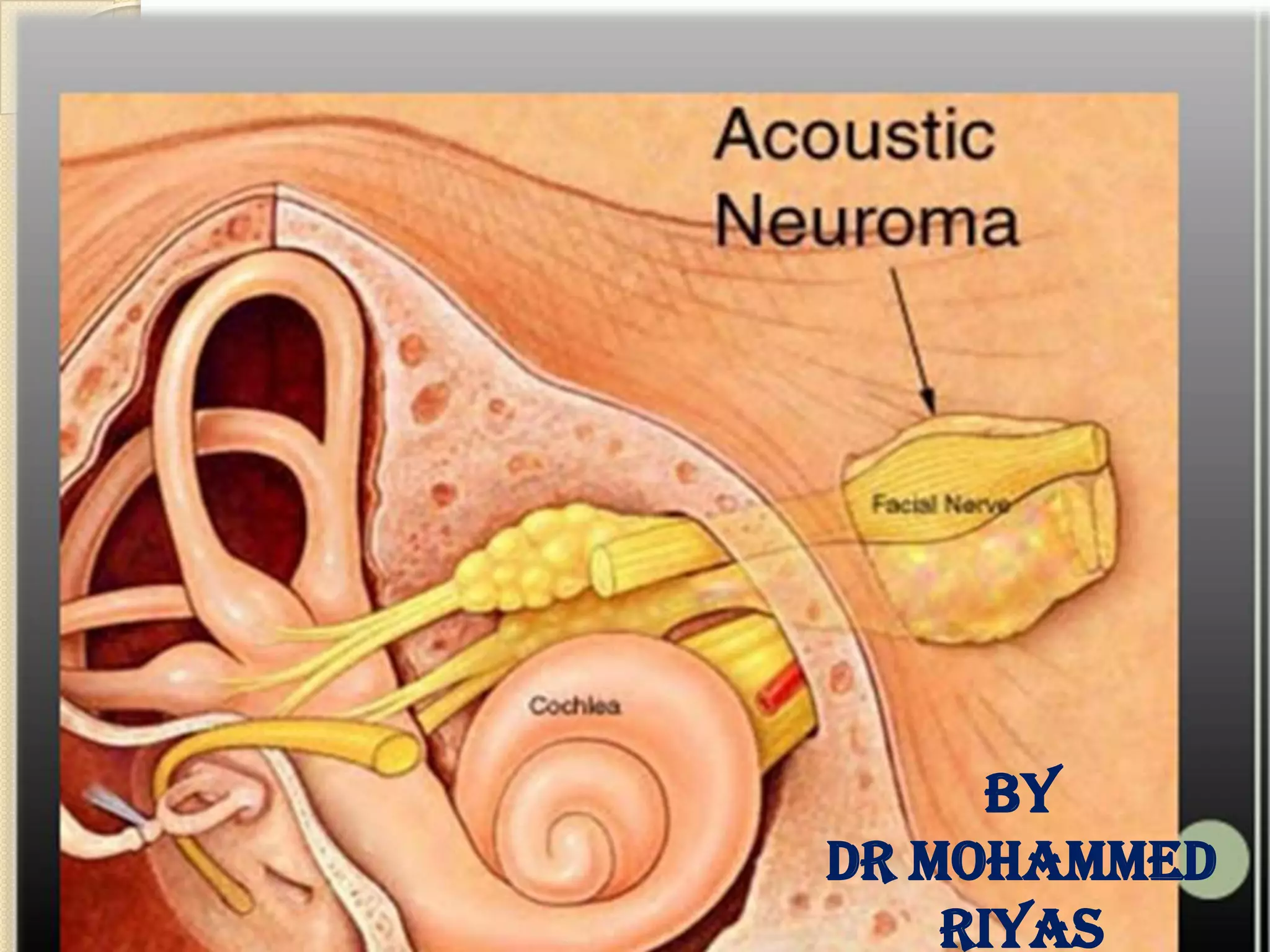
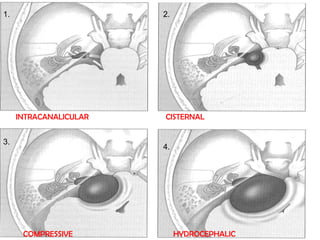
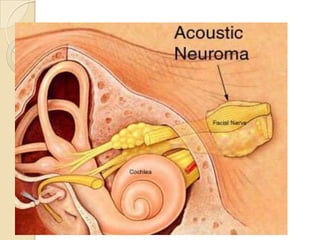
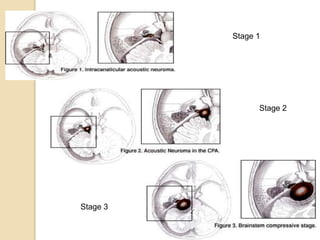
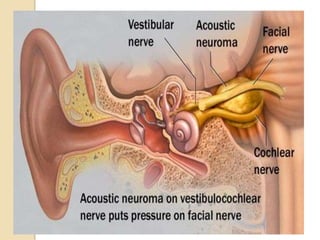
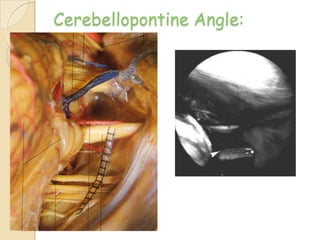
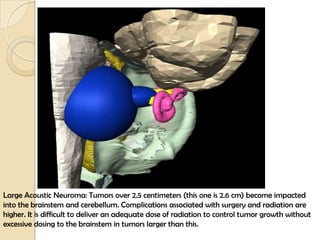
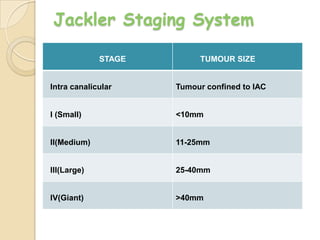
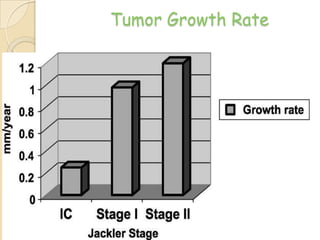
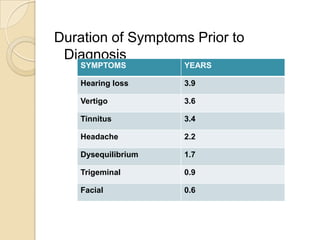
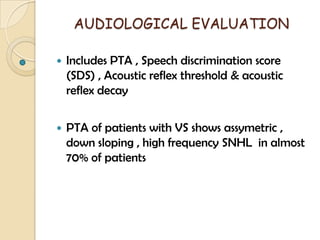
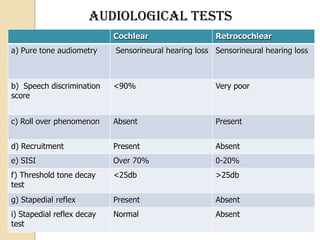
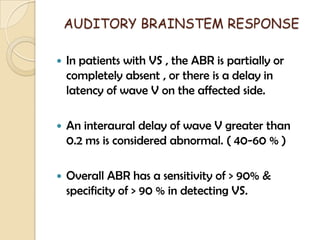
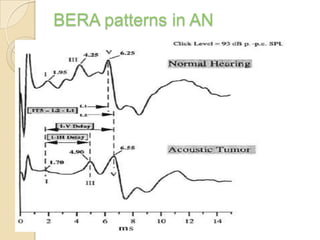
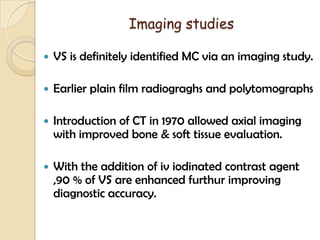
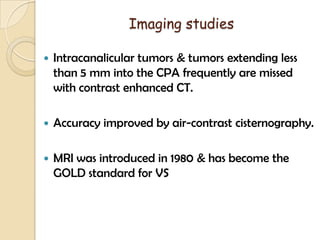
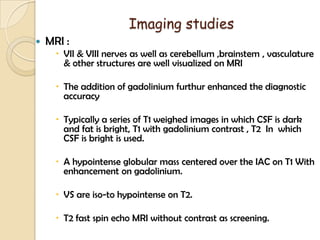
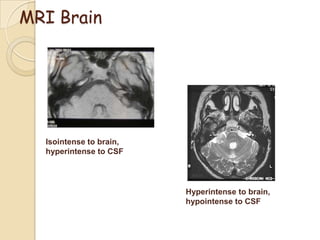
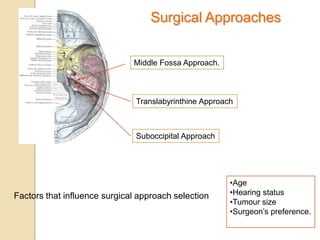
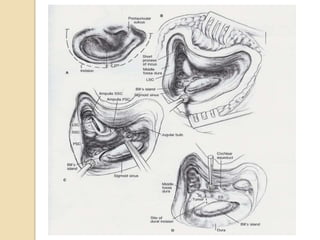
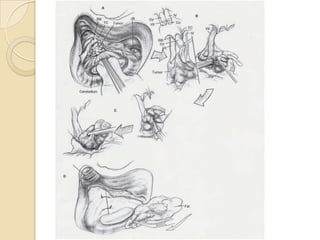
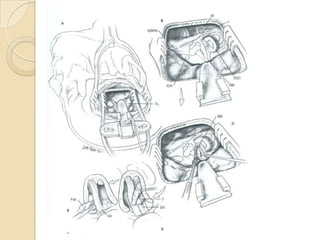
The translabrynthine approach is used to surgically remove vestibular schwannomas. It provides the most direct exposure of the cerebellopontine angle but results in total hearing loss. The key steps involve complete mastoidectomy and labyrinthectomy to access the internal auditory canal. This allows for identification and preservation of the facial nerve while fully exposing the tumor for removal. Though it sacrifices any residual hearing, it allows for quick recovery and excellent postoperative facial nerve function outcomes.