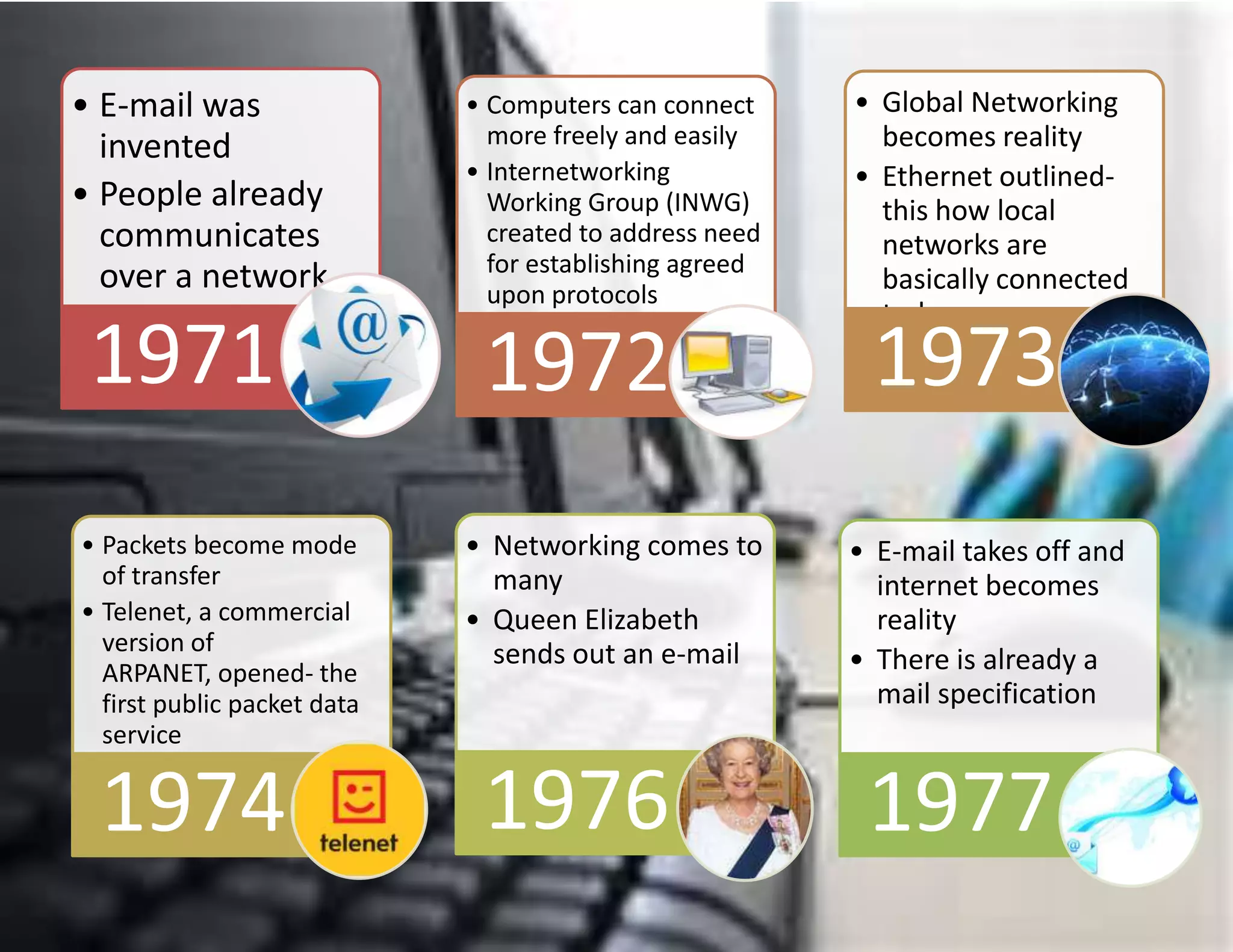
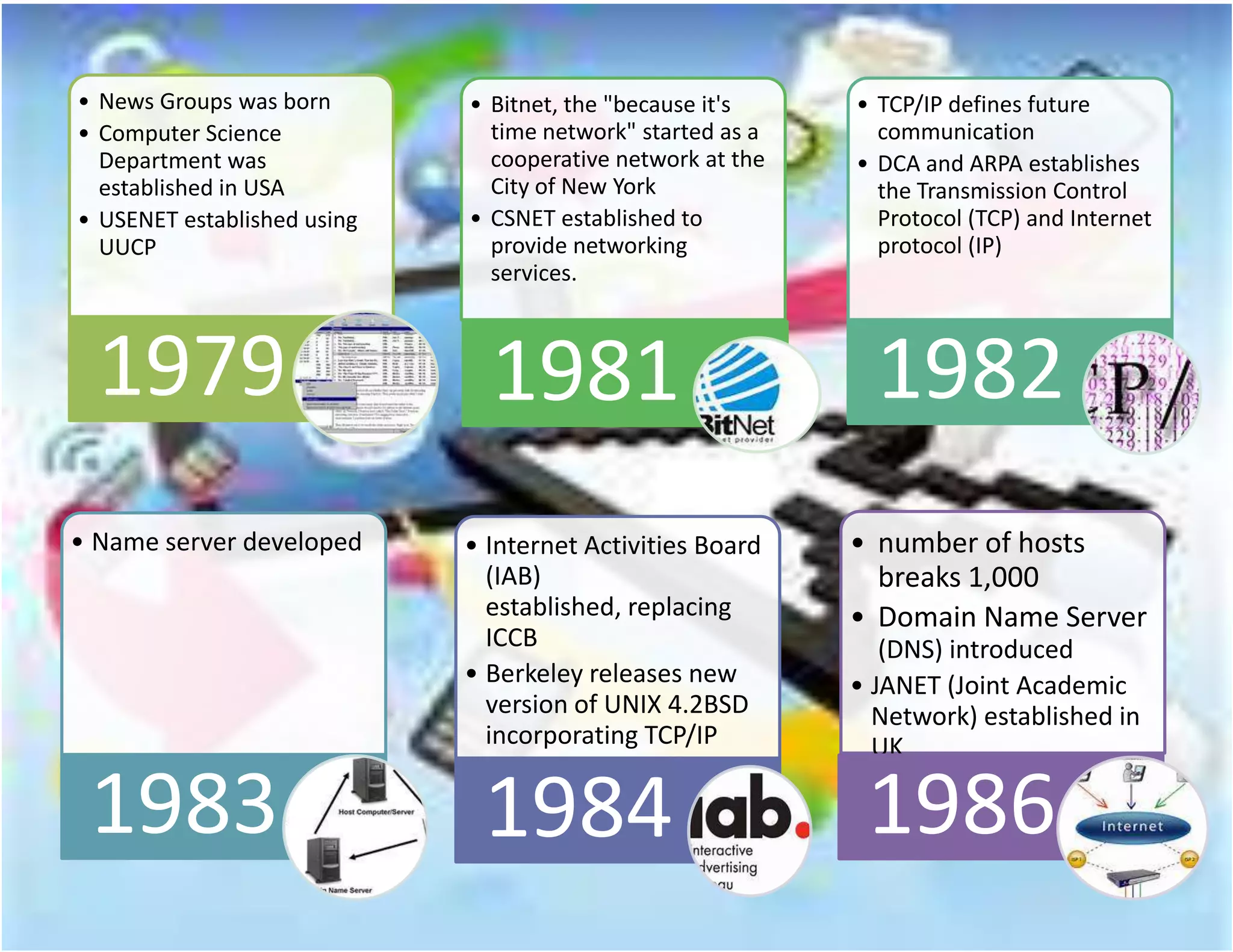
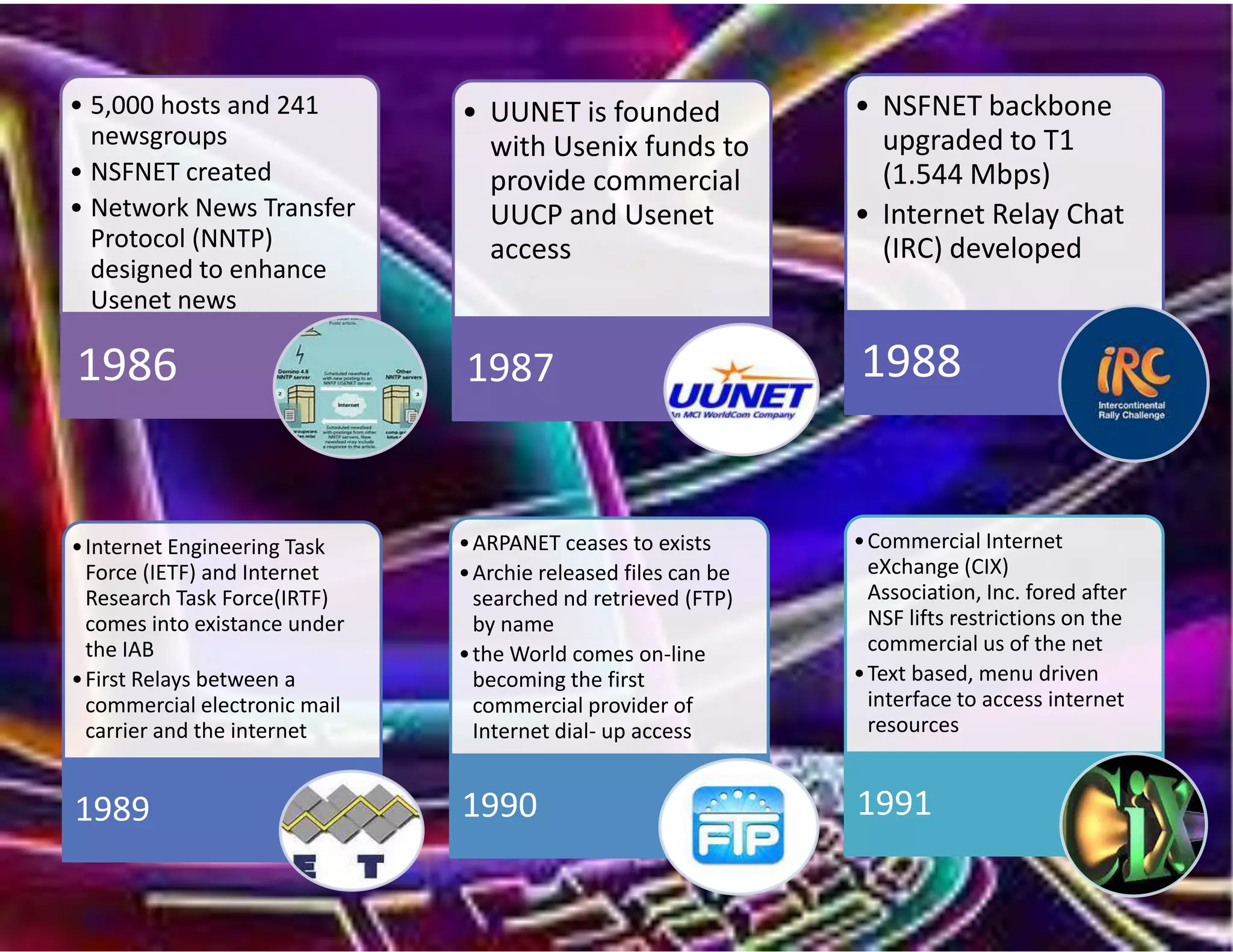
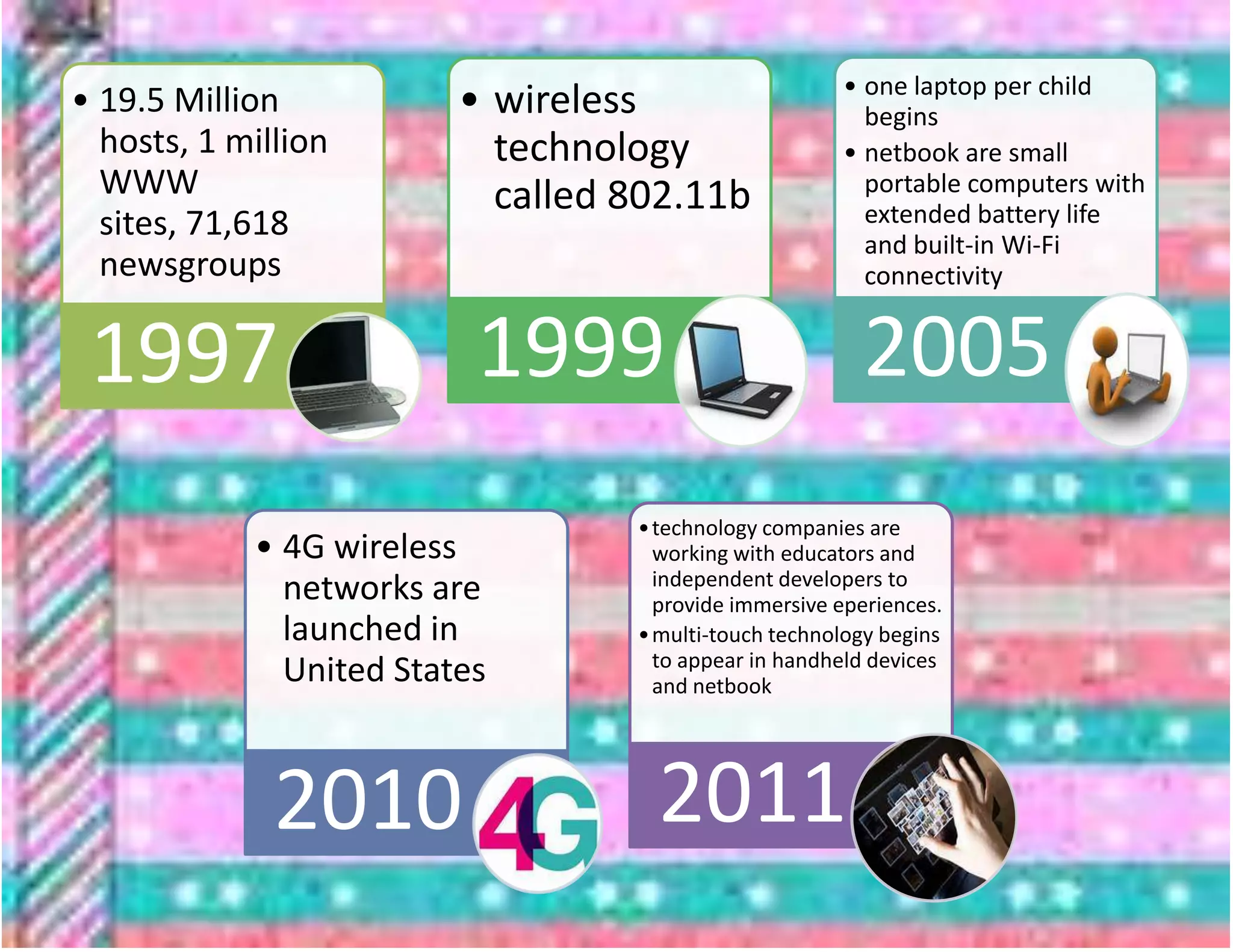
The document outlines the evolution of communication technologies from the invention of the telegraph and Morse code to the development of the internet and its commercial applications. Key milestones include the launch of the first artificial satellite in 1957, the establishment of ARPANET, and the introduction of protocols like TCP/IP and DNS. The document concludes with the rise of wireless technology and advancements in portable computing by 2011.